March 2024
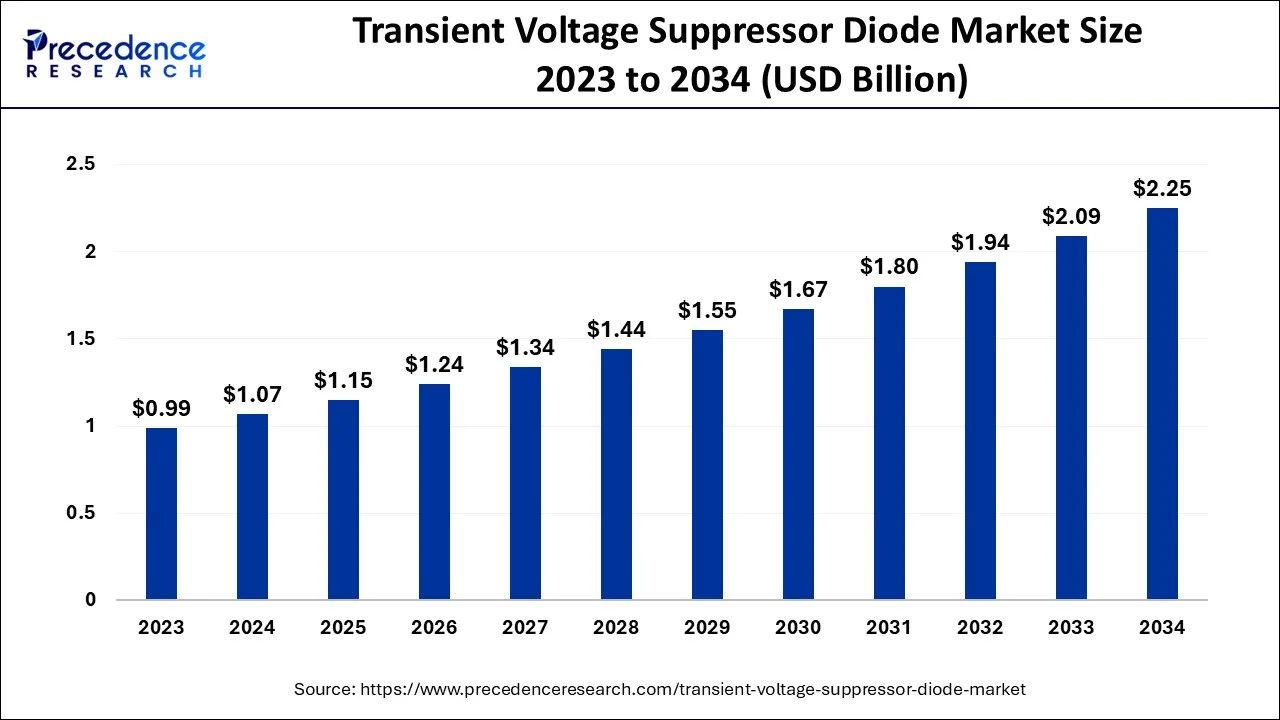
The global transient voltage suppressor diode market size accounted for USD 1.07 billion in 2024, grew to USD 1.15 billion in 2025 and is predicted to surpass around USD 2.25 billion by 2034, representing a healthy CAGR of 7.77% between 2024 and 2034.
The global transient voltage suppressor diode market size is estimated at USD 1.07 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 2.25 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 7.77% from 2024 to 2034
In order to handle strong transient currents, transient voltage suppressor diodes are specifically created with junctions that have a large cross-sectional area. The TVS diodes are particularly built, examined, and described for the suppression of transient voltages.
