The global supercomputer market size accounted for USD 10.79 billion in 2024, grew to USD 11.98 billion in 2025 and is predicted to surpass around USD 30.64 billion by 2034, representing a healthy CAGR of 11% between 2024 and 2034.
The global supercomputer market size is accounted for USD 10.79 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 30.64 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 11% from 2024 to 2034.
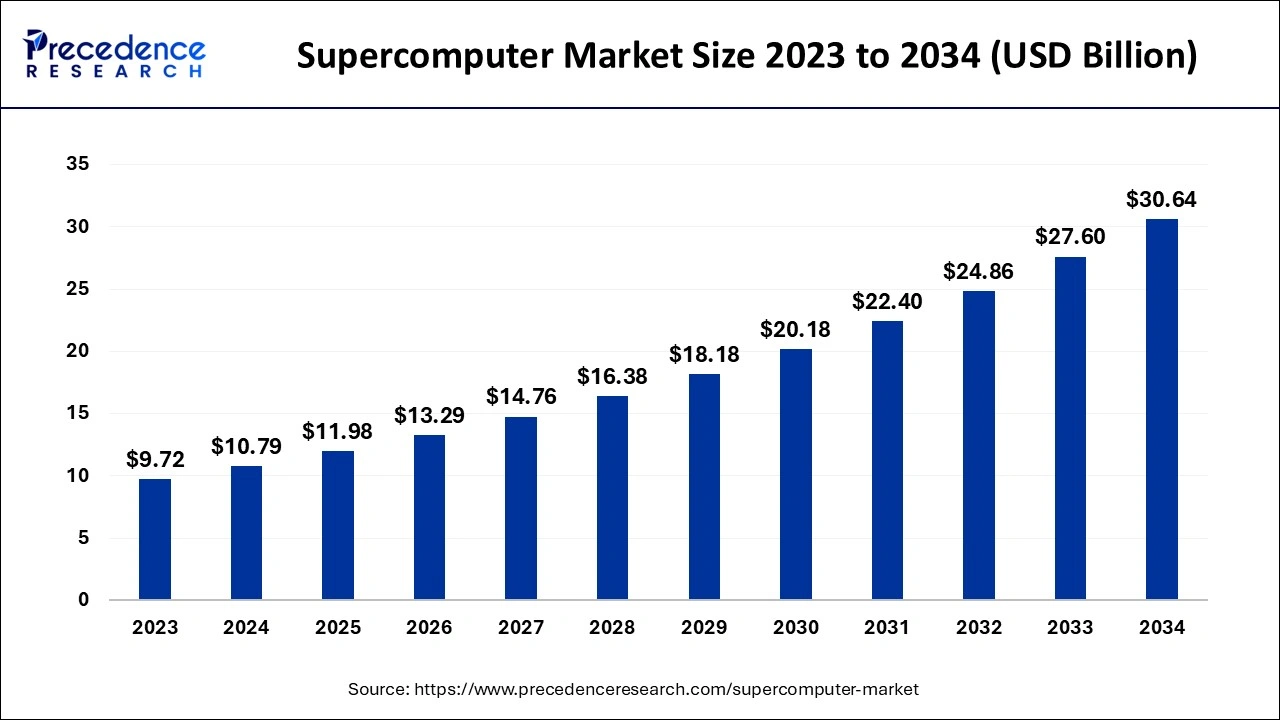
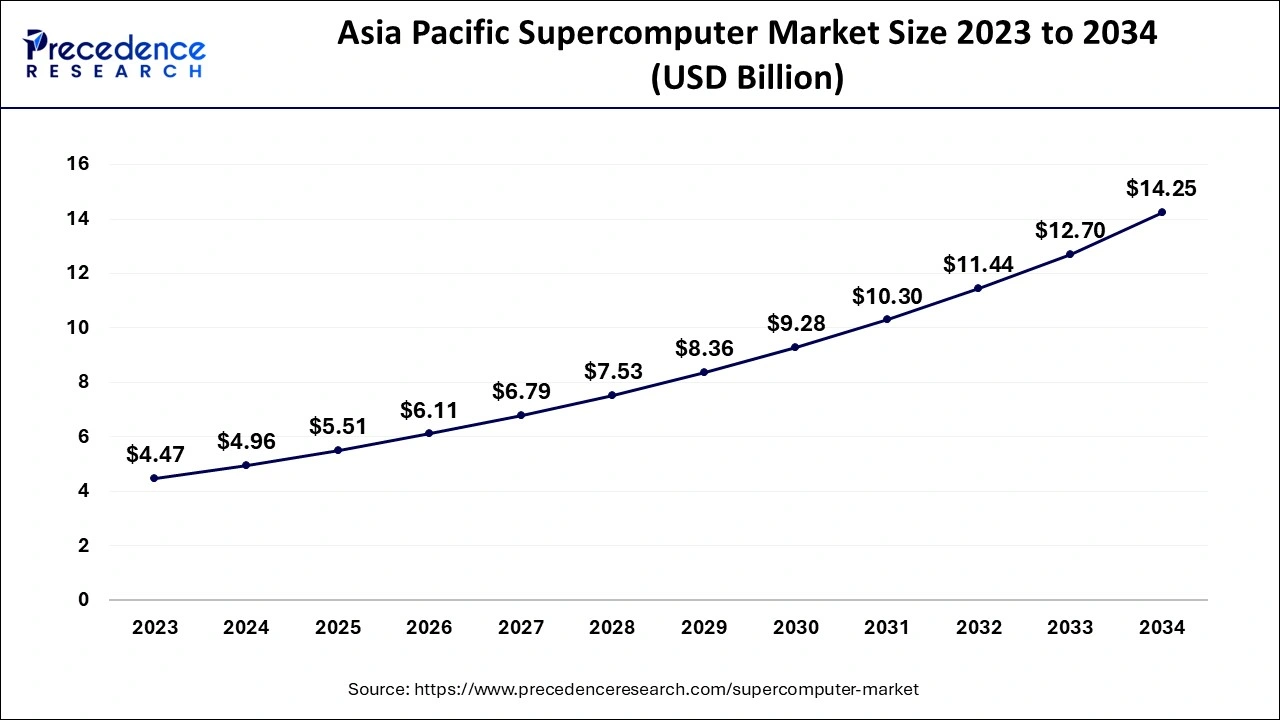
The Asia Pacific supercomputer market size is evaluated at USD 4.96 billion in 2024 and is