August 2024
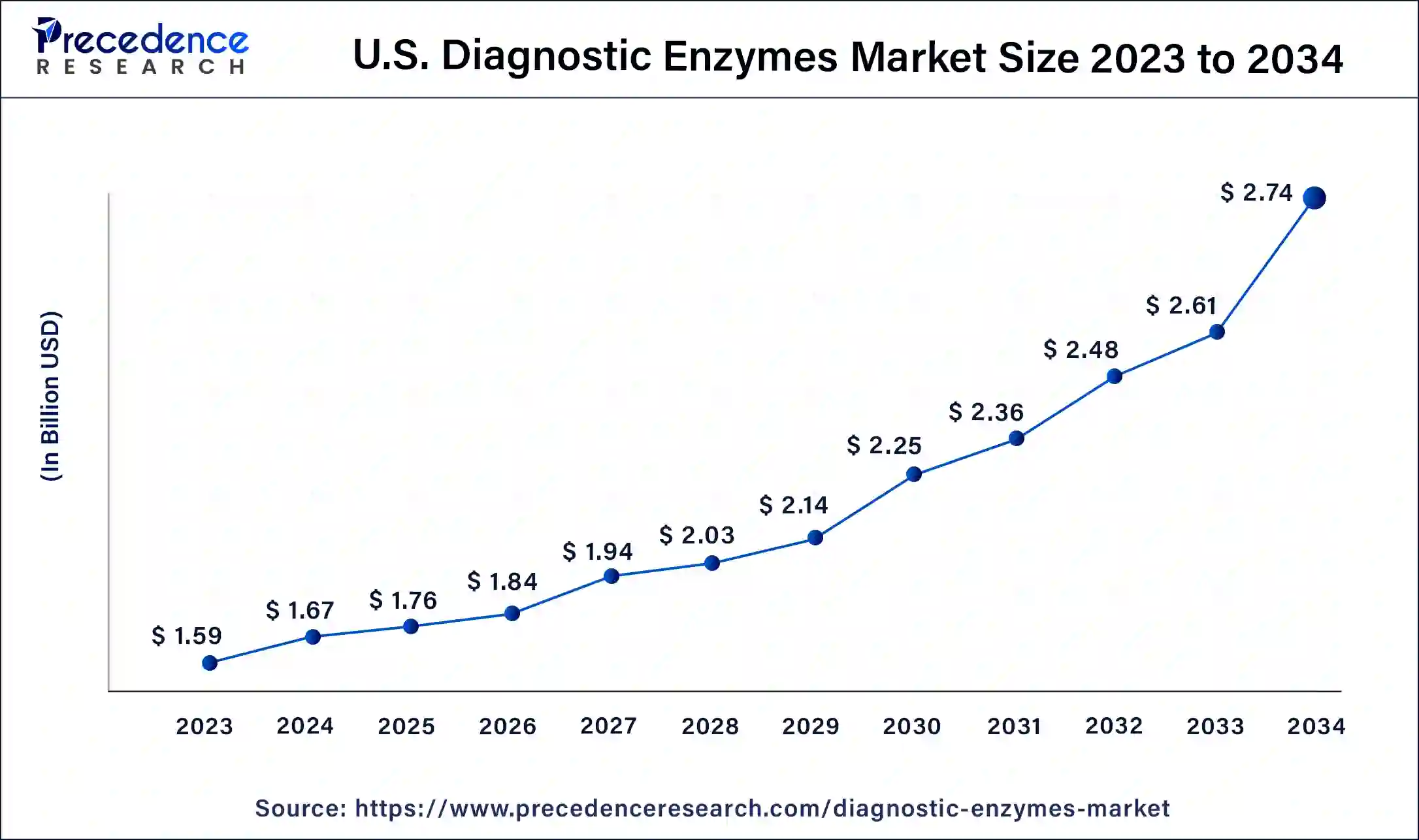
The global diagnostic enzymes market size was USD 5.04 billion in 2023, calculated at USD 5.29 billion in 2024 and is projected to surpass around USD 8.62 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 5% from 2024 to 2034.
The global diagnostic enzymes market size accounted for USD 5.29 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 8.62 billion by 2034, at a CAGR of 5% from 2024 to 2034. The North America diagnostic enzymes market size reached USD 2.12 billion in 2023.
