November 2024
The global sustainable finance Market size was USD 5.49 trillion in 2023, estimated at USD 6.61 trillion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 38.19 trillion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 19.2% from 2024 to 2034.
The global sustainable finance market size accounted for USD 6.61 trillion in 2024 and is predicted to reach around USD 38.19 trillion by 2034, growing at a solid CAGR of 19.2% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2034.
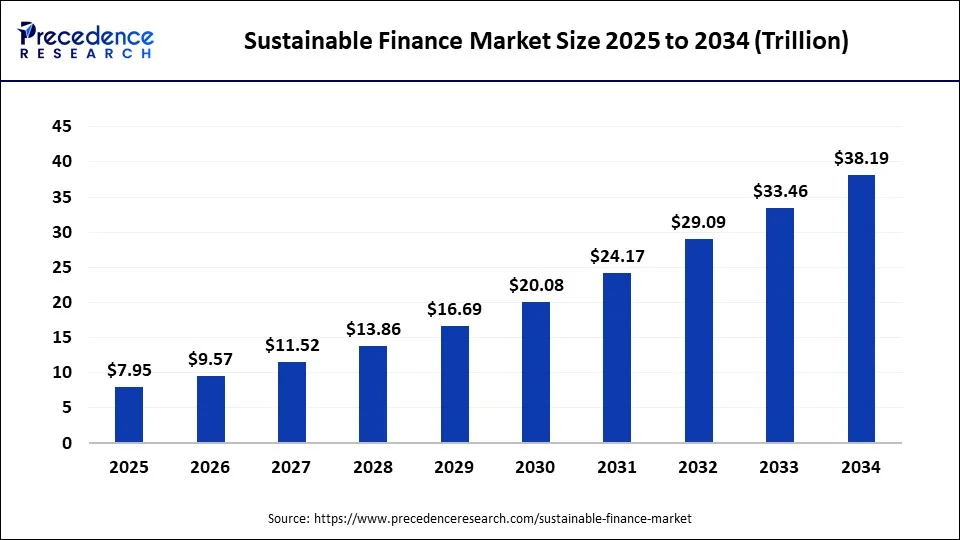
The Europe sustainable finance market size reached USD 6.61 trillion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 15.28 trillion by 2034, growing at a solid CAGR of 20% from 2024 to 2034.
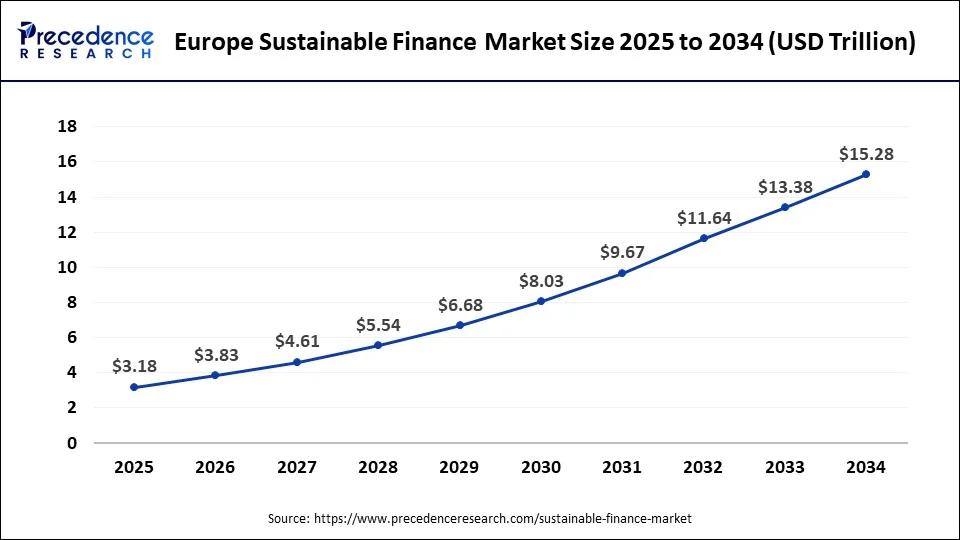
Europe dominated the sustainable finance market in 2023. European governments and institutions actively support and fund sustainable finance initiatives. For instance, the European Investment Bank (EIB) is a major player in green finance, providing funding for sustainable projects across Europe. European investors and consumers are increasingly aware of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) issues. This awareness drives demand for sustainable financial products, such as green bonds, ESG funds, and sustainable loans. Many European corporations have integrated sustainability into their business strategies, leading to a higher issuance of green bonds and sustainable financial instruments
North America held a notable share of the sustainable finance market in 2023. North America, primarily the United States and Canada, is also a prominent player in the sustainable finance market. Sustainable finance initiatives have gained traction, driven by the increasing demand for responsible investing and corporate sustainability practices. In the United States, companies are adopting sustainable strategies, and investors are showing greater interest in ESG-focused investments. Green bond issuance has increased, and institutional investors are integrating ESG factors into their decision-making processes.
