The global rockets and missiles market size is calculated at USD 75.62 billion in 2025 and is predicted to surpass around USD 118.55 billion by 2034, accelerating at a CAGR of 5.13% from 2025 to 2034. The North America rockets and missiles market size surpassed USD 25.15 billion in 2024 and is expanding at a CAGR of 5.15% during the forecast period. The market sizing and forecasts are revenue-based (USD Million/Billion), with 2024 as the base year.
The global rockets and missiles market size was estimated at USD 71.87 billion in 2024 and is predicted to increase from USD 75.62 billion in 2025 to approximately USD 118.55 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 5.13% from 2025 to 2034.
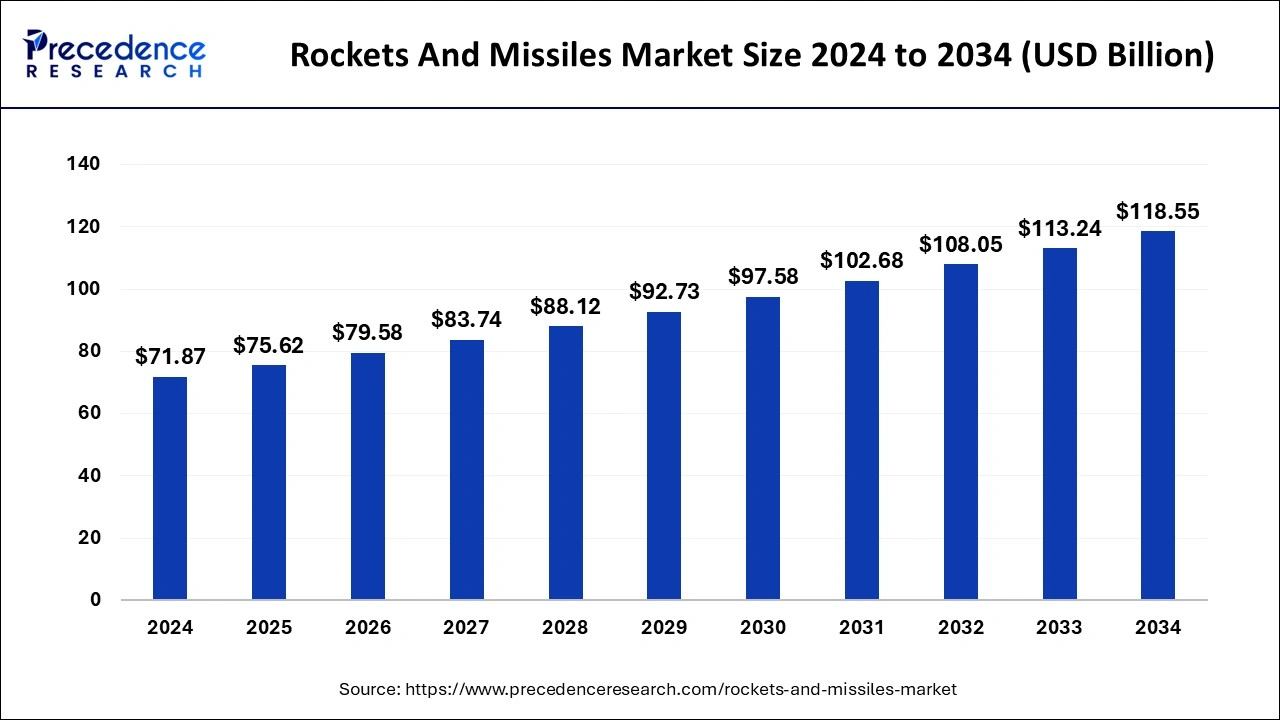
The U.S. rockets and missiles market size reached USD 17.30 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to be worth around USD 30.15 billion by 2034, poised to grow at a CAGR of 5.71% from 2025 to 2034.
