May 2025
The global electric vehicle charging infrastructure market size is calculated at USD 47.61 billion in 2025 and is forecasted to reach around USD 415.58 billion by 2034, accelerating at a CAGR of 27% from 2025 to 2034. The Asia Pacific electric vehicle charging infrastructure market size accounted for USD 25.43 billion in 2025 and is expanding at a CAGR of 26.70% during the forecast period. The market sizing and forecasts are revenue-based (USD Million/Billion), with 2024 as the base year.
The global electric vehicle charging infrastructure market size was estimated at USD 37.98 billion in 2024 and is predicted to increase from USD 47.61 billion in 2025 to approximately USD 415.58 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 27% from 2025 to 2034.
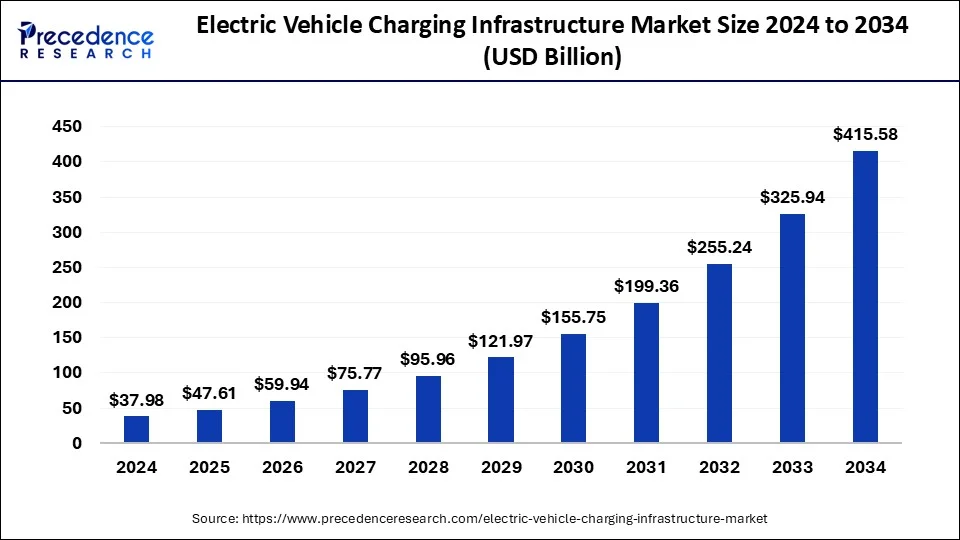
The Asia Pacific electric vehicle charging infrastructure market size was valued at USD 20.37 in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 213.61 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 26.70% from 2025 to 2034.
Asia Pacific (APAC) is on the verge of a major electric vehicle revolution. Nonetheless, most forecasts place the region 3 to 4 years behind Europe in terms of EV adoption. As APAC joins the race to become a fully electric fleet, it has a once-in-a-lifetime opportunity to turn its disadvantage into an advantage. China already has the most electric vehicle (EV) charging stations in the world (over 1.2 million in 2019), but thanks to an infrastructure stimulus package announced by the central government in March 2020, it plans to construct roughly 600,000 more. The package is aimed at "new infrastructure," which comprises initiatives in information technology, power, and transportation, and includes $1.4 billion for EV charging infrastructure.
Japan is dealing with a classic "build it and they will come" scenario, as Prime Minister Yoshihide Suga has declared that the country will be carbon neutral by 2050. Charging poles proliferated after the government provided 100 billion yen ($911 million) in subsidies to construct charging stations and encourage the adoption of electric vehicles in fiscal 2012. With electric vehicle adoption at around 1%, the country has hundreds of unused charging poles, while others (which have an average lifespan of roughly eight years) are being phased out entirely. According to Zenrin Co., the number of electric vehicle charging stations in Japan declined to roughly 29,200 in the 12 months ending March, down from more than 30,300 the previous year. It's the first drop since the publisher of maps began collecting data in 2010.