The Asia-Pacific region is witnessing rapid growth in the sustainable finance market, fuelled by both government initiatives and investor interest. Countries like China, Japan, South Korea, and Australia are taking steps to promote sustainable finance and green investments. China has seen a surge in green bond issuance as it addresses environmental challenges and seeks to fund sustainable projects. The region's large population and economic potential make it a crucial market for sustainable financial growth.
The sustainable finance market also known as green finance is a financial ecosystem that strives to incorporate environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations into investment decisions. The primary objective of this market is to direct capital towards projects and businesses that promote sustainable development, combat climate change, safeguard natural resources, and have a positive impact on society. In the sustainable finance market, the trend is the increasing prominence of green bonds and sustainable debt instruments. These financial products are specifically earmarked to fund environmentally friendly initiatives, such as renewable energy projects, sustainable infrastructure developments, and conservation efforts.
The rise of these instruments indicates a growing interest in supporting projects with tangible environmental benefits. Another significant trend is the integration of ESG factors into investment strategies by investors and financial institutions. Environmental, social, and governance risks and opportunities have become mainstream considerations in identifying sustainable and responsible investments. As a result, investors are seeking opportunities that align with their values and contribute to positive social and environmental outcomes.
The concept of sustainable investing has also gained traction in the market. Strategies like socially responsible investing (SRI) and impact investing have become popular, demonstrating a shift towards investments that promote sustainability and have a positive societal impact. Companies are experiencing mounting pressure to disclose their ESG practices and performance. Investors now demand transparency in the environmental and social impacts of businesses, which significantly influences their investment decisions.
This growing emphasis on corporate sustainability underscores the importance of responsible business practices in the financial realm. Supportive policies and regulations are playing a crucial role in driving the sustainable finance market forward. Numerous countries and regions are implementing measures to encourage sustainable finance initiatives. Governments and financial regulators are incentivizing green investments and integrating sustainable principles into the financial system, fostering an environment conducive to sustainable development.
The European Union (EU) has been proactive in promoting sustainable finance and introducing regulations to encourage investments in sustainable projects. The EU's Action plan on sustainable finance, introduced in 2018, has played a pivotal role in mobilizing private capital for sustainable initiatives and aligning the financial sector with climate and sustainability objectives. Consequently, Europe has seen a significant increase in green bond issuance and a strong focus on ESG integration within its financial landscape.
The primary drivers fueling the market growth are the increasing awareness and conscious consumerism among individuals and investors regarding environmental and social issues. There has been an increase in demand for sustainable investment options and financial products that are in line with people's beliefs and encourage ethical behavior as people become more conscious of the effects their financial decisions may have on the environment and society.
The financial sector has innovated and diversified financial products in response to the rising demand for sustainable investments. Numerous products, including green bonds, sustainability-linked loans, social impact bonds, and green mutual funds, are available to suit varied investor preferences and risk tolerances, encouraging accessibility and inclusion in sustainable finance.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2023 | USD 5.49 Trillion |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 6.61 Trillion |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 38.19 Billion |
| Growth Rate from 2024 to 2034 | CAGR of 19.2% |
| Largest Market | Europe |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2024 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | Investment Type, Transaction Type, Industry Verticals, and Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Innovation in financial products
A significant market driver in the sustainable finance sector is innovation in financial products. The financial sector responds to the rising demand for sustainable investments by creating novel solutions that are suited to investors' preferences and risk tolerances. There will also be the launch of social impact bonds, green mutual funds, green bonds, and other ESG-focused securities. These cutting-edge financial instruments give investors a variety of chances to fund socially and ecologically conscious initiatives while attaining their financial goals. More investors are drawn to sustainable financial products due to their ongoing growth and diversity, which helps the industry grow and reinforces the world's commitment to sustainability.