predicted to be worth around USD 14.25 billion by 2034, rising at a CAGR of 11.12% from 2024 to 2034.
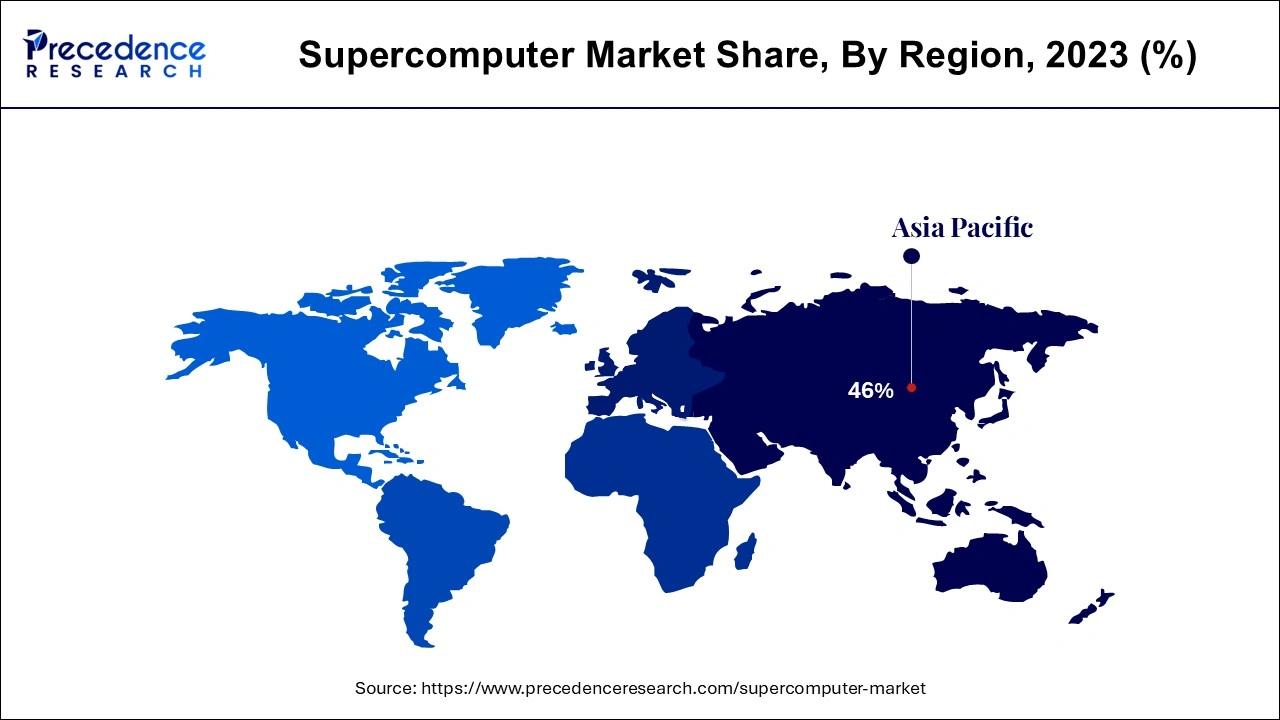
APAC has the highest installed base of supercomputers, accounting for over 46% of the total. Chinese enterprises are pursuing an ambitious approach to establish their own supercomputing systems based on locally generated software and hardware. In 2023, China covertly built the world's first exascale supercomputer, which was quickly followed by a second machine. The Next Platform originally reported on the supercomputers, but Kahaner explained them a few months later.
