January 2025
The global patient simulator market size was USD 574.28 million in 2023, estimated at USD 626.54 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 1480.13 million by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 8.98% from 2024 to 2034.
The global patient simulator market size accounted for USD 626.54 million in 2024 and is predicted to reach around USD 1480.13 million by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 8.98% from 2024 to 2034.
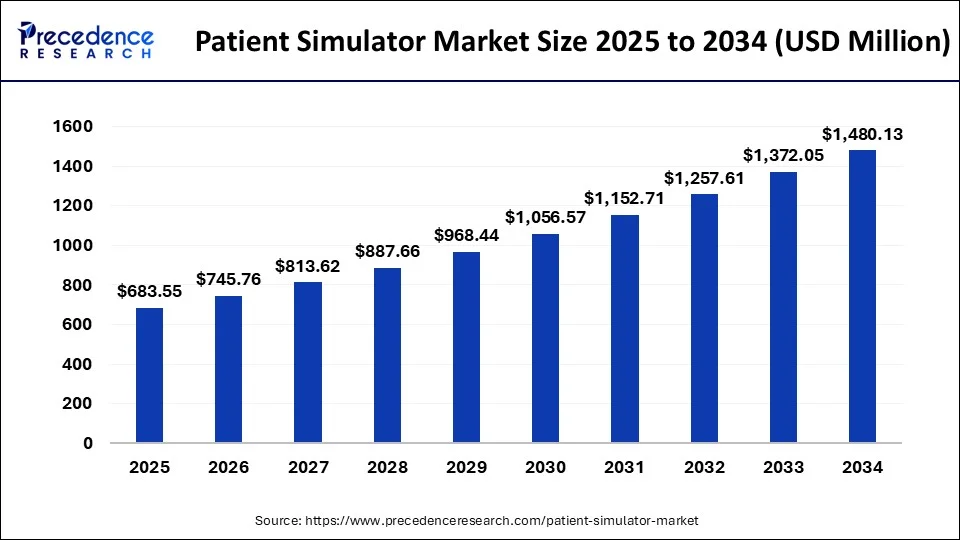
The U.S. patient simulator market size was valued at USD 152.76 million in 2023 and is expected to be worth around USD 397.09 million by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 9.06% from 2024 to 2034.
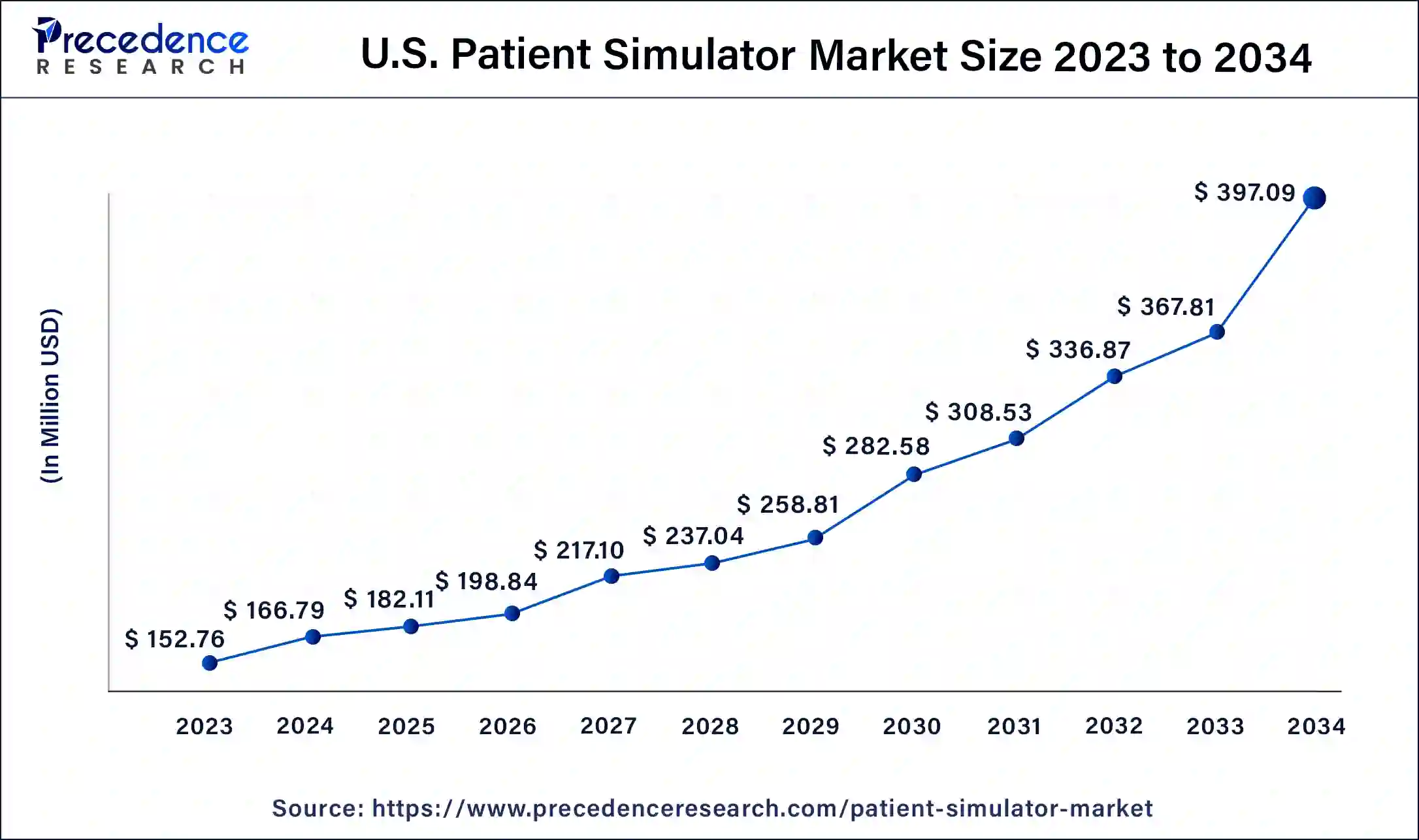
North America held the largest revenue share of 38% in 2023. North America is at the forefront of adopting advanced simulation technologies, including high-fidelity patient simulators with features like virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and artificial intelligence (AI). These technologies enhance the realism and effectiveness of patient simulators. Moreover, the region boasts numerous medical schools, nursing programs, and healthcare training institutions that extensively use patient simulators for educating and training future healthcare professionals. These institutions have been early adopters of simulation-based education.
Asia Pacific is estimated to observe the fastest expansion. The region is experiencing robust growth in the patient simulator market, driven by the increasing demand for healthcare professionals, the adoption of advanced medical technologies, and the growing emphasis on patient safety and quality healthcare. The market is experiencing significant growth, and as the region's healthcare and educational institutions continue to evolve and expand, the use of patient simulators is expected to play an increasingly vital role in healthcare training and patient safety initiatives across the region.
Europe patient simulator market is driven by the increasing demand for healthcare professionals, the incorporation of advanced medical technologies, and the growing emphasis on patient safety and high-quality healthcare. Europe has faced global health challenges, such as pandemics. Patient simulators have played a vital role in training healthcare professionals to respond effectively to emergencies and manage patient care during these crises.