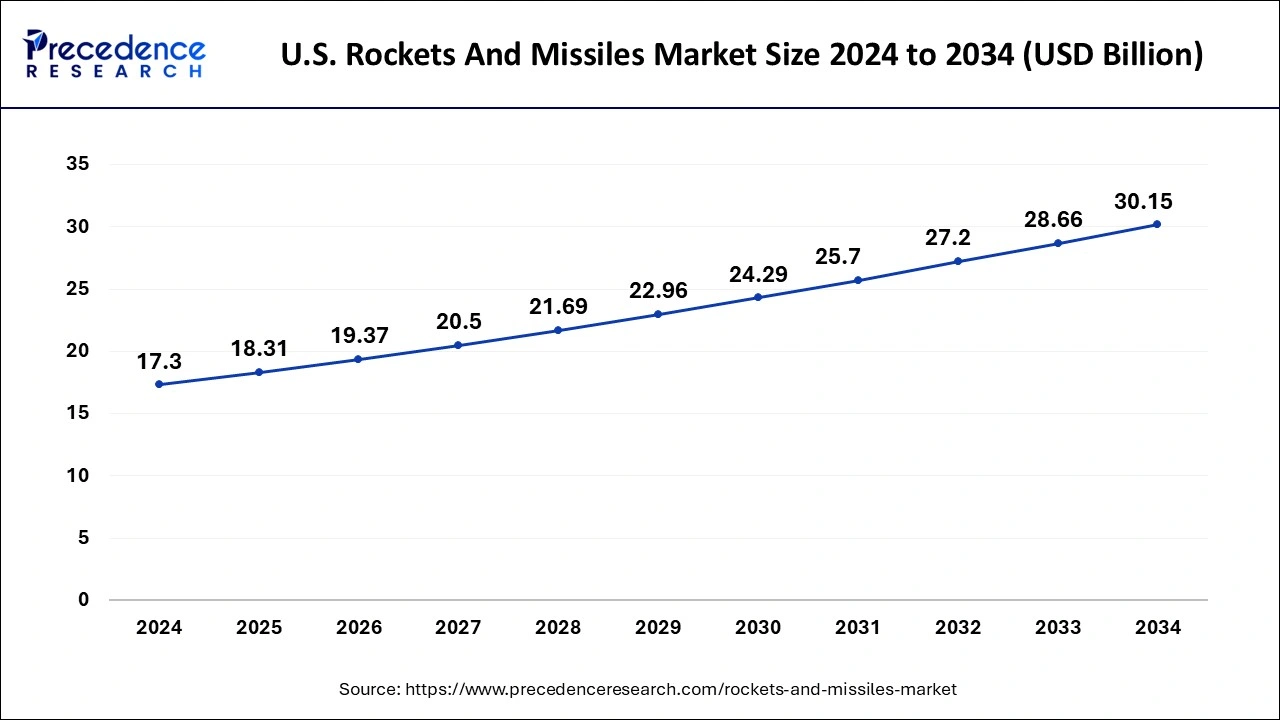
North America has held the largest revenue share in 2024. The United States is a major player in the global rockets and missiles market across the region. The U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) is one of the largest buyers of rockets and missiles in the region. Key defense contractors, such as Boeing, Lockheed Martin, Raytheon Technologies, Northrop Grumman, and General Dynamics, are involved in the development and production of various missile and rocket systems.
For instance, in August 2023, Raytheon Technologies received a contract from the U.S. Navy worth $124.2m to enhance the capabilities of maritime strike tomahawk missiles. It provides 42 maritime strike tomahawk seeker suites to boost tactical missile performance.
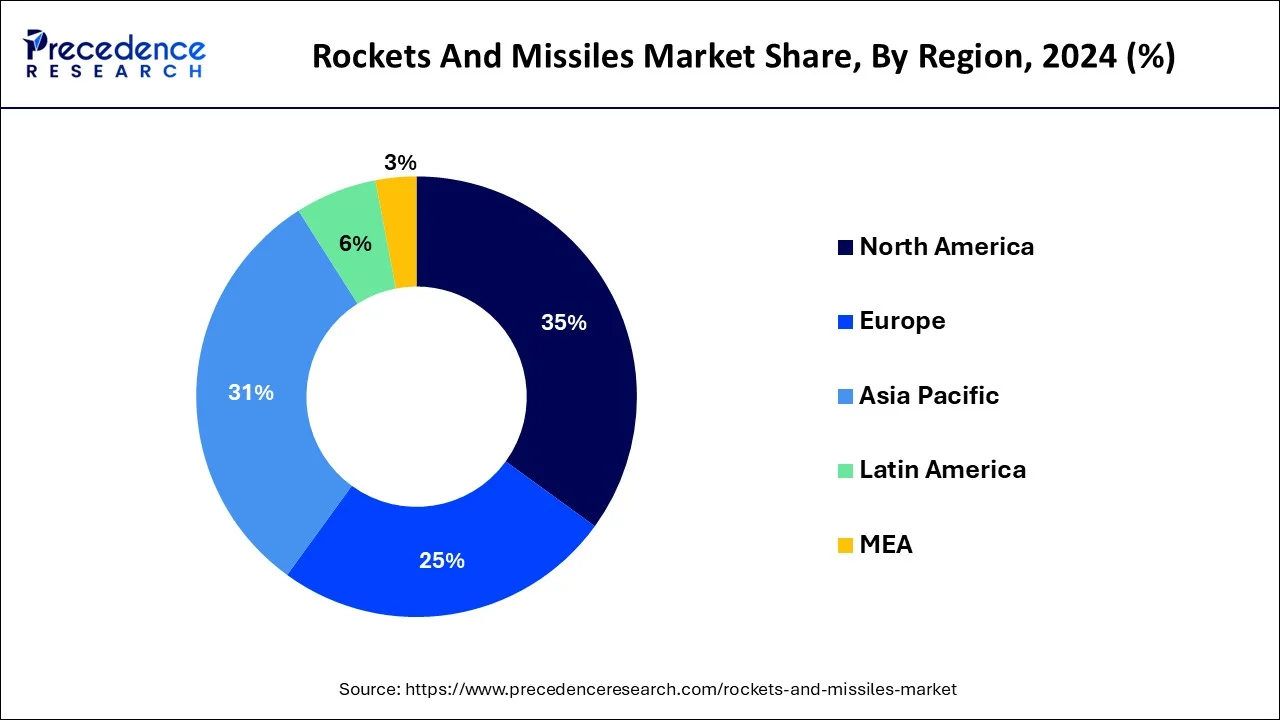
Asia-Pacific is estimated to observe the fastest expansion in the rockets and missiles market. Major players in the Asia-Pacific rockets and missile markets include China, India, South Korea, and Japan. Various countries in the region have robust defense infrastructure and are involved in the development and production of rockets and missiles. Moreover, the region is home to several longstanding and emerging geopolitical tensions, including territorial disputes, historical conflicts, and regional rivalries. These tensions drive demand for rockets and missiles as countries seek to enhance their defense capabilities and deter potential adversaries. Furthermore, the Asia-Pacific rockets and missiles market is shaped by a complex interplay of regional security dynamics, technological advancements, economic factors, and alliances. Geopolitical tensions and the need for deterrence and defense capabilities are primary drivers for investments in rockets and missiles in the region.
The European rocket and missile market is driven by various factors such as security concerns, modernization efforts, international commitments, technological advancements, and industrial collaboration. Geopolitical factors play a significant role in shaping the market as European nations seek to maintain their defense capabilities in an evolving security landscape.
For instance, in February 2023, Western allies announced that they supply precision rockets and missile systems to Ukraine to help retain control of the embattled eastern city of Bakhmut.
The growth of the market for rockets and missiles market can be attributed to various factors such as geopolitical factors, technological advancements, and expanding commercial opportunities. Ongoing geopolitical tensions and the need for national defense drive the demand for advanced missile systems, fostering continuous investment and modernization efforts by nations worldwide. Threats from ballistic missile proliferation and hypersonic weapons fuel the development of cutting-edge missile defense systems.
