February 2025
The global maternal mental health market size is calculated at USD 14.03 billion in 2024, grew to USD 18.10 billion in 2025 and is anticipated to reach around USD 179.71 billion by 2034, poised to grow at a CAGR of 29.05% between 2024 and 2034. The North America maternal mental health market size is calculated at USD 6.03 billion in 2024 and is estimated to grow at a fastest CAGR of 29.20% during the forecast year.
The global maternal mental health market size accounted for USD 14.03 billion in 2024 and is predicted to be worth around USD 179.71 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 29.05% between 2024 and 2034.
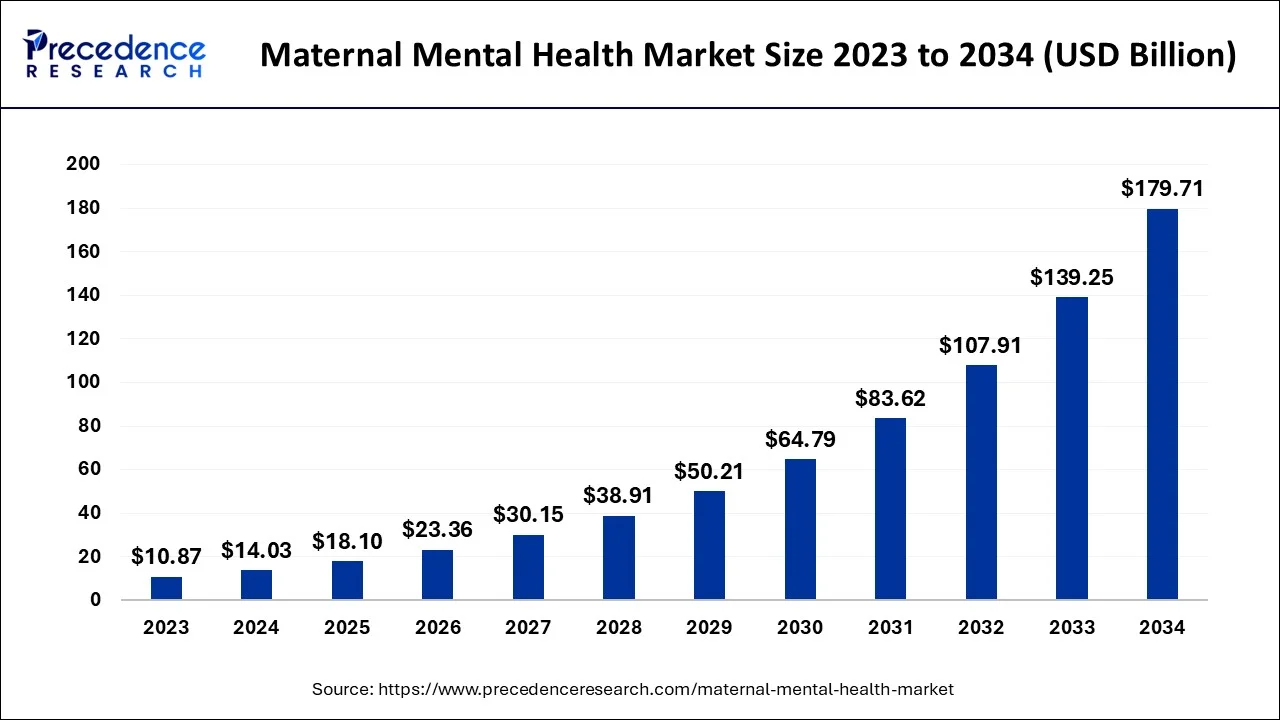
The U.S. maternal mental health market size is estimated at USD 4.22 billion in 2024 and is expected to expand around USD 179.71 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 29.05% between 2024 and 2034.