A patient simulator, often referred to as a medical simulation manikin or simulator, is a sophisticated medical training and educational device designed to replicate human physiological functions, anatomy, and responses for the purpose of medical training, education, and research. These simulators are used in healthcare settings such as medical schools, nursing programs, hospitals, and other healthcare institutions to provide a realistic and controlled environment for training healthcare professionals, students, and researchers. As healthcare professionals increasingly rely on simulation-based training to enhance their clinical skills and knowledge, the patient simulator market has grown to provide innovative solutions for medical education and research.
Patient simulators can range from simple, low-fidelity models to highly sophisticated, high-fidelity manikins that replicate various physiological functions and responses. They can simulate a wide range of medical scenarios, including cardiac arrest, respiratory distress, surgical procedures, and more. These simulators often incorporate computer technology, sensors, and software to mimic human anatomy, vital signs, and responses to medical interventions accurately. Thus, patient simulators play a crucial role in healthcare education, allowing students and professionals to gain practical experience, improve their clinical skills, and build confidence without putting real patients at risk. They are widely used to train healthcare providers, from medical students and nurses to paramedics and physicians, in a safe and controlled learning environment.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Growth Rate from 2024 to 2034 | CAGR of 8.98% |
| Market Size in 2023 | USD 574.28 Million |
| Market Size in 2023 | USD 626.54 Million |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 1480.13 Million |
| Largest Market | North America |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | Product Type, Technology, End User, and Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America and Middle East & Africa |
Emphasis on patient safety
Patient safety is an utmost priority, and healthcare institutions are continuously seeking innovative ways to enhance it. Patient simulators have emerged as a pivotal tool in achieving this goal by providing a safe and controlled environment for healthcare professionals to learn, practice, and refine their clinical skills without putting real patients at risk. The inherent risk involved in traditional on-the-job training, where inexperienced healthcare professionals may inadvertently make mistakes that can jeopardize patient well-being is one of the vital reasons for driving demand across the market.
Patient simulators offer a lifelike and risk-free alternative, allowing learners to confront a wide array of medical scenarios, from routine procedures to life-threatening emergencies, and make errors without harming real patients. This invaluable opportunity to learn from mistakes and develop critical decision-making skills in a secure setting ultimately translates to enhanced patient safety when these professionals transition to real clinical settings.
