March 2025
Industrial Robotics Market (By Type: Articulated robots, Cartesian coordinate robots, Cylindrical-coordinate robots, Spherical Coordinate robots, SCARA robots, Others; By Application: Welding & Soldering, Material Handling, Assembling & Disassembling, Dispensing, Processing, Others; By End-User: Automotive, Electrical & Electronics, Metals & Machinery, Plastics, Rubbers, & Chemicals, Food & Beverages, Others) - Global Industry Analysis, Size, Share, Growth, Trends, Regional Outlook, and Forecast 2024-2034
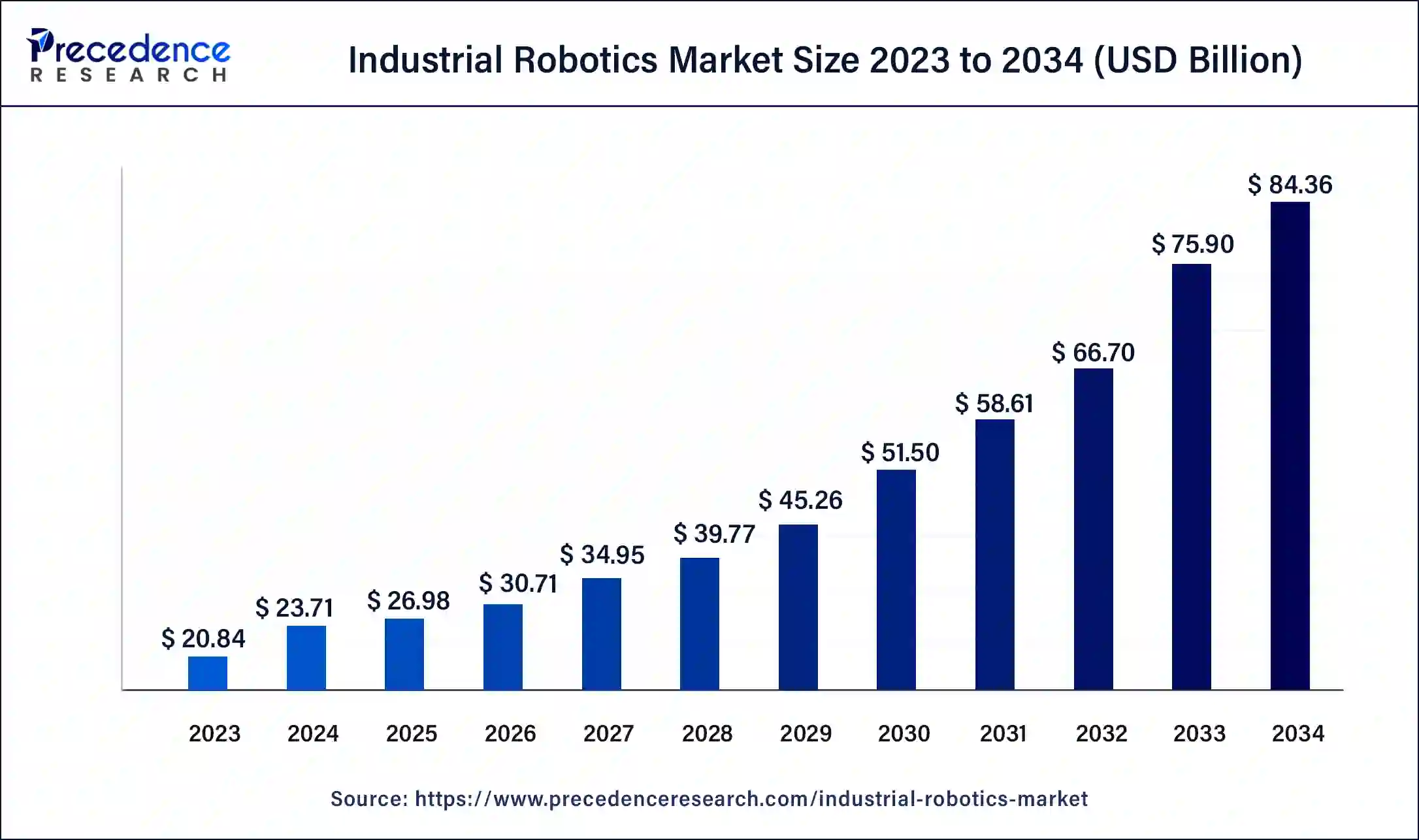
The global industrial robotics market size accounted for USD 23.71 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach around USD 84.36 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 13.8% from 2024 to 2034.