High initial costs
The market for sustainable financing is significantly constrained by high entry costs. Although sustainable initiatives have long-term advantages, the high upfront costs might turn away potential investors. Some firms and investors find it difficult to first commit to initiatives like the construction of sustainable infrastructure or the installation of renewable energy sources since they need large financial resources. Innovative financial strategies, financial incentives from the government, and public-private sector cooperation are frequently needed to overcome this constraint. Sustainable finance continues to hold promise for long-term value and beneficial effect despite the upfront expenses, necessitating the development of innovative solutions to this problem and maximizing the potential of sustainable investments.
Sustainable infrastructure development
In the market for sustainable financing, the development of sustainable infrastructure offers a compelling potential. There is an increasing demand for environmentally friendly and resilient infrastructure as nations throughout the world concentrate on tackling environmental concerns. This potential is spread throughout several industries, including water management, green buildings, renewable energy, and public transit. Such initiatives can be supported by sustainable financing, which can draw funding from both the public and commercial sectors. Sustainable infrastructure development is a compelling idea for investors aiming to match financial interests with sustainable aims, encouraging a greener and more sustainable future because of the possibility for long-term rewards and good environmental effects.
Regulatory uncertainty
Market participants have a unique chance to influence the direction of sustainable finance due to regulatory uncertainty. New laws and rules are being established as countries and financial authorities attempt to address sustainability issues on a global scale. This gives market players the chance to actively participate in debates, shape the regulatory environment, and work together to develop efficient frameworks.
Businesses, investors, and financial institutions may establish themselves as pioneers in sustainable finance, gain a competitive advantage, and influence good change by proactively adjusting to changing rules. Accepting legislative changes can promote a more stable and uniform sustainable finance industry, attracting more investment and quickening the transition to a sustainable and ethical financial ecosystem on a global scale.
Impact of Covid-19:
The COVID-19 pandemic has left a complex imprint on the sustainable finance market, evoking both positive and negative effects. The impact has been diverse, varying across industries and regions. During the early stages of the pandemic, the financial markets experienced turbulence and uncertainty, resulting in heightened volatility. Investors prioritized immediate risk management, leading to a temporary slowdown in capital flow into sustainable finance projects.
The pandemic shed light on the significance of social and health considerations within the Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) framework. Companies and investors emphasized employee well-being, 27n resilience, and community support, elevating the importance of the "social" aspect of ESG. COVID-19 acted as a catalyst for the adoption of digital technologies and remote work practices. Sustainable investments in sectors connected to digital transformation, such as renewable energy, clean technology, and e-commerce, gained traction and secured increased funding.
Governments and international organizations responded with green stimulus and recovery packages, supporting economic revival while advancing sustainability objectives. Investments in renewable energy projects, sustainable infrastructure, and climate resilience measures were pivotal components of these packages. Green bond issuance was initially impacted by the pandemic, particularly in sectors affected by lockdowns and restrictions. Nevertheless, the resilience demonstrated by green bonds during the crisis highlighted their appeal as stable and sustainable investments. COVID-19 triggered a shift towards long-term resilience and sustainability.
It served as a wake-up call to address pressing global challenges, such as climate change and social inequality, reinforcing the necessity of constructing resilient and sustainable economies. This realization fuelled growing interest in sustainable finance solutions. The pandemic underscored the importance of ESG factors in assessing a company's resilience and prospects. Investors and businesses recognized that robust ESG performance can improve risk management and foster sustainable growth. COVID-19 presented challenges in ESG data reporting for companies due to disruptions. However, it also accentuated the importance of transparent and reliable ESG reporting to satisfy investor demands for sustainability information.
The COVID-19 pandemic has left a significant impact on the sustainable finance market, encompassing short-term volatility, an increased focus on social and health aspects, and a long-term emphasis on sustainability and resilience. Government stimulus packages and greater investor interest in ESG factors have further amplified the market's role in fostering a sustainable and resilient global economy. As the world recuperates from the pandemic, sustainable finance is poised to assume a pivotal role in shaping the post-COVID-19 landscape.