The number of TOP500 installations in China has risen to 227, up from 219 six months earlier. Meanwhile, the percentage of systems headquartered in the United States remains near an all-time low of 118. However, systems in the United States are substantially larger on average, accounted for 37.9% of aggregate performance. China is close behind, with a performance share of 31.7%. However, as compared to six months ago, this performance disparity has narrowed. The United States accounted for 38.5% of the list's aggregate performance in June 2019, while China accounted for 29.8%.
Japan is still third in the number of TOP500 systems, with 29, followed by France (18), Germany (16), and the Netherlands (15). Lenovo (174), Sugon (71), and Inspur (70) are the top three system vendors in terms of number of installations, reflecting China's overwhelming dominance (65). Cray is fourth with 36 systems, while HPE is fifth with 35. Given that Cray is now owned by HPE, the two companies would essentially connect Sugon to 71 systems.
Supercomputers, in contrast to conventional computers, employ many central processing units (CPU). These CPUs are arranged into compute nodes, each of which consists of a memory block and a processor or group of processors (symmetric multiprocessing, or SMP). A supercomputer at scale may have tens of thousands of nodes. These nodes can work together to solve a particular problem thanks to their interconnect communication capabilities. Interconnects are another means by which nodes interact with I/O systems, such as networking and data storage. An important point to keep in mind is that data centers need cooling systems and appropriate facilities to accommodate everything due to the power consumption of modern supercomputers.
The first two purposeful supercomputers, IBM's 7030 Stretch and Sperry Rand's UNIVAC LARC, which were intended to be more powerful than the fastest commercial machines at the time, introduced the word supercomputer in the early 1960s. The development of cutting-edge, high-performance computer technology for military purposes first received regular financing from the US government in the late 1950s, which sparked a series of events that influenced the development of supercomputing.
The vast majority of installed modern mainstream computer systems cannot match the sustained performance offered by supercomputers. Supercomputers make it possible to generate information in applications like the analysis of intelligence data, weather forecasting, and climate modeling that would not otherwise be possible or that could not be produced in time to be useful. Scientific research in vital fields including physics, material sciences, biology, and medicine can be expedited by the use of supercomputing. In situations when tests are risky, expensive, or even impossible to perform or instrument, supercomputer simulations can supplement or replace experimentation. They can dilate space, allowing us to witness atomic phenomena, or contract space, allowing us to observe the core of a supernova. They can collapse time, allowing us to observe the change of the climate over centuries or the evolution of galaxies over billions of years. Better forecasts of a hurricane's landfall or the effects of an earthquake can save lives and money.
The fast rise in access to and usage of open and big data is enabling the worldwide digital transformation. The economic potential of data is becoming more apparent, and data-driven innovations are emerging as a fundamental driver - a platform of innovation - for the fast spread of disruptive technologies and business model breakthroughs. HPC, Cloud Computing, and mobile web service innovations, together with fast increasing access and usage of Big Data, are altering enterprises, public services, and society as a whole. As a result, HPC infrastructure and services are critical enablers of far-reaching innovations in scientific research, industry, and SMEs.
Supercomputers produce new discoveries by processing and analyzing ever larger and more useful data sets. As a result, today's primary advancements in supercomputing address the sheer magnitude of such data sets by incorporating payment systems artificial intelligence tools, big data analytics, and edge computing.
Payment Systems - While supercomputers have many uses, one of the most important for preserving global and local economies is payment fraud detection. Customers are frequently accustomed to the convenience of rapid payment processing and approval, but this also implies that fraud may occur virtually instantaneously, at least without the proper security safeguards in place.