To promote the use of environmentally friendly automobiles, South Korea wants to build 3,000 rapid charging stations for electric vehicles by the end of this year. While presiding over a meeting to promote the "Big 3" industries, Finance Minister Hong Nam-ki stated, "Creating convenient charging infrastructure is a very critical task to keep pace with the increase of electric vehicle supply." Green automobiles, biomedicine, and non-memory chips are the Big Three industries. The government will establish 2,280 charging stations at sites like express service facilities where private businesses have been hesitant to put charging stations due to high expenses.
Europe region is expected to grow with highest CAGR in upcoming years. Strong growth of the region and government initiatives supporting e-vehicle industry and innovations in charging infrastructure models across the region are the major factors that will boost the growth of the region. Developed countries such as France, Netherlands, Germany, Norway, and the U.K. are among the leading countries in electric vehicle adoption and installing charging points. EU set a target to install 1 million charging points on public places for electric vehicles by 2024, and this target is 3 million by 2029. Apart from these, other European countries are also trying to reduce carbon emissions by increasing electric car deployment.
Over the past few years, adoption of electric vehicles is growing constantly owing to their efficiency and eco-friendly feature. These factors drive the growth of charging infrastructure. In 2019 globally there were total of 2.1 million electric vehicle, and China, the EU, and U.S. together will have around 120 million electric vehiclesby 2030. The energy requirement to chargethese electric vehicles is expected to grow from 20 billion KW hours in 2020 to around 300 billion KW hours in 2030. Use of electric vehicles is expected to be seen for intercity travel as well as for long distance commute in coming years. Majority of the Electric vehicles do not have drive range of more than 150 km’s and also require charging solutions. Considering this fact, electric vehicle manufacturers are investing heavily in R&D costs focused mainly atproviding fast-charging solutions.
Charging stations equipped at public places may prove as optimal solutions and will support the high adoption rate of electric vehicles mainly in Europe, and China with these two regions being fastest growing markets in electric vehicle industry. Since last few years many cities in China are deploying charging stations on public places to cater the demand of electric vehicleowners. Hence, growing share electric vehicles in automotive industry worldwide will increases the requirement for charging stations during the forecast period.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 37.98 billion |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 47.61 billion |
| Market Size By 2034 | USD 415.58 billion |
| Growth Rate from 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 27% |
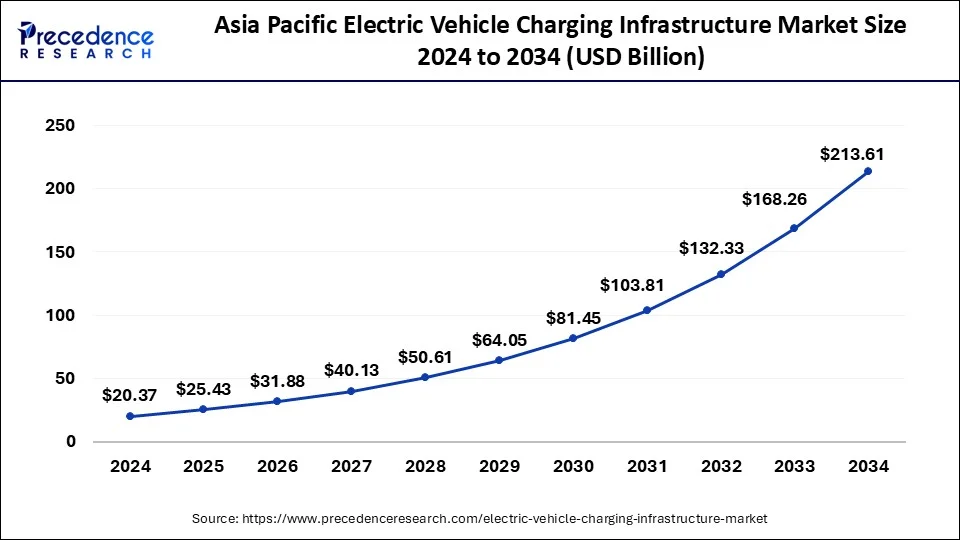
| Largest Market | Asia Pacific |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | Charger Type, Connector Type, Application, and Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America and Middle East & Africa |
Planning for megachargers to enable long-distance trucking to provide market opportunities
Until now, the majority of public charging infrastructure has been dedicated to supplying electric light-duty cars. Heavy freight truck (HFT) electrification is a longer-term project, with less than 40 electric HFTs on the road by 2020. To meet their needs for heavy-duty cycles and long-range operations, HFTs require high-capacity batteries, which necessitate high-power charging. Early-stage demonstrations, proof-of-concept initiatives, and efforts to facilitate standardization have been the most common charging alternatives for HFTs so far.