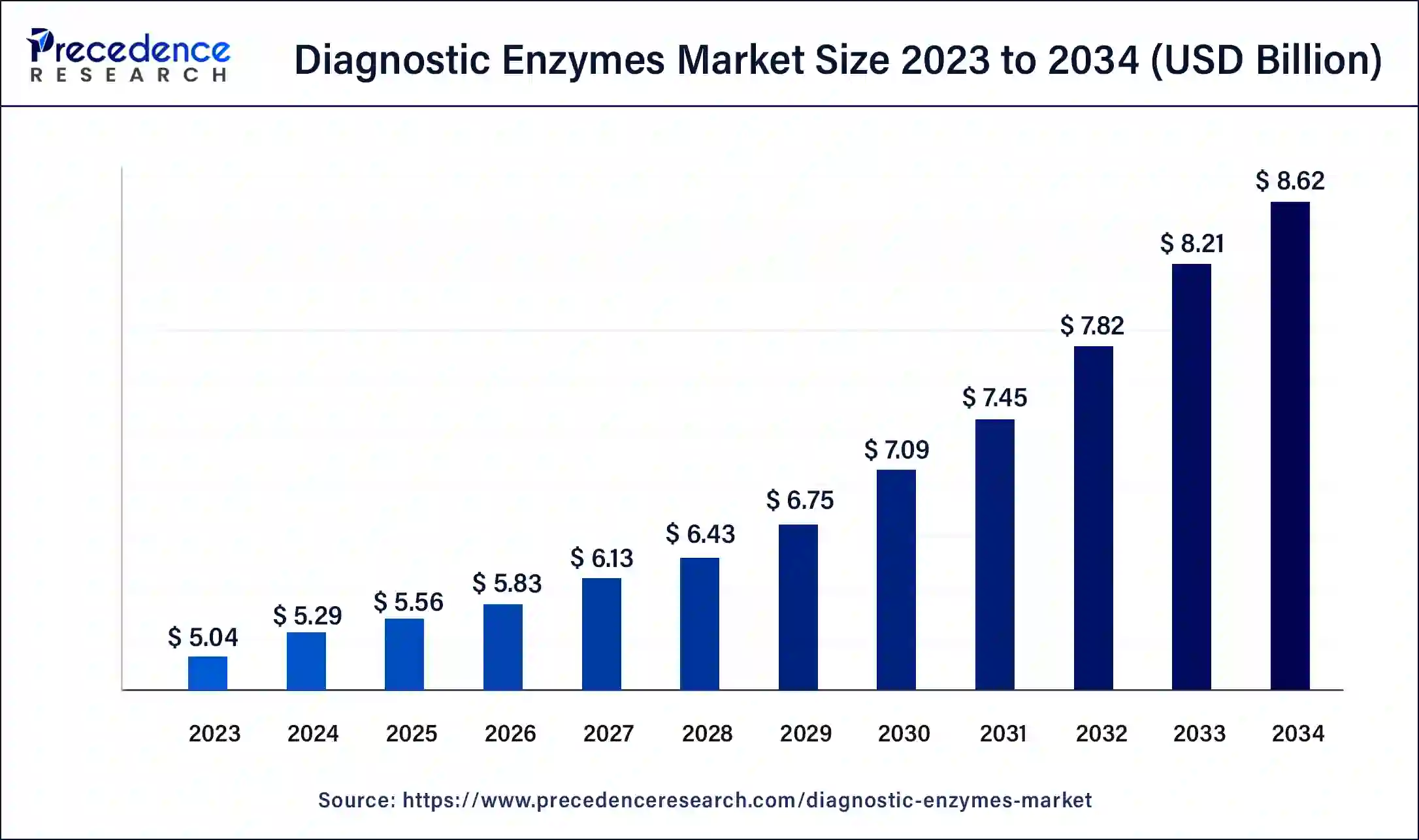
The U.S. diagnostic enzymes market size was estimated at USD 1.59 billion in 2023 and is predicted to be worth around USD 2.74 billion by 2034, at a CAGR of 5.1% from 2024 to 2034.
North America will likely experience significant growth in the market under study and hold a substantial share in the market for diagnostics enzymes during the forecast period due to significant funding for R&D from the government and private players, as well as the presence of key market players there.
Due to its technological superiority over the rest of the globe and significant R&D expenditure, the United States is predicted to have the most significant growth in North America. In 2018, the United States spent around USD 606.1 billion on R&D, according to the National Center for Science and Engineering Statistics. Additionally, it was predicted that the overall capital investment in R&D will be close to USD 656 billion in 2019, based on performance statistics. The existence of prominent market participants who are developing and introducing new products, top-notch research facilities led by some of the most renowned scientists (including Nobel laureates), technologically cutting-edge biotechnology firms, and public awareness are the other factors contributing to the United States' significant market share. For instance, San Diego-based Mesa Biotech Inc., a provider of molecular diagnostics, was acquired by Thermo Fisher Scientific in January 2021.
Canada and Mexico may hold the second and third-largest shares of the North American market for diagnostic enzymes after the United States. In addition to enhancing its health infrastructure and public awareness, Canada is following the United States' lead and investing extensively in R&D in the biotechnology and pharmaceutical sectors.
Due to factors such as the rising frequency of infectious diseases, the high demand for enzymes, the growing inclination for novel treatments, and the growing patient awareness, the market for diagnostic enzymes is expanding.
The detection and measurement of diverse compounds frequently employ diagnostic enzymes. Various aberrant metabolic processes, infections, infectious and non-infectious disorders, and inflammatory states can all be detected by changes in biomolecule concentration. Rapid & severe accurate disease diagnosis and appropriate treatment support ideal clinical outcomes and general public health.
