December 2024
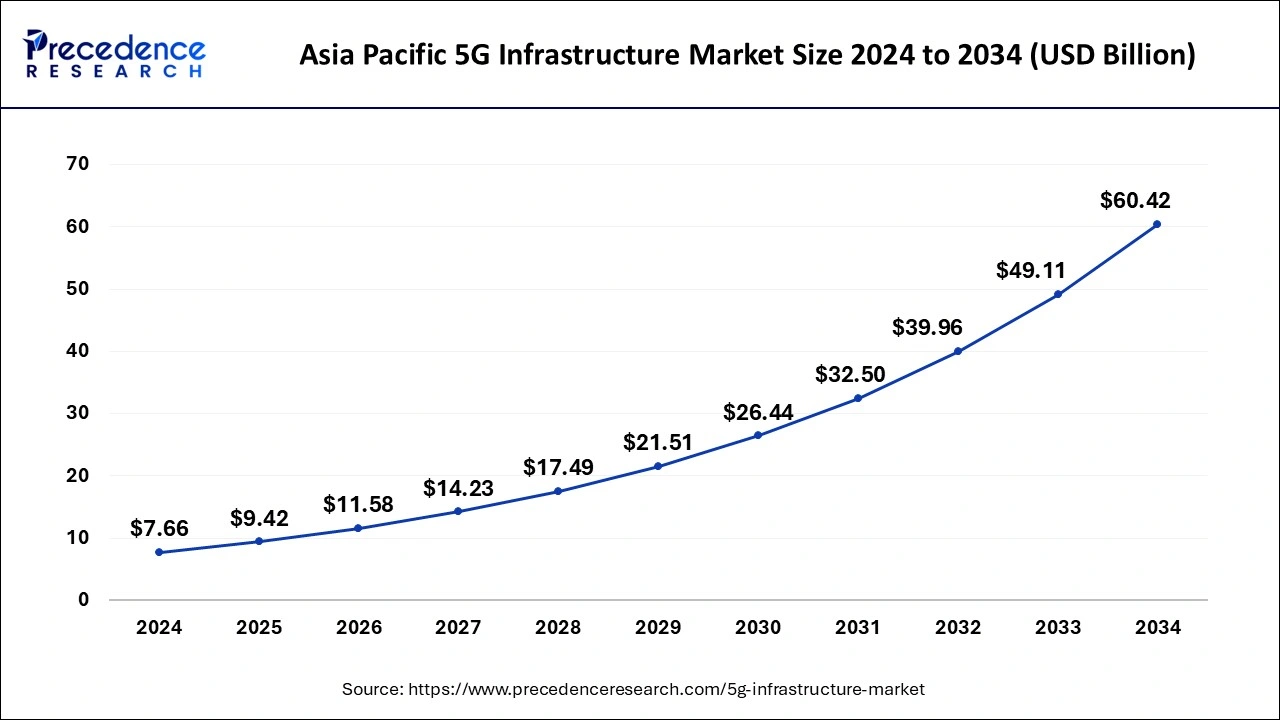
The global 5G infrastructure market size is calculated at USD 20.55 billion in 2025 and is forecasted to reach around USD 131.77 billion by 2034, accelerating at a CAGR of 22.93% from 2025 to 2034. The Asia Pacific 5G infrastructure market size surpassed USD 9.42 billion in 2025 and is expanding at a CAGR of 22.94% during the forecast period. The market sizing and forecasts are revenue-based (USD Million/Billion), with 2024 as the base year.
The global 5G infrastructure market size was estimated at USD 16.72 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 131.77 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 22.93% from 2025 to 2034.