To combat fraud in real time, payment processing and fraud detection analysis must be similarly quick. When thousands of transactions must be completed every second, achieving real-time performance becomes increasingly difficult. Such high demands can only be met by supercomputers with super-processing capability. Financial services firms such as Mastercard and Visa make significant investments in HPC, harnessing the capability of high-performance computers to conduct data mining, machine learning, and fraud detection algorithms on thousands of financial transactions every second. Financial technology firms are also involved in payment fraud detection, providing machine learning technologies that try to improve fraud detection systems.
Artificial intelligence - AI approaches enable supercomputers to draw conclusions from ever huge data sets. However, AI requires computing capacity to evaluate all of that data, which exascale can do far faster. Scientists will be able to ask and receive answers that they could not previously.
Big data analytics - Big data has emerged as a significant motivator for new and extended HPC deployments. For the time being, the majority of HPC big data workloads are based on classical simulation and modelling. However, the technical and business forces shaping big data will lead to new types of HPC configurations to gain insights from unimaginably large data sets in the future.
Edge computing - Edge computing has exploded as a source of fresh data sets. These data sets are generated by both single instruments that capture massive volumes of data and billions of linked devices dispersed throughout the planet. The lidar telescope in the Andes, for example, and the Square Kilometre Array radio telescope in Western Australia and South Africa both create massive volumes of data. But so do the wise.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 10.79 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 30.64 Billion |
| Growth Rate from 2024 to 2034 | CAGR of 11% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | Operating System, Type, End User, Application and Geography |
Based on operating system, the worldwide supercomputer market is divided into Linux and Unix. Over the projection period, Linux is expected to account for a sizable market share. Extreme scalability, consistency, and flexibility are expected to drive the expansion of this industry in the next years. According to the most recent Top 500 report, Linux now runs on all of the world's fastest 500 supercomputers. Back in 2017, the last two supercomputers ran Unix, therefore the previous number was 498.
Top 500 is a non-profit effort that began in 1993 to benchmark supercomputers. It distributes information on the top 500 fastest supercomputers in the world twice a year. When it comes to customization, Unix, being a closed source and proprietary operating system, is a costly proposition. In contrast, Linux is free and easy to modify. For each of the supercomputers, engineering teams may quickly design a Linux-based operating system.
Based on application, the global supercomputer market is divided into commercial, space & research centers, hospitals & laboratories, and government entities. The government sector controlled a sizable portion of the entire supercomputer industry. The rising public awareness of the growing relevance of economic competitiveness and security is expected to fuel demand for these computers. Scientists utilize supercomputers to analyses solar systems, satellites, and other nuclear research fields in this discipline. Data mining is a technique used by large organizations to extract usable information from data storage warehouses or a cloud system. Life insurance firms, for example, employ supercomputers to lower actuarial risks.
Weather forecasting: A climatologist can use the forecasting capacity of supercomputers to anticipate the chances of rain or snowfall in the area. It can also forecast the actual route of storms and cyclones, as well as their likelihood of striking. Supercomputers are used by government intelligence organizations to monitor communication between private persons and fraudsters. These agencies primarily require supercomputers' numerical processing power to encrypt cell phones, emails, and satellite transmission.
Military and Defence: Supercomputing enables military and defence agencies to conduct simulated tests of nuclear explosions and weapon ballistics.
Automobile: Using supercomputers, an automobile firm may assist clients in acquiring vehicles by allowing them to test the simulation environment provided by supercomputers prior to purchasing a vehicle.
In the laboratory, many scientists and climatologists utilize supercomputers to anticipate fog and other pollution and smog levels in a certain location. Supercomputers are used in the entertainment sector to make animations. In addition, supercomputers are commonly used by online gaming businesses to generate animation games.
In May 2020, Microsoft stated that, in collaboration with OpenAI, it has developed one of the top five publicly reported supercomputers in the world to train massive artificial intelligence models. The Azure-hosted supercomputer was expressly developed to train the company's AI algorithms. The new supercomputer designed for OpenAI includes more than 285,000 CPU cores, 10,000 graphics processing units, and 400 gigabits per second of connection for each GPU server, according to the statement made at its virtual Build developers conference.
D-Wave has announced the public availability of their quantum computer D-Wave, a firm located in Canada, has announced the general availability of its quantum computer with 5000 Qubits connection. Advantage as the business calls it, will be made available to clients via the Leap quantum cloud service. The platform includes new hardware, software, and tools designed to allow and speed the delivery of in-production quantum computing applications. It also offers a hybrid solver service with over 5000 qubits, which can answer large issues.
By Operating System
By Type
By End User
By Application
By Geography
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client