Megachargers with a power output of 1 megawatt (MW) or more would be capable of charging trucks traveling large distances in a reasonable amount of time. To avoid detrimental effects on the electrical system, long-term planning for megacharger infrastructure is required now. Given the large power requirements of megachargers, some grid effect is unavoidable. Grid reinforcements, modernization, storage, and interaction with power systems may all require significant expenditure. Electricity generators, distribution system operators, and megacharging operations must plan and coordinate their efforts.
Regional initiatives to construct megacharging infrastructure are also underway. Iberdrola, a Spanish multinational electric provider, has stated interest in implementing megacharger infrastructure in heavy-duty freight truck corridors in Spain by 2025, backed by stimulus financing. In September 2021, ElaadNL (the Dutch grid operators' EV knowledge center) and local and national government bodies created an open-access test center for companies and academia that offers megacharger testing facilities. The West Coast Clean Transit Corridor Initiative in the United States plans to establish charging stations capable of charging HDTs at 2 MW along important transit lines from Mexico to the Canadian border by 2030.
Working of smart EV charging stations
Smart EV charging is enabled by an intelligent back-end technology that provides charging station owners with real-time data from linked charging devices and charging events. Because the stations are connected to the cloud, they may be handled depending on a variety of signals, including erratic energy output, local electricity consumption, the number of other vehicles being charged, and the use of electrical equipment on a nearby site. EV charging must be smart to establish a more sustainable energy system based on renewable energy sources.
Smart charging necessitates the identification of an electric vehicle driver at the charging station. Identification establishes a link between the EV driver, the charging station, and the charging event. The appropriate fee will be charged to the appropriate customer, and funds will be directed to the appropriate charging station owner. Everything happens automatically because it's clever.
Wireless Charging for electric vehicle
Wireless Power Transfer (WPT) technology allows electrical energy to be transferred wirelessly from a transmitter to a receiver. WPT technology, in comparison to wired power transfer, is a more acceptable and suitable solution for many industrial applications due to its numerous advantages. Wire irritation will be reduced, and power transfer mechanisms will be improved, thanks to the use of WPT technology. The WPT has recently focused a lot of work on charging the onboard batteries of electric vehicles (EV). Several well-known automobile manufacturers have begun efforts to embrace WPT technology and improve its capabilities. As a result, WPT can be accomplished via a low-cost inductive coupling between two coils known as a transmitter and a receiver coil. Transmitter coils are positioned beneath the road in EV charging applications, and receiver coils are installed in the vehicle. Because it offers superior energy efficiency, inductive WPT of the resonant type is commonly used in medium-high power transfer applications such as EV charging.
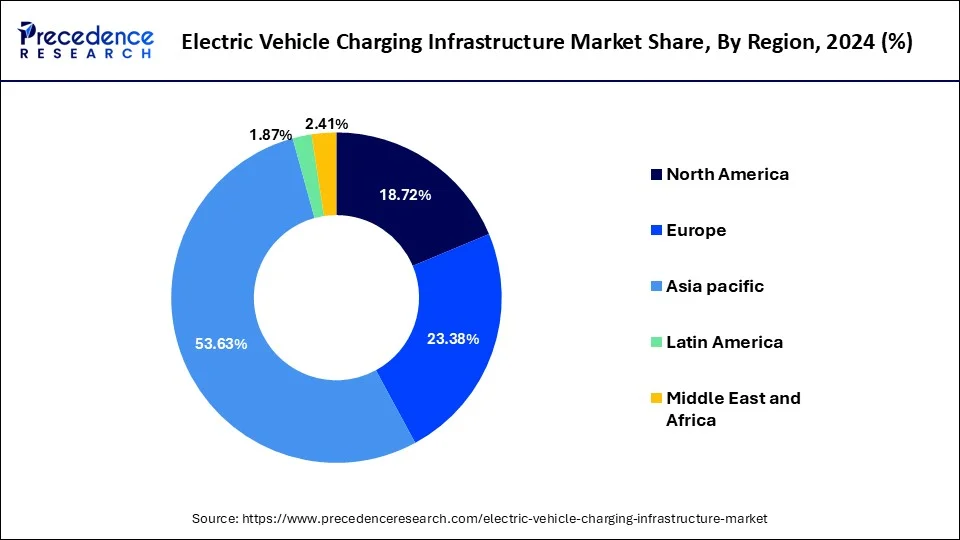
The electric vehicle charging infrastructure market is segmented into slow charger and fast charger. Among these, fast charger segment holds the major market share of 89.5% in 2024.