Furthermore, the rapid expansion of the space exploration industry, along with commercial ventures such as satellite deployment and space tourism, produces new markets for space launch vehicles and related technologies. Technological innovations, including materials, propulsion systems, and advanced manufacturing techniques, allow the development of more capable and cost-effective rocket and missile systems.
In addition, international collaboration in space exploration and partnerships for global security contribute to the industry's growth. With a competitive landscape driving innovation and government funding supporting key initiatives, the rockets and missile market continues to play a pivotal role in shaping modern technology, security, and global geopolitics.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 75.62 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 118.55 Billion |
| Growth Rate from 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 5.13% |
| Largest Market | North America |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | By Speed, By Product, By Guidance, and By Platform |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Increase in geopolitical tensions
Geopolitical rivalries and conflicts often necessitate a robust and credible defense posture, with missile systems playing a pivotal role in a nation's deterrence strategy. Whenever tensions escalate, countries seek to bolster their military capabilities to protect their sovereignty and national interests. Advanced missile systems, including ballistic missiles, cruise missiles, and anti-missile defenses, become vital components in this pursuit. These systems function as powerful tools for both offensive operations and defensive measures, deterring potential aggressors and providing a means of retaliation if necessary.
Furthermore, regional conflicts and security concerns often trigger arms races, with neighboring countries striving to match or surpass their adversaries' missile capabilities. This competitive dynamic further fuels demand for rocket and missile systems as nations aim to maintain strategic parity or gain a technological edge. In this environment, defense contractors and manufacturers find lucrative opportunities to supply advanced missile technologies and systems. They work closely with governments to develop cutting-edge solutions that may address evolving threats and enhance national security. Thus, as geopolitical tensions continue to rise, the rocket and missile market is projected to witness growth, driven by the imperative for nations to protect their interests and maintain a credible defense posture in an increasingly uncertain world.