Furthermore, the implementation of patient simulators aids in the standardization of training protocols, ensuring that healthcare professionals are consistently trained to the highest standards. This uniformity in education contributes to a more vigilant and competent workforce, reducing the likelihood of medical errors and adverse events. As healthcare institutions, medical schools, and regulatory bodies recognize the irreplaceable role that patient simulators play in improving patient safety, the demand for these simulation systems continues to escalate, fostering a safer and more reliable healthcare environment for all.
High initial costs
Patient simulators offer numerous benefits for healthcare education, training, and patient safety, but the substantial upfront investment required can be a significant restraint on their widespread adoption. The initial cost of purchasing high-quality patient simulators, especially advanced, high-fidelity models that closely mimic human physiology, can be considerable. These simulators often come with a substantial price tag, making them less accessible to smaller healthcare institutions, medical schools, and training programs with limited budgets. These organizations may find it challenging to allocate the necessary financial resources for procuring patient simulators.
Furthermore, the financial commitment doesn't end with the purchase price. Operating and maintaining patient simulators also incur ongoing costs, including software updates, equipment maintenance, and the replacement of consumable supplies. These expenses can strain the budgets of institutions, further contributing to the perceived high cost of implementing simulation-based training programs. Therefore, some healthcare institutions and educational programs may be hesitant to invest in patient simulators or may opt for lower-fidelity models to reduce initial expenses. While cost-effective options are available, they may not provide the same level of realism and functionality as their more expensive counterparts, potentially limiting the effectiveness of the training provided.
Advancements in simulation technology
The continuous progress in virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), artificial intelligence (AI), and haptic feedback systems has substantially elevated the capabilities and impact of patient simulators, creating a dynamic landscape of opportunities. Moreover, high-fidelity simulators can closely mimic human physiology, anatomy, and responses, providing learners with an immersive and lifelike training experience. This realism is crucial for healthcare professionals, as it enables them to practice a wide range of medical scenarios and procedures with a sense of authenticity that was previously unattainable.
Furthermore, the interactivity and immersion brought about by VR and AR technologies are transforming the learning process. Learners can engage in 3D environments, manipulate virtual instruments, and interact with computer-generated patients, promoting a deeper understanding of clinical tasks and enhancing decision-making skills.
AI-powered patient simulators introduce adaptability and personalization into training. These simulators can adjust scenarios and responses based on learner actions, thereby tailoring the training experience to individual skill levels and tracking progress over time. This adaptability enhances the efficiency of training and ensures that healthcare professionals are challenged and engaged at their appropriate level of expertise.
The ability to facilitate remote and collaborative learning is another remarkable opportunity arising from these advancements. Learners can engage in simulated scenarios from different locations, and instructors can guide and assess their performance in real-time. This is particularly pertinent in today's educational landscape, where remote and distributed learning has become increasingly important.
In 2023, the adult patient simulator segment had the highest market share of 47% on the basis of the product type and is anticipated to rapidly expand over the projected period. Adult patient simulators are designed to replicate the anatomy, physiology, and responses of an adult human. They are used for training healthcare professionals, such as doctors and nurses, in a wide range of medical scenarios, from routine patient assessments to critical care and emergency situations. These simulators often include features like vital sign monitoring, airway management, and the ability to simulate various medical conditions and responses to interventions.
In 2023, the low-fidelity simulators segment had the highest market share of 43% on the basis of the technology. Low-fidelity simulators are basic and less technologically advanced models that provide a simplified representation of human anatomy and physiological functions. These simulators are suitable for introductory or foundational training in healthcare. While they may not offer the same level of realism as higher-fidelity models, they are cost-effective and serve as entry-level tools for teaching basic clinical skills, such as CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation) or basic patient assessments.
The medium-fidelity simulators segment is anticipated to expand fastest over the projected period. Medium-fidelity simulators offer a balance between realism and cost-effectiveness. While they may not replicate human physiology and responses as accurately as high-fidelity simulators, they provide a realistic training environment for a broad range of medical scenarios. Medium-fidelity simulators are often used in healthcare education and training programs where a high level of realism is required, but budget constraints may limit the use of high-fidelity models. They offer valuable hands-on experience in a more affordable package.
In 2023, the hospitals segment had the highest market share of 45% on the basis of the end user. Hospitals are major end-users of patient simulators. These healthcare facilities use patient simulators for a variety of purposes. They are particularly valuable for training and assessing healthcare professionals within the hospital environment. Hospitals use patient simulators to enhance the skills and preparedness of their clinical staff, including doctors, nurses, and other healthcare personnel. Simulated scenarios may include emergency response training, surgical procedures, and critical care situations. Patient simulators in hospital settings also help in onboarding new staff and ongoing professional development.