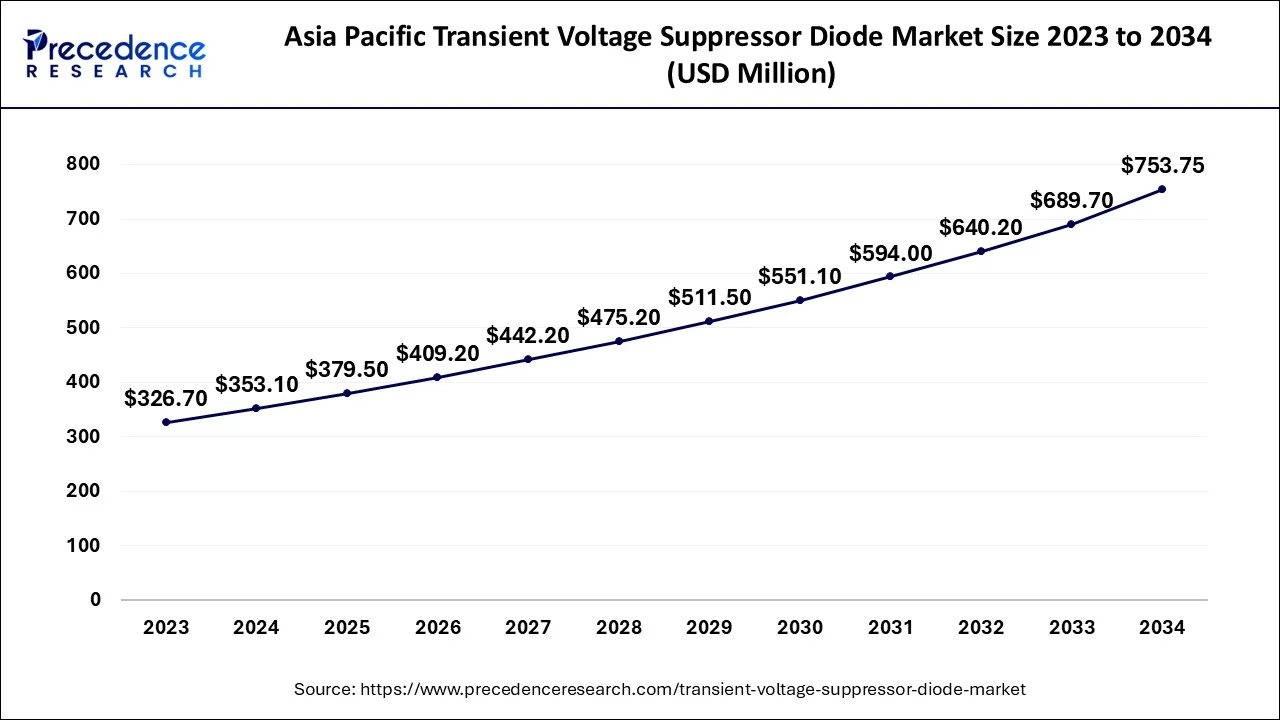
The Asia Pacific transient voltage suppressor diode market size is estimated at USD 353.10 million in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 753.75 million by 2034, rising at a CAGR of 7.75% from 2024 to 2034.
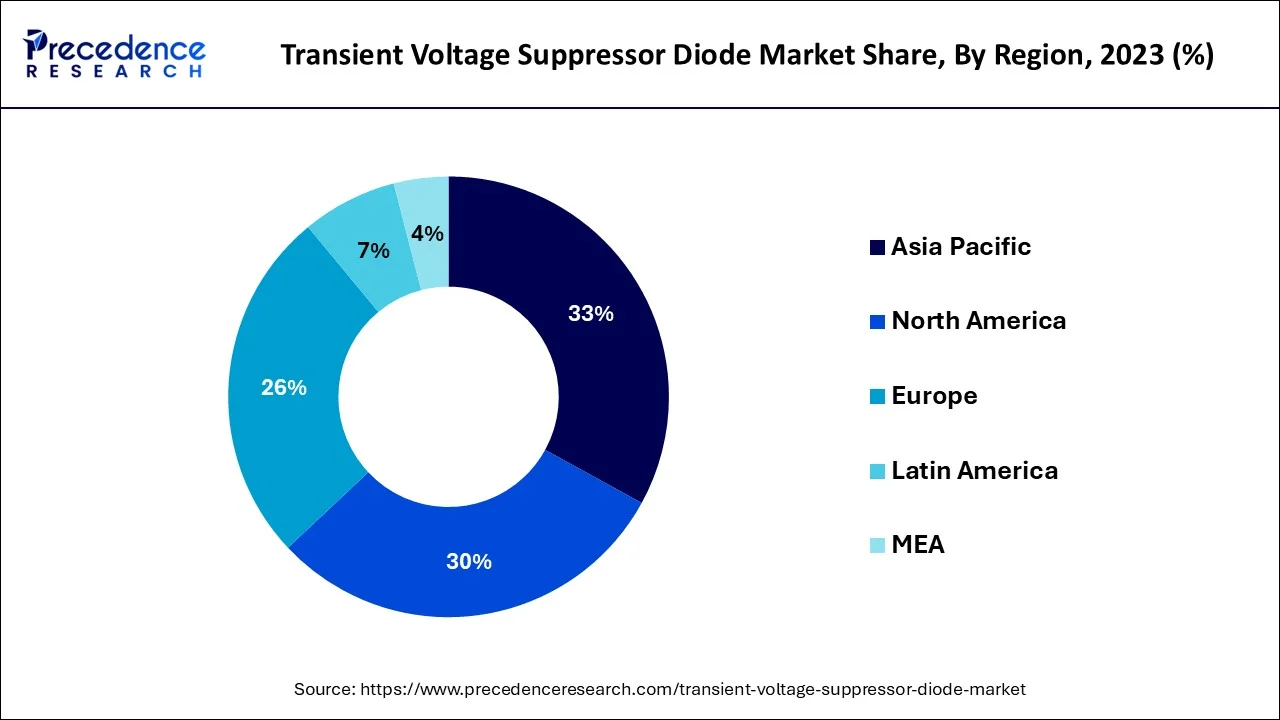
Because of the region's higher demand for and consumption of electronic devices as well as the widespread installation of voltage suppressors in the industrial sector to help reduce excessive energy flow during peak periods, North America is anticipated to account for a sizably large revenue share in the market during the forecast period.