Stringent regulations
The rocket and missile industry is heavily regulated, mainly due to fears related to international security, the proliferation of advanced missile technology, and the potential for misuse by rogue states. The Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR) is one of the most prominent regulatory frameworks, which aims to restrict the proliferation of missiles capable of carrying weapons of mass destruction. Under the MTCR, member countries agree to limit the export of specific missile-related technologies and systems to non-member states. This may significantly impede manufacturers' ability to enter new markets or sell their products internationally, especially when dealing with countries that are not MTCR members.
In addition, national export controls and licensing requirements further complicate international sales of rocket and missile technology. Governments often scrutinize and restrict the transfer of sensitive technologies, including those related to guidance systems, propulsion, and re-entry vehicles. These restrictions may lead to delays in procurement processes and limit market access. Furthermore, the enforcement of export control regulations may sometimes result in diplomatic tensions and trade disputes, affecting the overall flow of missile-related products and technologies. Exporting nations must navigate complex legal and political landscapes to ensure compliance with regulations while pursuing business opportunities. Therefore, stringent regulations, particularly those related to the MTCR and national export controls, present significant hurdles for the rockets and missiles market.
Rise in the adoption of hypersonic missile systems
Hypersonic missiles are a revolutionary class of weapons characterized by their exceptional speed, agility, and precision. Their unique capabilities have spurred considerable interest among defense organizations and nations worldwide, driving demand for advanced rocket and missile technologies. It offers several advantages, including the ability to deliver payloads over great distances with unprecedented speed, making them exceptionally challenging to intercept or defend against. Various countries are investing heavily in the development and deployment of hypersonic missile systems to enhance their military capabilities and strategic deterrence.
For instance, in September 2023, Russia provided its first crew to use hypersonic, air-launched Kinzhal missiles during a military operation in Ukraine. The Kinzhal hypersonic missile will be used by Su-34 aircraft during the special military operation.
Developing and producing the guidance, propulsion, and control systems required for hypersonic missiles is a complex endeavor, necessitating cutting-edge technologies and expertise. Companies specializing in rocket and missile components, such as propulsion systems, composite materials, and advanced sensors, stand to benefit from these emerging requirements. Furthermore, the development and production of hypersonic missile systems often involve collaboration between defense contractors, aerospace firms, and research institutions, creating a dynamic and competitive landscape within the rocket and missile market.
For instance, in September 2023, Huntington Ingalls Inc. (HII) received a contract worth $154.8 million to modernize the US Navy’s USS Zumwalt (DDG 1000) destroyer, arming the vessel with a hypersonic missile system. This surge in demand for hypersonic missiles has created opportunities for manufacturers and suppliers in the rockets and missiles market.
According to the speed, the hypersonic segment has held the largest revenue share in 2024 and is anticipated to expand at a significant CAGR during the projected period. Hypersonic missiles travel at extremely high speeds, typically exceeding Mach 5. It provides exceptionally high speed and maneuverability which helps in quickly destroying targets. It offers reduced response times and the ability to strike targets with minimal warning. Moreover, it has a wide range of applications, such as rapid strike capabilities, anti-satellite missions, and strategic deterrence. They are being developed for both offensive and defensive purposes.
Based on the product, cruise missile is anticipated to hold the largest market share in 2024. Cruise missiles are unmanned, and self-propelled guided missiles that are designed for precision strikes against specific targets. They are mainly powered throughout their entire flight and may be launched from various platforms, including sea, land, and air. It is used for a wide range of missions, including anti-ship operations, land attacks, and strategic strikes. They are known for their ability to fly at low altitudes and evade enemy radar, making them suitable for stealthy and precise strikes.
On the other hand, the ballistic missile is projected to grow at the fastest rate over the projected period. Ballistic missiles are guided or unguided missiles that follow a ballistic trajectory and are initially powered by rocket engines but then follow a free-falling path under gravity's influence. They are mainly segmented based on their range and purpose, including short-range, intermediate-range, medium-range, and intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs). It has both strategic and tactical applications. Short-range and medium-range ballistic missiles can be used for theater-level conflicts, while ICBMs are capable of delivering nuclear or conventional warheads over intercontinental distances.
