January 2025
The global food enzymes market size accounted for USD 2.34 billion in 2024, grew to USD 2.49 billion in 2025 and is projected to surpass around USD 4.47 billion by 2034, representing a healthy CAGR of 6.70% between 2024 and 2034. The North America food enzymes market size is calculated at USD 870 million in 2024 and is expected to grow at a fastest CAGR of 6.86% during the forecast year.
The global food enzymes market size is estimated at USD 2.34 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 4.47 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 6.70% between 2024 and 2034.
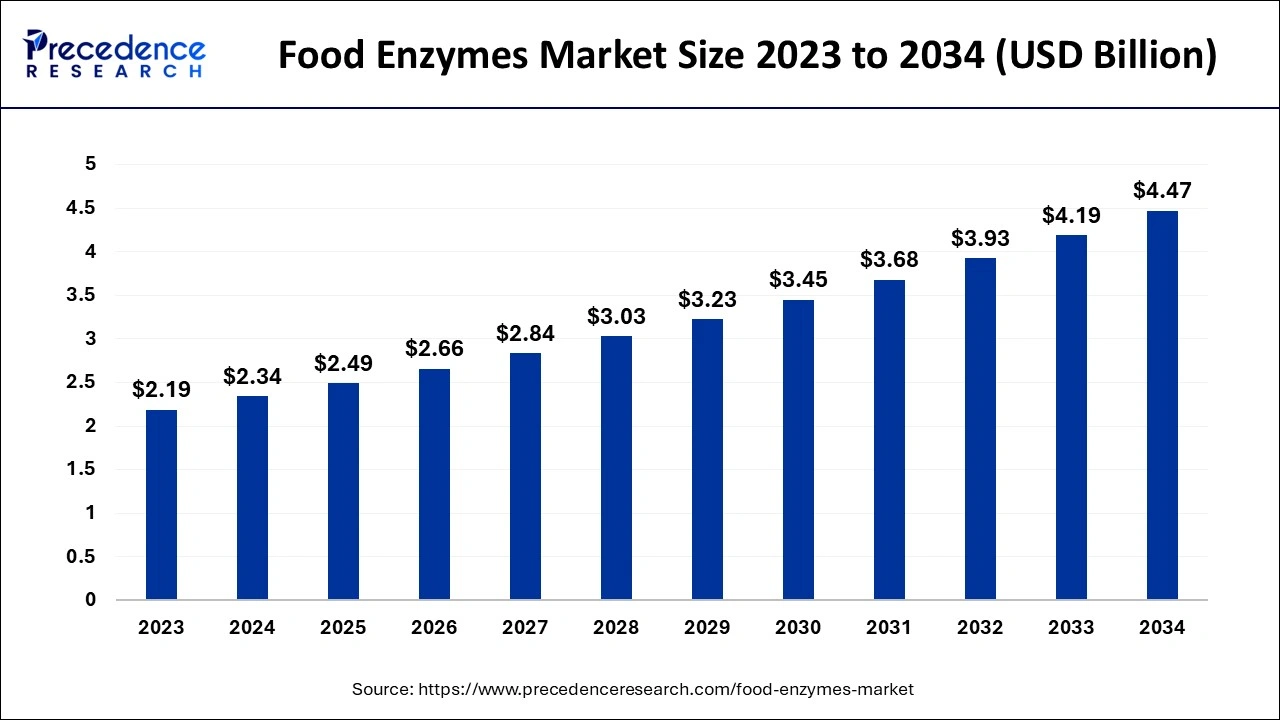
The U.S. food enzymes market size is exhibited at USD 606.06 million in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 1181.76 million by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 6.86% between 2024 and 2034.