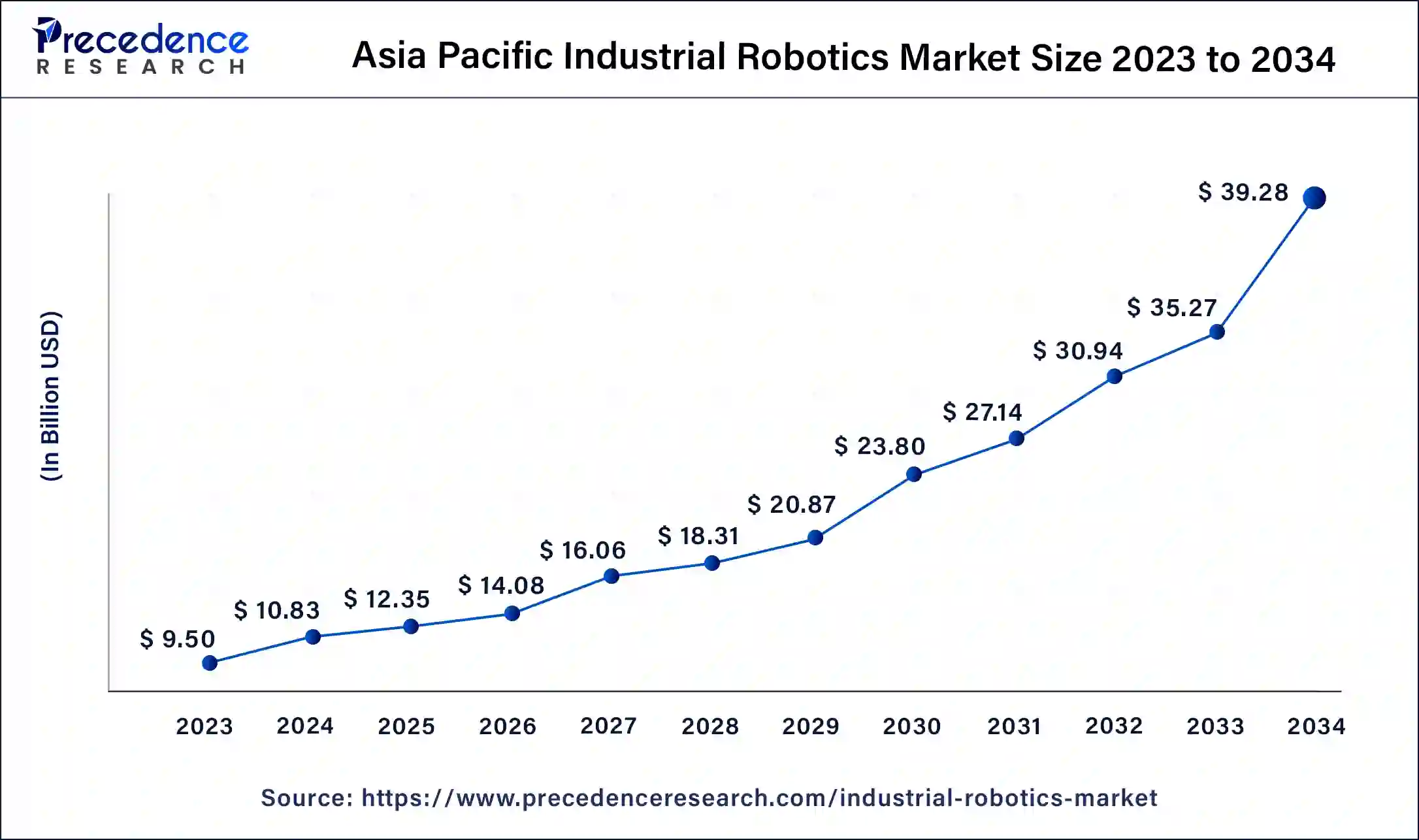
The Asia Pacific industrial robotics market size was estimated at USD 9.50 billion in 2023 and is predicted to be worth around USD 39.28 billion by 2034, at a CAGR of 14% from 2024 to 2034.