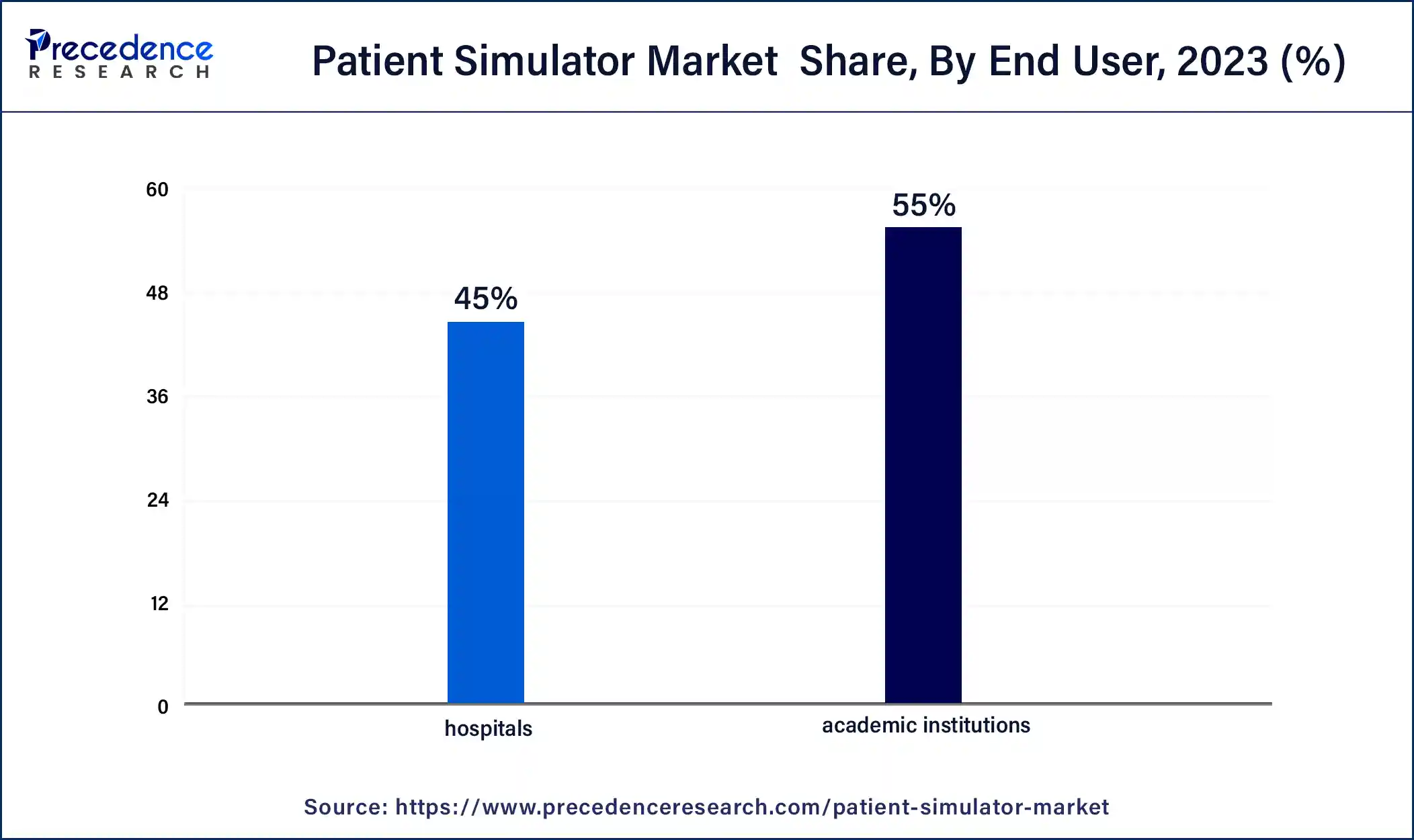
The academic institutions segment is anticipated to expand fastest CAGR of 8.3% over the projected period. Academic institutions, such as medical schools, nursing programs, and other healthcare educational institutions, are prominent end-users of patient simulators. These institutions use patient simulators as integral components of their educational curricula. They offer students a realistic and safe environment for hands-on learning and clinical skill development. Academic institutions use patient simulators to train future healthcare professionals, including medical students, nursing students, and allied health students. These simulators are vital tools for preparing students to enter the healthcare workforce with the essential clinical competence required to provide high-quality patient care.
Segments Covered in the Report
By Product Type
By Technology
By End User
By Geography
For questions or customization requests, please reach out to us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
January 2025
March 2025
September 2024
January 2025