In 2024, the guided missiles accounted for the highest market share and were anticipated to expand at the fastest rate over the projected period based on the guidance. Guided missiles are armed with sophisticated guidance systems that enable them to actively adjust their flight path and target accuracy during their course of journey. These systems may include GPS, radar, inertial navigation, laser, or optical guidance, and others. It is highly accurate and can be precision-guided to hit specific targets with a high degree of reliability. They are used in a wide range of applications, including anti-aircraft, anti-ship, anti-tank, and land-attack missions. They are employed for both offensive and defensive purposes.
Unguided missiles, commonly referred to as rockets, lack sophisticated guidance systems. They follow a ballistic trajectory, often with no ability to actively adjust their flight path once launched. Unguided missiles are generally less accurate compared to guided missiles. Their accuracy relies on factors such as launch angle, initial velocity, and wind conditions. Rockets are used in various roles, including artillery support, ground attack, and saturation attacks.
The ground segment held the largest revenue share in 2024. Ground-based missiles, often referred to as land-based missiles, are launched from stationary or mobile land-based platforms, including missile launchers, transporters, and launch vehicles. It serves various purposes, such as land attack (striking enemy ground targets), missile defense (intercepting incoming missiles), and tactical battlefield support. They are used for both offensive and defensive operations on land.
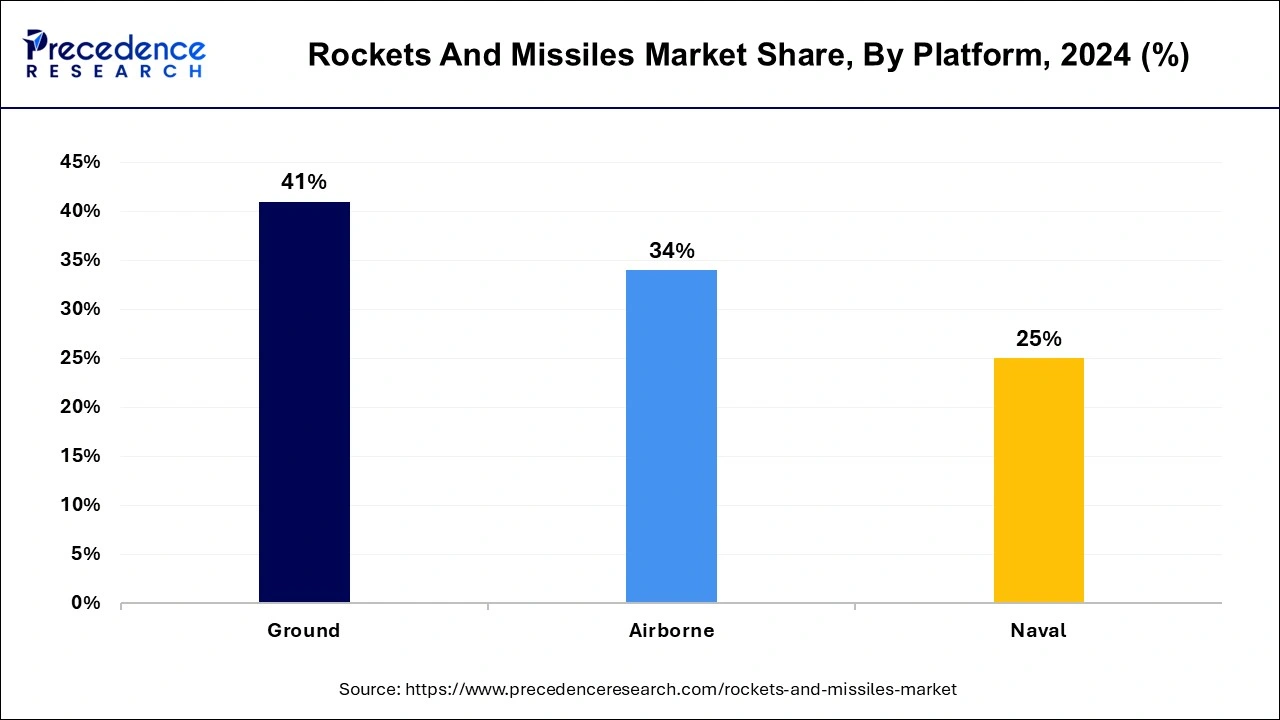
The naval segment is anticipated to grow at a significantly faster rate over the predicted period. Naval missiles are specifically designed for launch from naval vessels, including surface ships, submarines, and other maritime platforms. It is used by Naval missiles for anti-ship warfare (targeting enemy surface vessels), anti-submarine warfare (engaging enemy submarines), and anti-aircraft defense (protecting naval assets against aerial threats). They are essential for maintaining maritime security and power projection.
By Speed
By Product
By Guidance
By Platform
By Geography
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client