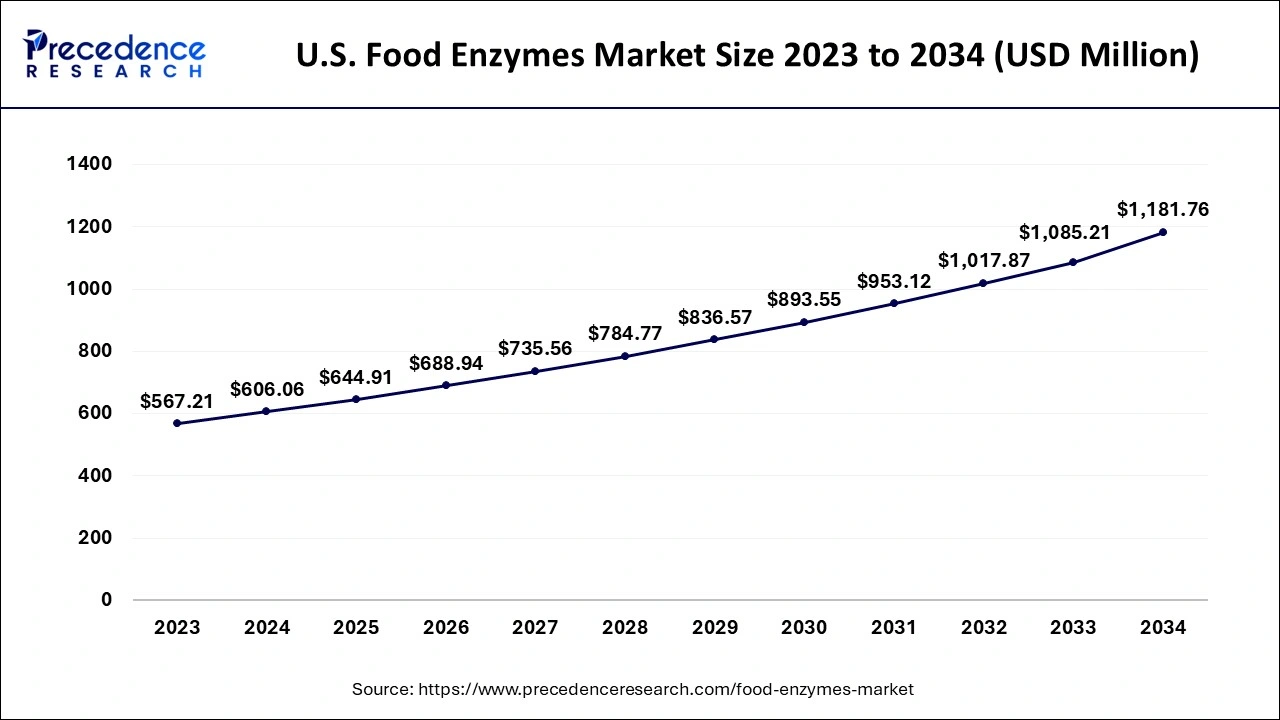
Based on geography, North America has the highest market share in the food enzymes market, and it is expected to retain its dominance for the forecasted period. The growing trend of adopting naturally derived foods is related to the market's robust expansion in North America. The rising consumer impression that organic additives are healthy and safe is driving up demand for food enzymes in the area.
The increasing demand for premium processed meals free of chemical additives has expanded the use of enzymes in various food systems. Major players' increased investments in novel solutions, such as enzymes with high precision, are fuelling the region's market expansion.
Furthermore, thanks to the thriving food and beverage business, Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing food enzyme market region. The region's adoption of Western diets, connected with rising demand for bread items, dairy products, and drinks, is continuing to rise. These products are anticipated to use food enzymes rather than synthetic chemicals in response to growing concerns about sustainability and food safety. The increase in the working population is expected to increase the demand for processed food, which will directly boost the Asian-Pacific region's market growth.
Enzymes are proteins that initiate or increase biological events and are often utilized to accelerate and target specific chemical reactions. Enzymes are derived from several sources, the most common being plant & animal extraction or fermentation from microbes, including genetically engineered microorganisms. Food enzymes are frequently employed in food processing due to their numerous advantages, which include texture, flavor, aroma improvement, preservation, viscosity, and tenderization. Enzymes are widely utilized in the baking, fruit juice, and cheese-producing industries, as well as in brewing.
The significant factors leading to the growth of the food enzymes market are attributed by increase in demand of food enzymes market have been pushed due to the rise in demand for processed food by working individuals, which is fueling the market. The emergence of developing countries as strong consumers of nutritional products.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 2.34 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 4.47 Billion |
| Growth Rate from 2023 to 2032 | CAGR of 6.7% |
| Largest Market | North America |
| Fastest Growing Market | Asia Pacific |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | By Source, By Type and By Application |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America and Middle East & Africa |
Growing awareness about the nutritional benefits of digestive enzymes
The rise in knowledge about the importance of healthy food items is steadily expanding among global consumers. This nutritional knowledge is linked to increased development, pollution, health complications, and changing dietary patterns.