Enzymes are frequently used to diagnose numerous diseases due to their excellent bio-catalytic properties. The metabolic activity of all living things, including plants, microbes, animals, and people, depends on enzymes, and multiple metabolic problems can result from aberrant enzyme activity. As a result, parts of the enzyme metabolism systems have been used as unique markers to diagnose diseases.
The prompt control of the transmission of infectious illness and the reduction of the dangers to public health depends on adopting proper diagnostic techniques. Significant efforts and breakthroughs have been made to achieve the WHO ASSURED criteria for assays in developing viral diagnostic technologies.
However, due to worries about healthcare spending and an increase in the usage of diagnostic enzyme testing, the financial pressure on these tests has increased during the past ten years. For product approvals, the diagnostic industry is likewise subject to strict rules. At first, the only prerequisite for the registration of diagnostic tests in the EU was CE mark approval. Regulating bodies, however, also need evidence of significant test benefits and affordable costs due to financial constraints.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2023 | USD 5.04 Billion |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 5.29 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 8.62 Billion |
| Growth Rate from 2024 to 2034 | CAGR of 5% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | By Type, By Application, and By Product Type |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America and Middle East & Africa |
The sector for glucose oxidase/glucose dehydrogenase had the highest revenue share of 10.7% in 2023. Glucose oxidase is a common endogenous oxidoreductase in all living things (GOx). The biomedical sector has recently shown interest in it because of its inherent biocompatibility, lack of toxicity, and distinct catalysis against -d-glucose.
To efficiently speed up glucose oxidation into hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and gluconic acid, which can be used to detect cancer biomarkers, a variety of biosensors can use GOx. Demand for glucose oxidase is expected to increase due to the enzyme's critical involvement in the diagnosis of diabetes.
Throughout the forecast period, the lactate oxidase sector is anticipated to increase faster as more people are using molecular devices to manage their diabetes. In the cells of various living systems, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) is widely distributed and catalyzes the interconversion of pyruvate and lactate using the NAD+/NADH coenzyme system.
Human and animal blood plasma and serum include LDH enzymes directly derived from tissues and cells with a unique profile. This profile depends on the quantity of all tissue's intracellular isoenzymes, which create a pool of LDH in serum and plasma due to typical cell deterioration. Certain forms of cancer can be diagnosed using LDH. Additionally, it can be used for the diagnosis and follow-up of illnesses that result in cell destruction, to gauge the seriousness of some cancers, and keep tabs on patients. At the same time, they get therapy and examine aberrant fluid collections in the body.
In 2023, the segment dealing with infectious diseases had the largest market share. The widespread use of PCR technology has made it possible to identify and treat infectious diseases early. Now, it is possible to identify organisms with greater accuracy and sensitivity that were previously difficult to find. When diagnosing infectious disorders, PCR can identify common pneumonia, streptococcal pharyngitis, TB, ulcerative urogenital infections, and several chronic conditions. The polymerase DNA gene expression in Thermusthermophilus Escherichia coli permits effective activity, reverse transcriptase, for one-step identification of cellular mRNA expression.
The oncology category will likely increase fastest during the forecast period. The use of diagnostic enzymes in this market is driven by the widespread adoption of ISH techniques and the development of high-throughput technologies for diagnosing human tumors, such as comparative genomic hybridization and next-generation DNA sequencing.
The US government launched the COVID-19 pandemic-related Cancer Moonshot in February 2022 to increase cancer screening rates and locate instances that had gone undiagnosed. The government intends to cut cancer-related fatalities by 50% over the next 25 years through early detection and treatment, which will propel the demand for cancer diagnostic enzyme testing.
Due to the growing usage of enzymes in clinical chemistry, which is connected to examining body fluids for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes, the clinical segment accounted for the most significant revenue share of over 62% in 2023. Slight variations in the concentrations of body fluids like blood, plasma, or serum may signal the beginning of an illness that could be fatal. As a result, the analytical methods used in clinical chemistry should be quick, focused, and extremely sensitive.
The selectivity and speed of the enzymes make them an essential component of clinical chemistry diagnostic processes. The substrate in an assay can be evaluated using enzyme specificity, or interferences can be eliminated from another function. Enzymes are additionally used to measure inhibitors, co-factors, and activators. Enzymes are also ideal for use as labels in immunoassay processes because of their catalytic activity.
The molecular market will likely grow at a profitable rate. Different enzymes are mostly used in molecular diagnostics through PCR tests, NGS assays, and others. One of the most used molecular biology methods is PCR. The technology is widely used in various industries, such as cloning, sequencing, forensic investigation, and diagnostic testing.
Transcription-Mediated Amplification (TMA) and Isothermal Nucleic Acid Amplification Technology (INAAT) are other molecular biology tests that use enzymes (TMA). A target nucleic acid sequence can be found more quickly and exponentially with INAAT. This gets around the problems with thermal cycling.
Segmentation of the Report
By Type
By Application
By Product Type
By Geography
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
August 2024
January 2025
January 2025
January 2025