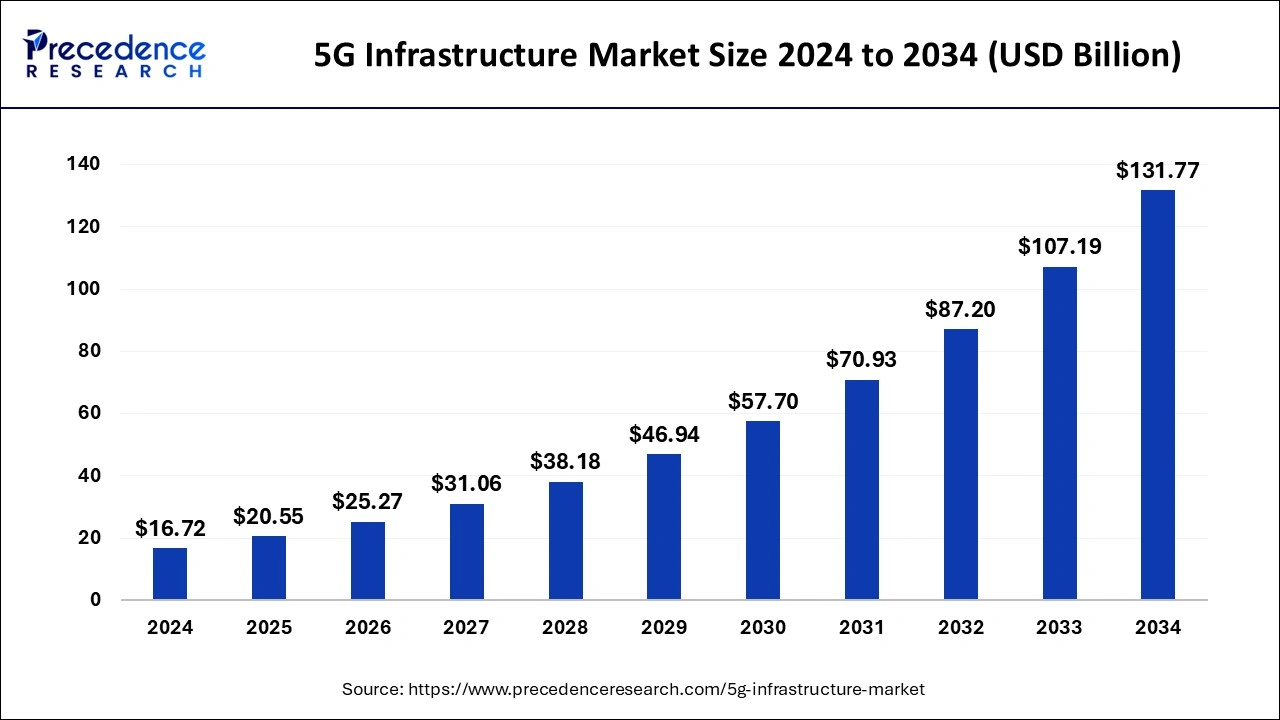
The Asia Pacific 5G infrastructure market size was evaluated at USD 7.66 billion in 2024 and is predicted to be worth around USD 60.42 billion by 2034, rising at a CAGR of 22.94% from 2025 to 2034.
The highest market share and dominant position in the 5G Infrastructure market belongs to North America during the forecast period. This region includes U.S. and Canada. Growth of the market in this region is mainly attributed to increasing R&D activities in 5G technology and significant presence of key market players. In addition, as the region is a home to leading 5G Infrastructure industry leaders, there is comparatively higher R&D investment. This factor is expected to create lucrative growth opportunities for the 5G Infrastructure market.
Also, increasing wireless 5G connections in the region is further projected to boost North America market. For instance, according to data from Omdia, North America accounted for a total of 44.6 million 5G connections by the end of second quarter of 2021, which is 67% quarter over quarter growth as compared to previous year. In addition, heavy government investments in 5G infrastructure is further anticipated to fuel growth of North America 5G infrastructure market.