The market revenue growth in North America is being driven by factors such as increasing computing device adoption, the rapidly growing electronics industry, ongoing research initiatives for developing advanced devices, as well as administrative regulations and policy standardization in the countries in the region.
Voltage transients are defined as rapid bursts of electrical energy that are the result of the unexpected release of energy that was previously stored or started by other mechanisms, such as intense inductive loads and lightning. This energy can be expelled in an unexpected manner through regulated exchanging activities in electrical /electronic circuits, or it can be arbitrarily triggered into circuits from outside sources.
The factors including doping concentration junction area as well as substrate resistivity influence the diodes' electrical properties. To absorb strong transient currents, TVS diodes are built with massive junction cross-sections. The diodes' VI properties are the same as those of zener diodes. Zener diodes are built for voltage control, TVS diodes are designed specifically, characterized and tested for transient voltage suppression. TVS diodes are known for reacting relatively immediately. The TVS diode's response time is one of its key features.
The quick reaction time of TVS diodes suggests that the PC board traces as well as lead inductance are to blame for the voltage overshoot. TVS diodes come in a wide variety of working voltages; typical device voltage ranges for discrete devices vary from 5V - 440V.
Arc contacts, filters, and solid-state semiconductor devices are only a few examples of the diverse types of transient suppression equipment. The Metal-oxide Varistor, or MOV, is one of the most widely used discrete semiconductor transient suppression devices because it comes in a variety of energy-absorbing and voltage ratings, allowing for precise control over undesirable and sometimes harmful transients or voltage spikes.
Transient suppression devices can be connected in series or parallel with the load to restrict or clamp the residual voltage or to redirect the transient away, often to ground, so attenuating or reducing the energy value of a transient and stopping its propagation through the circuit.
Transient Voltage Suppressor Diodes provide a number of advantages, including less incremental surge resistance and the capacity to protect large currents of 6 KA to 10 KA. Also, the rapid reaction time of the diode is the main driver of the TVS diode market.
The time between 0 volts and BV is often less than one NS. Low energy handling and the associated expense are the main factors limiting the expansion of transient voltage suppressor diodes. Compared to zener diodes and metal oxide varistors, TVS diodes are more costly. However, some of the TVS diodes provided by Semtech Corporation function at 2.8V and 3.3V due to technological advancements.
In the near future, it is anticipated that operating the diodes at such a low voltage would accelerate the growth of the TVS diode market. Transient voltage suppressor (TVS) demand is expected to increase in major end-use applications due to the growing trend of component miniaturization, which has increased electrical sensitivity and is anticipated to remain one of the key growth drivers for the transient voltage suppressor market over the course of the study.
The fast reaction time of the diode (less than 1ns from 0 volts to BV), growth in trend of component shrinking, technological breakthroughs, rise in demand from diverse end-use applications, and increase in sensitivity to electrical stressors are the main market drivers for TVS diodes. The quick reaction time suggests that lead inductance and PC board traces are to blame for the voltage overshoot.Arc contacts, filters, and solid-state semiconductor devices are only a few examples of the diverse types of transient suppression equipment. The Metal-oxide Varistor, or MOV, is one of the most widely used discrete semiconductor transient suppression devices because it comes in a variety of energy-absorbing and voltage ratings, allowing for precise control over undesirable and sometimes harmful transients or voltage spikes.
Transient suppression devices can be connected in series or parallel with the load to restrict or clamp the residual voltage or to redirect the transient away, often to ground, so attenuating or reducing the energy value of a transient and stopping its propagation through the circuit.
Transient Voltage Suppressor Diodes provide a number of advantages, including less incremental surge resistance and the capacity to protect large currents of 6 KA to 10 KA. Also, the rapid reaction time of the diode is the main driver of the TVS diode market.
The time between 0 volts and BV is often less than one NS. Low energy handling and the associated expense are the main factors limiting the expansion of transient voltage suppressor diodes. Compared to zener diodes and metal oxide varistors, TVS diodes are more costly. However, some of the TVS diodes provided by Semtech Corporation function at 2.8V and 3.3V due to technological advancements.