During the forecast time period DC fast-charging (DCFC) segment is expected to register prominent and highest CAGR. Rapid growth of DCFC segment is mainly because of the growing initiatives from government bodies and investments in fast-charging stations, facilities such as offering rebate on purchasing DC fast-charging stations, and added benefits of DCFCs in providing fast charging in comparison with Level 1&2 charging stations.
Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Market, by Charger Type, 2022-2024 (USD Billion)
| Charger Type | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 |
| Slow Charger | 2.6 | 3.2 | 4 |
| Fast Charger | 21.7 | 27.1 | 34 |
The market is divided into CHAdeMO, combined charging system (CCS), others. In this type, combined charging system (CCS) segment held the largest market share of 40.07%% in 2024. CCS charging sockets use shared communications pins to combine AC and DC inlets. As a result, the CCS charging socket is less than the comparable space required for a CHAdeMO or GB/T DC socket with an AC socket. Because CCS1 and CCS2 share the same DC pin architecture and communications protocols, manufacturers can easily switch the AC plug portion for Type 1 in the US and (possibly) Japan for Type 2 in other markets. CCS employs PLC (Power Line Communication) as the communication technique with the automobile to initiate and control charging, which is the same technology used for power grid communications. This allows the car to communicate with the grid as a "smart appliance," but also renders it incompatible with the CHAdeMO and GB/T DC charging systems without the use of special adaptors that are difficult to come by. Tesla has accepted the CCS2 standard for DC charging for the European Tesla Model 3 rollout, which is an interesting recent development.
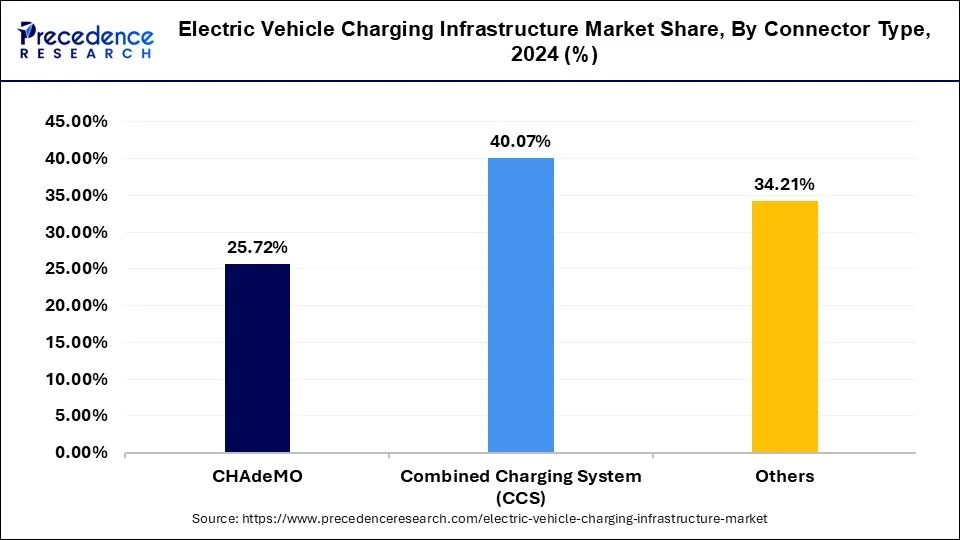
European and North American automakers are the primary proponents of CCS. North and Central America, Korea, and Taiwan are the most common locations for Type 1 and Combo 1 chargers, whereas North and South America, Europe, South Africa, Arabia, India, Oceania, and Australia are the most common locations for Type 2 and Combo 2 chargers. China uses the competing GB/T standard for DC charging, while Japan uses CHAdeMO. In the majority of the remaining nations, no standard is currently preferred; however, CharIN recommends using Type 2 and Combo 2. All high-power DC charging points installed after November 18, 2017, in the European Union must be equipped with Combo 2 connectors for interoperability purposes, according to Directive 2014/94/EU. This does not preclude the use of other charging technologies, such as CHAdeMO or AC Rapid.
Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Market, by Connector Type, 2022-2024 (USD Billion)
| By Connector | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 |
| CHAdeMO | 6.5 | 8 | 9.8 |
| Combined Charging System (CCS) | 9.4 | 11.9 | 15.2 |
| Others | 8.3 | 10.4 | 13 |
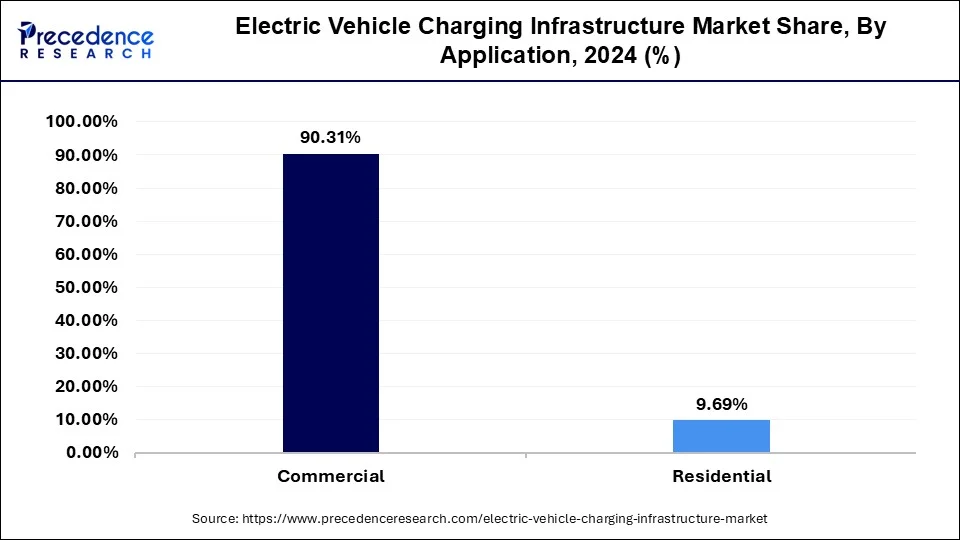
On the basis of application, the market is fragmented into commercial and residential. In this type, commercial segment held the largest market share of around 90.31% in 2024. Globally, there is an increasing demand for public EV charging infrastructure. The implementation of charging infrastructure has not kept up with the surge in sales of electric passenger vehicles. As the cost of these vehicles falls and they reach new markets, the demand for public charging stations will only grow. This is especially true for people who live in multi-unit buildings or rent their homes.
Retailers are great candidates for serving as site hosts for electric vehicle charging stations, both as places of business and as employers. Retailers can gain a variety of advantages by hosting electric vehicle charging stations, including:
There are two main business models for EV charging site hosts: owner-operator and third-party owned and operated. The owner of the charging station is responsible for installation, management, and maintenance, as well as the price at which vehicles are charged and the overall client experience.
Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Market, by Application, 2022-2024 (USD Billion)
| By Application | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 |
| Commercial | 21.9 | 27.3 | 34.3 |
| Residential | 2.4 | 3 | 3.7 |
By Charger Type
By Connector Type
By Application
By Geography
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
May 2025
May 2025
January 2025
September 2024