The equity investment segment dominated the sustainable finance sector in 2023. It entails purchasing stock or other ownership interests in businesses that exhibit sound environmental, social, and governance (ESG) principles. These companies are often leaders in sustainability within their industries and operate with a focus on long-term value creation while considering their impact on the planet and society. Equity investors seek to align their portfolios with companies that contribute positively to sustainability and are likely to benefit from the growing demand for sustainable products and services.
Fixed-income investments in the sustainable finance market primarily consist of green bonds, social bonds, and sustainability-linked bonds. Green bonds are specifically earmarked to fund environmentally friendly projects, such as renewable energy initiatives and energy-efficient infrastructure. Social bonds focus on projects with social objectives, such as affordable housing and healthcare. Sustainability-linked bonds, on the other hand, link the bond's financial terms to the issuer's sustainability performance, incentivizing improvements in ESG metrics. Fixed-income investors often prefer these instruments as they offer stable returns and align with their sustainability goals.
Mixed allocation strategies in the sustainable finance market involve blending both equity and fixed-income investments to achieve a balanced portfolio. These strategies allow investors to diversify their sustainable holdings across different asset classes, mitigating risks and capturing opportunities in both equity and fixed-income markets. Mixed allocation approaches cater to investors seeking a well-rounded and sustainable investment portfolio by providing exposure to various sectors and themes.
The green bond segment dominated the sustainable financing market in the sector in 2023. Green Bonds are specialized financial instruments designed to raise capital exclusively for projects and initiatives with positive environmental impacts. Issuers of green bonds earmark the proceeds for projects like renewable energy installations, sustainable infrastructure development, energy efficiency improvements, and climate change mitigation efforts. These bonds provide investors with an opportunity to support environmentally friendly initiatives while also generating financial returns.
Social Bonds are another segment of the sustainable finance market that focuses on financing projects with clear social objectives. The proceeds from social bonds are directed towards projects that address specific social issues, such as affordable housing, access to healthcare and education, employment generation in underserved communities, and initiatives promoting social welfare. Social bonds attract investors who seek to make a positive impact on society while earning financial returns.
Mixed Sustainability Bonds, also known as Sustainability Bonds, combine elements of both green and social bonds. The proceeds from these bonds are allocated to projects that contribute to both environmental and social goals. These projects typically aim to address multiple sustainability challenges, creating a holistic impact on both the planet and society. Mixed sustainability bonds offer investors a balanced approach to sustainability, allowing them to diversify their impact across various focus areas.
The transport and logistics sectors dominated the sustainable finance market in 2023. The transport and logistics sector presents opportunities for sustainable finance by addressing the environmental impacts of transportation, including emissions reduction and fuel efficiency. Sustainable finance in this vertical supports investments in electric vehicles, sustainable aviation fuels, public transportation infrastructure, and eco-friendly logistics solutions. Social bonds may also be utilized to fund projects that enhance accessibility and mobility in underserved communities.
The Utilities sector plays a crucial role in the sustainable finance market, especially in the context of renewable energy generation and distribution. Sustainable finance initiatives within this vertical focus on financing projects such as solar and wind power plants, hydroelectric facilities, energy storage solutions, and grid modernization. Utilities are significant beneficiaries of green bonds, attracting investments from both institutional and individual investors aiming to support the transition to a low-carbon economy.
The Chemicals industry vertical faces growing pressure to adopt sustainable practices and reduce its ecological footprint. Sustainable finance initiatives in this sector focus on funding projects related to sustainable chemistry, eco-friendly manufacturing processes, and the development of biodegradable or non-toxic materials. Investors interested in promoting environmentally responsible practices are attracted to this industry segment.
The Food and Beverage sector holds significant potential for sustainable finance, with a focus on sustainable agriculture, food waste reduction, and ethical sourcing. Investors in this vertical seek opportunities to support projects that promote responsible land use, water conservation, and social development within the food supply chain.
Governments and municipalities are essential participants in the sustainable finance market as they issue green bonds to fund sustainable infrastructure projects and climate change mitigation initiatives. The government sector plays a significant role in setting policies and regulations that incentivize sustainable practices across various industries, fostering the growth of sustainable finance in the broader economy.
By Investment Type
By Transaction Type
By Industry Verticals
By Geography
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
November 2024
October 2024
February 2025
February 2025