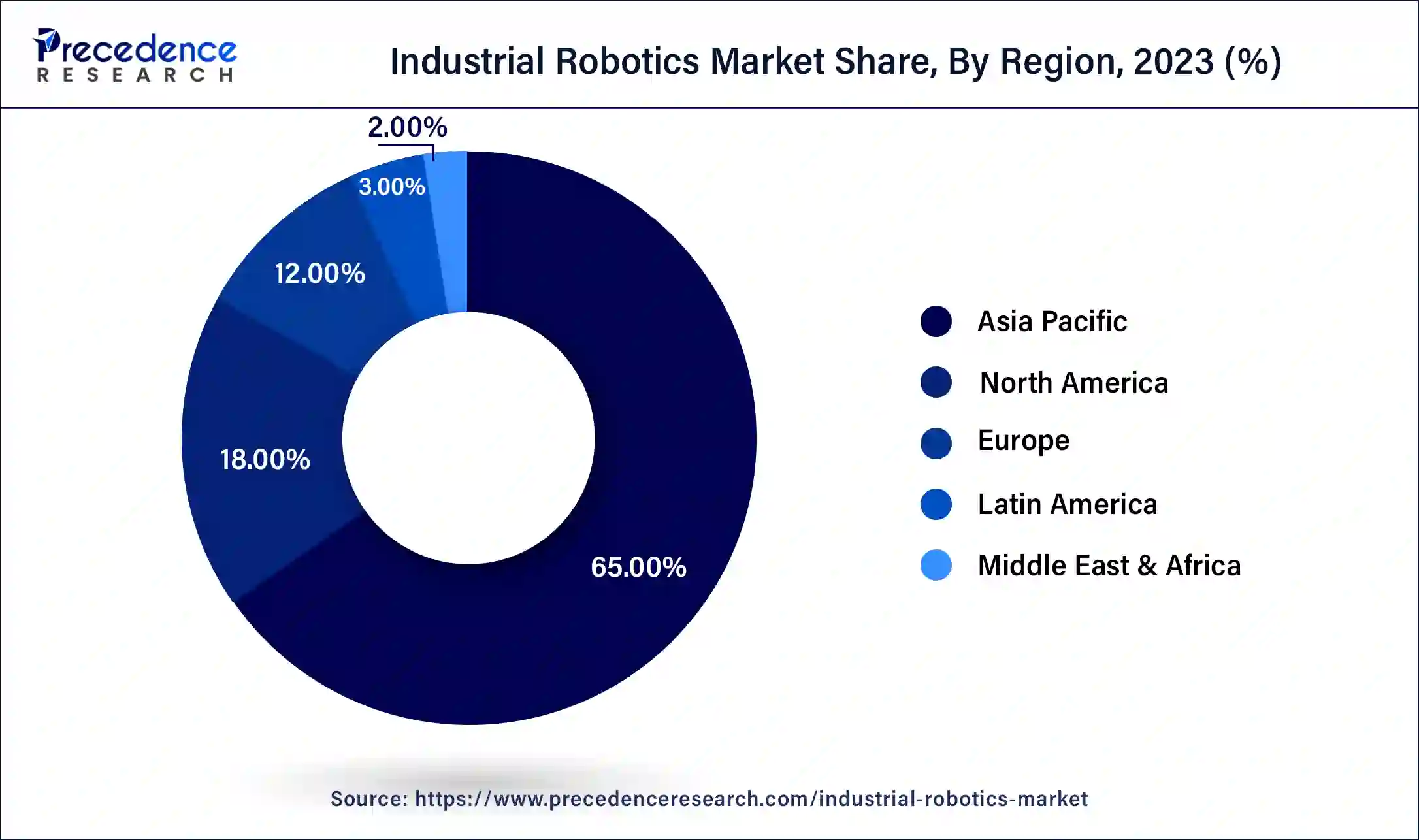
Asia Pacific dominated the global industrial robotics market and generated more than 65% of the revenue share in 2023. The dominance is due to rising automation, specifically in Japan, China, and India. China has massively invested in industrial robots, which has led them to be the top-ranking country for robot density, surpassing the US. The number of operational industrial robots per 10,000 employees in the manufacturing industry has reached 322 units. China is currently ranked fifth. South Korea, Singapore, Japan, Germany, and China are the top five most automated countries in manufacturing by 2021.