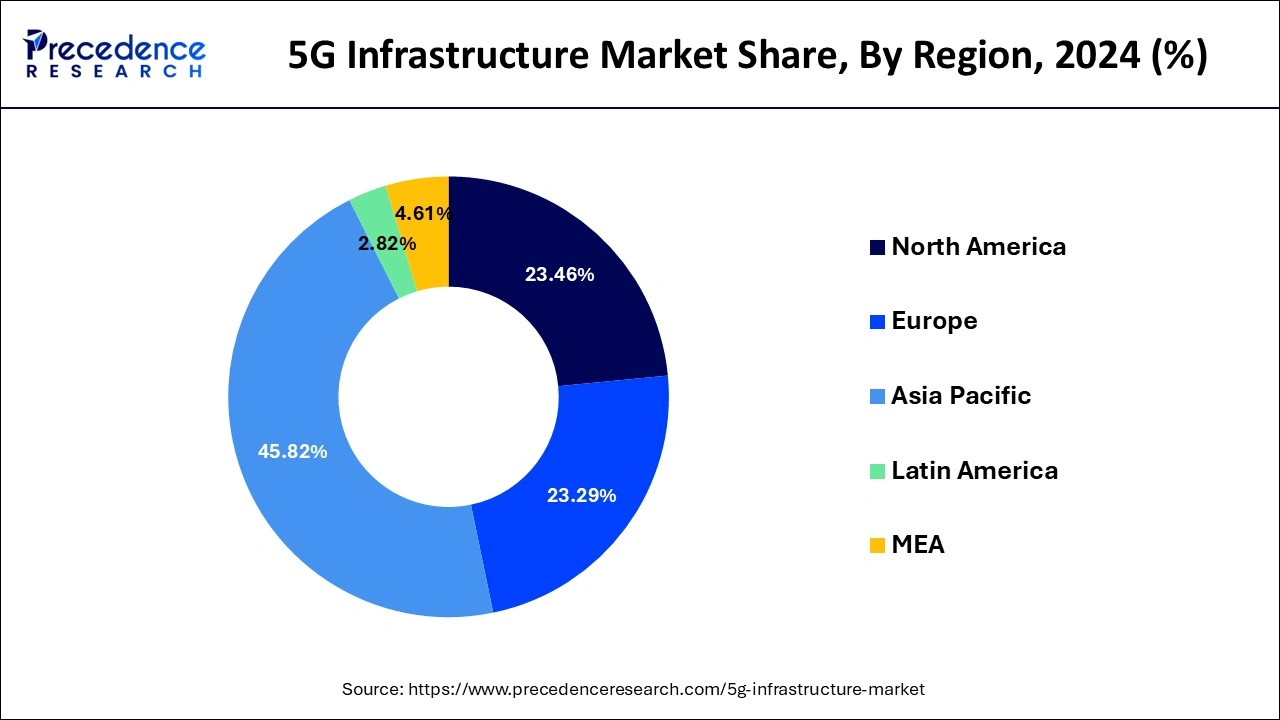
Asia-Pacific is considered as highest growing region in 5G Infrastructure market. This region includes China, India, Japan, South Korea, and rest of the world. The number of 5G subscriptions is growing at rapid pace in Asia-Pacific coupled with an increased network traffic. For instance, according to the GSMA estimates, this region is anticipated to lead the worldwide 5G connections with China accounting for 828 million 5G connections (about 50% of all global connections). This will make telecom operators to install rising number of cutting-edge network solutions to efficiently manage network traffic.
On the other hand, ongoing investments in infrastructure development in this region is boosting deployment trend of 5G networks. For instance, as per the data from the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology (CAICT), the country is estimated to invest over $215 billion in the 5G network infrastructure by 2025. Further, according to the Ericsson AB’s latest Mobility Report, Asia Pacific is anticipated to be the one of the fastest growing region with about 10% of all subscriptions being 5G in 2022. Such factors are opportunistic for growth of the 5G infrastructure market.
5G infrastructure comprises of a network of small-cell and macrocell base stations needed for fifth-generation of cellular networks. Usually, the 5G network has two infrastructure options including standalone and non-standalone (NSA) infrastructures. Out of these infrastructures, a non-standalone infrastructure partially depends on existing 4G LTE infrastructure; however, standalone infrastructure does not rely on LTE networks. Both of these infrastructures has an edge computing capabilities which is desired for functionality of 5G technology. It offers low latency coverage for data streams associated with applications such as semi-autonomous vehicles, IoT devices, and augmented reality. Businesses are rapidly implementing 5G technology as it provides them with a highly reliable form of wireless connectivity in the form of speed and capacity.
This infrastructure can support about 10 times more bandwidth as compared with 4G infrastructure. A productive feature of 5G infrastructure include higher multi-Gbps peak data speeds, more reliability, increased availability, ultra-low latency, massive network capacity, and an uniform user experience to large number of users. An emerging range of 5G infrastructure applications consists of improved remote education, enhanced agricultural productivity, smarter logistics, personalized and efficient retail, advanced healthcare, improved manufacturing operations, and modernized mining, oil and gas operations. Along with aforementioned applications, 5G technology infrastructure is anticipated to boost global innovation across enterprise networking, critical communications, and industrial Internet of Things (IoT).
5G technology offers significantly lower latency rate, which is the delay between the receiving and sending information. This decrease in end-to-end latency improves user experiences and creates new opportunities for innovative use cases. Also, there is a trend of Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communications (URLLC), a subdivision of 5G network architecture which enables an efficient scheduling of data transfers and caters various advanced services across applications such as factory automation, the industrial internet, smart grid, autonomous driving, and or robotic surgeries. Hence, demand for lower latency rate among aforementioned applications is significantly boosting growth of the global 5G infrastructure market.