Furthermore, government programs to educate rural people about nourishment, a rising share of working women and qualified individuals, and the lack of time for meal preparation have raised the demand for healthful food. Concurrently, with the expanding population in Asia-Pacific nations, the arrival of new food categories, accessibility to Western products, and the growing number of nuclear families led to increased demand for nutritional food.
Each of these contributing factors drives the requirement for enzymes from nutritional food product manufacturers, as products manufactured with enzymes have high levels of nutrients and aid in food digestion which assists in the breakdown of food products into recombinant proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates o provide nourishment.
Furthermore, the population is shifting toward more significant food categories, and their health quest significantly influences nutritional items. As a result, consumers increasingly seek nutritionally dense, healthful foods, leading to greater output by food manufacturers. As a result of the growing need to address the nutritional needs of the population, nutritious food manufacturers are progressively adding enzymes into their offerings, propelling the global food enzymes market forward.
Regulatory uncertainty to stymie market expansion
The increased use of dietary enzymes as processing components in the food business has resulted in the rapid evolution and improvement of the safety regulatory framework. Enzymes are classified as food additives or food processing aids under food regulation. Food enzyme classification is critical since pre-market authorization, including safety review, is only required for food ingredients in some countries.
Furthermore, the varieties of elements and chemical additives differ among nations and regions, resulting in regulatory ambiguities that impede market expansion. For instance, in Canada, the United States, and Japan, all dietary enzymes are controlled as food additives. However, in the EU and Australia, most dietary enzymes are classified as processing aids, with only a handful classified as additives.
Regulation on enzymes as food processing aids vary significantly between European Union (EU) member states. These proteins are subject to the licensing procedure in France, Denmark, Poland, and Hungary, but in the UK, a unilateral approval system exists, resulting in a geographical disparity. The Asia Pacific area is varied, and its authority oversees each country's food standards.
Global harmonization of safety laws about food catalysts, specifically food additives, has yet to be conceived. A disjointed and fragmented approach to ingredient regulation is predicted to have a detrimental influence on the expansion of food enzymes in the region's food industry.
Temperature change slows down the reaction rate of enzymes
The activity of dietary enzymes is heavily regulated by environmental circumstances. Temperature decreases the reaction substantially, but thermal stimulation inactivates the food enzyme, degrading its structure and rendering it non-functional.
On the other hand, changing the pH beyond the enzyme's operating range lowers enzyme activity and, therefore, can eventually lead to irreversible denaturation. Food enzyme producers are working hard to develop enzymes that can function in a wide pH range and temperature range; nevertheless, there is still a long path before enzymes are used in all food and beverage manufacturing processes.
To make the most of the opportunity, vendors are advised to focus on growth prospects in the fastest-growing segments while being rigid in the slow-growing part.
Based on source, food enzymes are segmented into microorganisms, plants, and animals. Microorganisms are projected to dominate the industry since they are less expensive and more reliable than animal and plant enzymes.
Microorganism enzymes may be efficiently created utilizing various fermentation processes, including solid-state and immersed fermentations. Microorganism enzymes are easier to produce on a big scale than animals and plants.
Based on type, food enzymes are segmented into carbohydrase, lipase, protease, and others. Carbohydrases have the highest proportion due to their widespread application in the food sector. Carbohydrases are enzymes that catalyse the conversion of carbohydrates into simple sugars. Carbohydrates' general use in the food business propels the segment's expansion.
Amylases, a carbohydrate, are commonly utilized as flavour enhancers and anti-staling agents in the brewery and baking sectors to enhance nutritional quality. Glucoamylase is widely used in manufacturing modified starches such as glucose syrups and high-fructose syrups.
Based on application, food enzymes are segmented into bakery products, beverages, dairy products, nutraceuticals, and others. The substantial expansion of the bakery industry worldwide is one of the primary reasons driving the market growth. In the bread, pastry, and biscuit industries, enzymes are commonly used to adjust dough rheological characteristics, preservation, and crumb tenderness.
The increased demand for clean-label, organic, and high-quality bakery items in industrialized countries drives food enzyme sales. Consumer lifestyle changes in emerging countries have increased demand for luxury bakery items. Bakery goods' qualities, particularly taste, texture, flavor, and shelf life, are critical, and this is accomplished through the employment of baking enzymes.
Segments Covered in the Report
By Source
By Type
By Application
By Geography
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
January 2025
April 2025
September 2024
January 2025