Korea hit an all-time high of 1000 industrial robots per 10,000 employees in 2021. This is more than three times the number achieved in China, placing the country first in the world. The Korean economy benefits from two large customer industries for industrial robots due to its globally recognized electronics industry and distinct automotive sector. Singapore ranks second, with 670 robots per 10,000 employees in 2021. Since 2016, Singapore's robot density has increased by 24% on average per year.
There is a significant difference between Japan (399 robots per 10,000 employees), which ranks third. Japan's robot density has increased by 6% on average per year. China has by far the world's fastest-growing robot market. The country has the most annual installations and the largest operational stock of robots.
Market Overview
The market for industrial robots has witnessed a surge in growth owing to their ability to automate laborious production processes, particularly those that are part of a fast-paced assembly line. The adoption of robots in the manufacturing industry is on the rise due to various factors such as government policies, increasing labor costs in developed regions like North America and Europe, and the rise of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) globally. Moreover, the trend of automation in industries such as automotive and electronic engineering, along with the focus on minimizing human labor, is expected to create significant growth opportunities for market players.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2023 | USD 20.84 Billion |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 23.71 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 84.36 Billion |
| Growth Rate from 2024 to 2034 | CAGR of 13.8% |
| Largest Market | Asia Pacific |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | By Type, By Application, and By End-User |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Robots are gradually being adopted in various industries, and manufacturing represents the oldest and most highly recognized use case. At first, large robotic arms were programmed to handle heavy objects, such as automobile parts, in factory settings. However, with the emergence of advanced technologies, such as visual recognition, machine learning, failure prediction, and collaborative robots (co-bots), machines have significantly improved their capabilities, revolutionizing the manufacturing processes.
Manufacturing robots are mainly utilized for repetitive tasks, leading to more streamlined assembly workflows. When working alongside humans, robots assist in producing high-quality products. Numerous manufacturing jobs involve dangerous materials or working conditions, which can put human workers at risk. Repetitive tasks can also cause employee fatigue or distraction, resulting in errors, even in the short run. In contrast, robots possess the necessary machine-learning abilities and dexterity to prevent such mistakes. Robots in manufacturing continue to expand, promoting efficiency, safety, and productivity.
According to the International Federation of Robotics, an all-time high of 517, 385 new industrial robots were installed in 2021 in factories worldwide. This represents a 31% year-on-year increase and a 22% increase over the pre-pandemic record of robot installation in 2018. Recently, the global stock of operational robots has reached a new high of approximately 3.5 million units.
The advent of Industry 4.0 has paved the way for the integration of manufacturing processes with the external world, including the deployment of collaborative robots. However, with the increasing interconnectivity of processes, cybersecurity threats are also on the rise.
The vulnerability of cobots can result from a lack of software updates, which can leave them susceptible to cyber-attacks. Additionally, inadequate network administration can expose connected cobotics to malicious activities such as industrial espionage, malware installation, or automated attacks. It is crucial to address these security concerns to ensure the safety and integrity of collaborative robots and connected manufacturing processes in the Industry 4.0 landscape.
High cost of integration
Robot hardware affordability has recently increased, making it a more accessible option for businesses seeking to introduce automation to their manufacturing processes. However, the cost of purchasing a robot represents only a small fraction of the total expense associated with automation.