In the near future, it is anticipated that operating the diodes at such a low voltage would accelerate the growth of the TVS diode market. Transient voltage suppressor (TVS) demand is expected to increase in major end-use applications due to the growing trend of component miniaturization, which has increased electrical sensitivity and is anticipated to remain one of the key growth drivers for the transient voltage suppressor market over the course of the study.
The fast reaction time of the diode (less than 1ns from 0 volts to BV), growth in trend of component shrinking, technological breakthroughs, rise in demand from diverse end-use applications, and increase in sensitivity to electrical stressors are the main market drivers for TVS diodes. The quick reaction time suggests that lead inductance and PC board traces are to blame for the voltage overshoot.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 1.07 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 2.25 Billion |
| Growth Rate from 2024 to 2034 | CAGR of 7.77% |
| Largest Market | Asia-Pacific |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | By Type, By Application and By End User |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America and Middle East & Africa |
TVS is in greater demand for key end-use applications
In recent years, the market's revenue growth has been significantly impacted by the need for constant electricity supply, growing emphasis on dynamic mobility, and greater awareness of its importance among individuals in developed countries.
Traditionally designed to protect fragile electrical equipment from being damaged by high voltage transients, transient voltage suppressors are now widely used in the automotive, computing, and telecommunications industries. They give a far faster reaction time than their conventional diode-based counterparts. Electrical stress sensitivity has increased due to the trend toward smaller components, which has increased the requirement for TVS in important end-use applications.
Frequent failure of TVSS (Transient Voltage Surge Suppressors) devices
The predicted period of market growth would be hampered by the failure of TVSS devices caused by an overflow of power levels exceeding the capability of microprocessors or integrated circuits.
Commonly installed at AC as well as DC inputs and outputs, TVSS devices serve as barriers against transients and long-term power changes. Also High installation costs, the availability of several conventional instruments for regulating the energy supply, uneven suppression in certain models, the unavailability of TVS in some places, and poor customer awareness might all constrain market revenue development over the anticipated timeframe.
Factors like fluctuating advanced diode raw material prices, low energy handling capacity, complicated manufacturing processes, an absence of appropriate Research & Development (R&D) systems in developing countries, and strict governmental regulations may also seriously hinder the market's potential for revenue growth.
Rising government initiatives
Increasing public and private sector investments, rising government measures to improve electrical infrastructure, and rising market revenue growth are anticipated throughout the projection period. TVS are carefully built, tested, and characterized for transient voltage suppression. TVS are designed with large cross sectional area junctions to absorb strong transient currents.
Additionally, as electronic devices are used more often and people become more aware of the advantages of TVS, such as their low incremental surge resistance and the availability of high current protection for 6KA to 10KA, more industries are adopting them.
The market is divided into uni-polar and bi-polar TVS segments based on type in 2023, the market's greatest revenue share was accounted for by the uni-polar TVS segment. Because bi-polar TVS are becoming more and more popular with customers, the bi-polar TVS category is anticipated to increase at the quickest pace throughout the projection period.
This segment's revenue growth is anticipated to be driven by the ability to instantly clamp transient voltages to safe levels before they may harm a circuit and the growing usage of bi-polar TVS for diversion in low-energy circuits and systems. Additionally, bi-polar TVS are more in demand since they operate on a bi-directional flow of charge, are simple to use, quick to act, and perform perfectly under moderate-frequency applications.
The market is divided based on application into operational amplifier protection, DC supply protection, DC load protection, AC supply protection, electromagnetic interference limitation, and others. Due to the rising usage of alternate current in residential power supply stations, the AC supply protection sector had the biggest revenue share in 2022 and is anticipated to maintain its dominance over the projected period. The increasing usage of TVS to safeguard delicate AC circuitry in series connections and supply fluctuations caused by lightning are anticipated to propel this market's revenue growth.
The market is divided into automotive, industrial power supply, military/aerospace, communications, computer, consumer products, and other segments based on end users. Due to rising power consumption in industries, ongoing technological advancements, and support from the government for the installation of transient voltage suppressors that are required, the industrial power supplies segment is anticipated to experience the fastest revenue growth rate during the forecast period.
The industrial sector is anticipated to adopt TVS at a higher rate because to the growing usage of heavy equipment such air conditioners, manufacturing machines, decompressors, and lighting and heating equipment, which is anticipated to enhance this segment's revenue growth. Due to the growing use of TVS in office buildings and data centers, which use a significant amount of electricity daily at a streamlined flow of voltage, the telecommunications segment had the second-largest revenue share.
By Type
By Application
By End User
By Geography
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
March 2024
March 2025
December 2024
November 2024