In addition, continuous growth in smartphone adoption coupled with an upsurge in video consumption is significantly boosting mobile data traffic. This has also led to enhancements in performance of deployed networks to meet demand posed by improved device capabilities. According to various researches, the overall mobile data traffic is expected to grow at a rapid pace in upcoming years. This growth in mobile data traffic is considerably boosted demand for higher network infrastructure capabilities of 5G technology. For instance, as per the recent Ericsson study, the share of 5G technology in global mobile data traffic was about 10% in 2021; however, this share is expected to grow to around 60% in 2027.
On the other hand, ongoing demand for 5G technology across various industry verticals is expected to create lucrative growth opportunities for the global market. For instance, in healthcare sector, 5G has enabled high levels of connectivity for new health ecosystem to meet patient and provider needs conveniently, accurately, efficiently, and cost-effectively at substantial scale. 5G connectivity is expanding use cases of artificial intelligence (AI) and health-related IoT devices to monitor patients and making the recommendations related to the treatment of disease has driven demand for 5g technology. Furthermore, healthcare organizations are actively moving towards 5G technology under their digital transformation plans. Such factors are projected to create lucrative growth opportunities for the market.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 20.55 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 131.77 Billion |
| Growth Rate from 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 22.93% |
| Largest Market | Asia Pacific |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | Communication Infrastructure, Core Network Technology, Network Architecture, Spectrum, Component, End User, and Geography |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Depending upon the communication infrastructure, the small cell segment is the dominant player and is anticipated to have the biggest impact on 5G Infrastructure market. Small cells are an essential component in 5G infrastructure to provide high-band 5G across the indoor areas and dense urban environments including downtown, malls, stadiums, train stations, and other areas that need high data capacity and coverage. In addition, the small cell base stations are mainly designed to merge with an existing landscape, taking up least real estate. Hence, implementation of small cell infrastructure allows a smooth network evolution as well as a high frequency 5G radio spectrum.
Moreover, as the 5G commercial networks are going live around the globe, the telecom operators are actively prioritizing a need to improve user experiences. Due to this, new generation 5G small cells are being developed to meet market expectations for enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB), ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC), and massive machine-type communication (MTC). Different types of 5G small cells including picocells, femtocells, and microcells are used to provide different coverage limits.
On the other hand, there is an emerging challenge of industry definitions and standards for 5G small cells. Hence, the Small Cell Forum (SCF) has been introduced by industry players including Airspan, CommScope, Ericsson, Nokia, Qualcomm, Samsung, AT&T, Cisco, Huawei, and Vodafone. This association is publishing consensual and informed overview of 5G small cell network architectures along with the product definitions. This association is offering an informed view of important specifications and configurations for enterprises that are deploying small cells by year 2025.
Depending upon the end user, the residential segment is the dominant player and is anticipated to have the biggest impact on 5G Infrastructure market. A number of factors including growing dependency on the internet and upsurge in demand for fast data has led to growth of this segment. Communication service providers (CSPs) are rapidly deploying 5G networks across the suburban areas and an increasing number of cities to address demands created by video streaming and other high-bandwidth residential applications.
Most of the densely populated areas around the globe are creating need for high-speed and high-bandwidth connectivity. Due to this, telecom operators have rapidly been introducing 5G technology. For instance, in August 2019, China Unicom and China Telecom signed an agreement to cooperatively build and share 5G network infrastructure. Also, some of smartphones are getting discounts over their 5G models such as Vivo, Xiaomi, and Samsung. Such strategies are further boosting growth of the global 5G infrastructure market.
Furthermore, in January 2021, the Ministry of Science and ICT in South Korea announced to increase coverage of 5G mobile networks to 85 cities. Under this strategy, the government has also introduced an extended support for local firms for transition towards ultra-fast networks. In addition, the government of South Korea is significantly investing in research and development (R&D) of mobile edge computing which is an essential component for 5G in virtual reality applications. Such government strategies are opportunistic for growth of residential segment.
By Communication Infrastructure
By Core Network Technology
By Network Architecture
By Spectrum
By Component
By End User
By Geography
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
December 2024
January 2025
June 2025
May 2025