A study reveals that many businesses view high integration costs as a significant obstacle to the adoption of robotics in manufacturing. Large manufacturers using industrial robots face difficulties integrating new robotics technologies with 15- to 20-year-old infrastructures and technologies present on the same production line. For SMEs with smaller production processes, the prohibitive cost of integration often makes automation unjustifiable, particularly when dealing with smaller production lot sizes. Despite the numerous benefits that robotics can bring to manufacturing, the high cost of integration remains a significant challenge for businesses of all sizes.
Government support and policies for the adoption of industrial robots
Robots are gaining acceptance in both the public and private sectors in India. The government of India's technological push and experiments by the Ministry of Defence laboratory are regarded as key drivers of robot popularity. This has encouraged the manufacturing sector, particularly automotive and assembly, as well as start-ups and education, including T-schools, to pursue new experiments in this field.
Covid-19 Impact:
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly impacted the global industrial robotics market. Initially, the market experienced a decline due to supply chain disruptions, factory shutdowns, and reduced demand for non-essential goods. However, as the pandemic continued, the demand for automation solutions increased as manufacturers looked to improve worker safety, increase productivity, and optimize supply chains. The pandemic has accelerated the adoption of industrial robots in various industries, including healthcare, logistics, and e-commerce. For example, hospitals deployed robots for tasks such as disinfection and patient care. In contrast, in the logistics and e-commerce sectors, robots were used for order fulfillment and delivery.
On the other hand, the pandemic also highlighted the vulnerabilities of global supply chains, which led to a renewed interest in reshoring and onshoring manufacturing. This trend is expected to further boost the demand for automation solutions as manufacturers seek to increase efficiency and reduce reliance on overseas suppliers.
Based on the type, the market is segmented into Articulated robots, Cartesian coordinate robots, cylindrical coordinate robots, Spherical Coordinate robots, SCARA robots, and Others. SCARA robots segment is estimated to grow at a faster rate during the forecast period. The growth of this segment is driven by its rising adoption in the electronics industry. SCARA robots are widely used in manufacturing for pick-and-place and assembly operations that require high speed and accuracy. Their ability to operate at high speeds and with cleanroom specifications makes them particularly popular in the electronics industry, which is rapidly automating with industrial robots like the FANUC SR-3ia. SCARA robots are used to automate various processes in electronic manufacturing, including assembly, engraving, labeling, and material handling applications.
One of the primary reasons electronic manufacturers are adopting SCARA robots is their incredible speed, which is ideal for the high-volume production of electronic devices like smartphones. SCARA robots are among the fastest, second only to delta robots, but they have the edge over their counterparts due to their superior precision. Their small size makes them a popular choice for electronic manufacturers, as they can easily handle the numerous small components used in electronic devices. SCARA robots require little space and can be tabletop mounted, freeing up floor space and making integration into production lines easier.
Based on the application, global industrial robotics is segmented into material handling, welding & soldering, assembling & disassembling, dispensing, processing, and others. In 2023, the material handling segment accounted for the largest market share. The growth of this segment is driven by the demand from the food and beverages, pharmaceutical, and electrical and electronics industries. Material handling is also significant in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries as certain chemicals are concentrated and transport hazardous compounds. In such cases, robots are frequently used to reduce accidents and ensure employee safety.
Based on the end-user, the industrial robotics market is segmented into automotive, electrical & electronics, metals & machinery, plastics, rubber & chemicals, food & beverages, precision engineering & optics, pharmaceuticals & cosmetics, and others. In 2023, the automotive segment accounted for the highest market share. In the past decade, the production of passenger cars has undergone a significant transformation, with a growing need for robotic automation in various manufacturing processes.
Hybrid and electric vehicle manufacturers and traditional car makers are experiencing a surge in demand for a diverse range of vehicle models. Additionally, to meet the climate goals set for 2030, there will be a higher demand for low- and zero-emission cars. Automobile manufacturers are looking to invest in collaborative robots for their final assembly and finishing operations. Although SMEs, which make up the majority of second-tier automotive part suppliers, are taking longer to adapt to full automation, the trend is likely to change with the development of smaller, more versatile, easily programmable, and less capital-intensive robots.
Recent Developments:
Segments Covered in the Report:
By Type
By Application
By End-User
By Geography
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
March 2025
January 2025
December 2024
November 2024