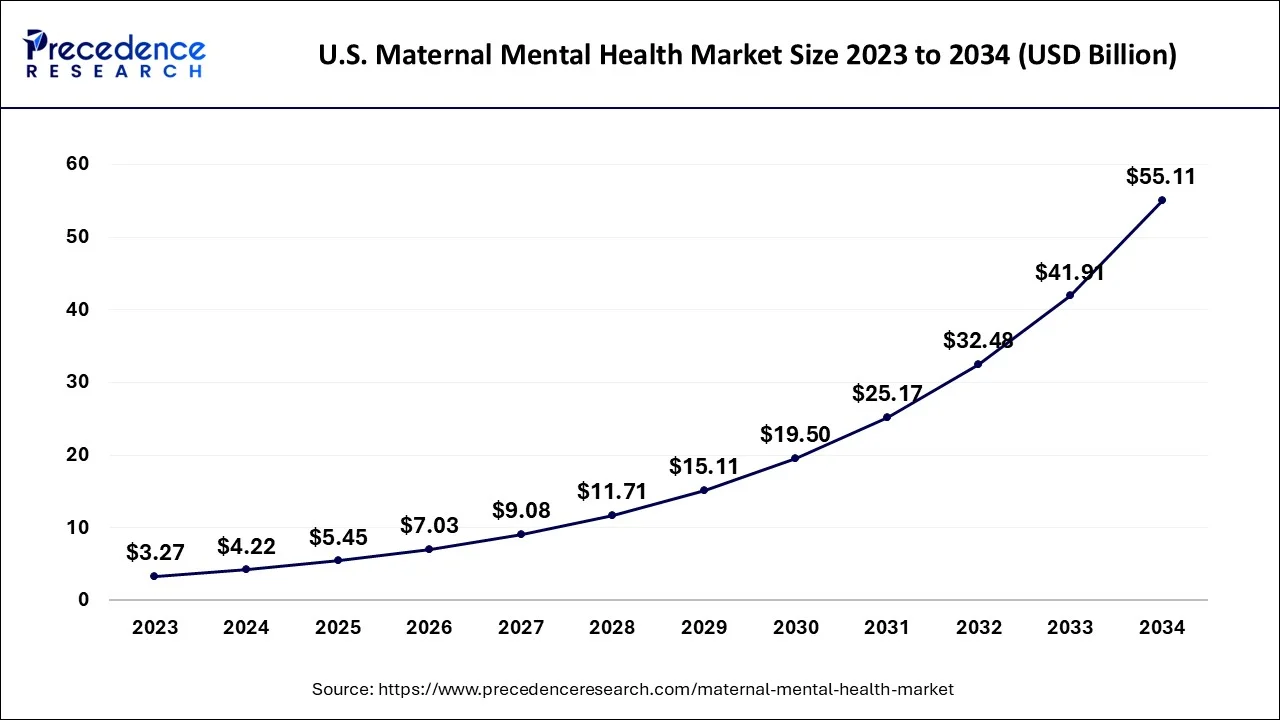
In 2023, North America held a significant share of the maternal mental health market. The region benefits from increasing awareness, well-established healthcare systems, and government initiatives promoting maternal mental health. Access to healthcare services and technological advancements, such as telehealth, further contribute to supporting pregnant women and new mothers in managing their mental health.
The maternal mental health market refers to the healthcare industry segment that focuses on the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of mental health disorders experienced by pregnant women and new mothers. These mental health issues can range from perinatal depression and anxiety to postpartum depression and psychosis. There has been a growing understanding of the significance of maternal mental health as medical professionals, decision-makers, and the general public become more aware of the occurrence and implications of mental health disorders during pregnancy and the postpartum period.
Significant market developments have resulted from this rising knowledge, particularly regarding the incorporation of technology in healthcare services. Technology advancements like telehealth, digital health, and mobile applications have completely changed how easily pregnant women and new mothers can get mental health care and support. No matter where they are in the world, women may now more easily obtain aid remotely due to these developments.
The degree of support offered to women during their pregnancies and postpartum journeys has been significantly improved by the integration of mental health services into maternity care facilities, offering all-inclusive and holistic care. Healthcare professionals are increasingly adopting individualized therapy approaches for maternal mental health. Specific mental health issues can be addressed more effectively by therapies that are more specifically adapted to the requirements and circumstances of everyone. NGOs and organizations that advocate for maternal health have been actively raising awareness and providing services to help impacted mothers.
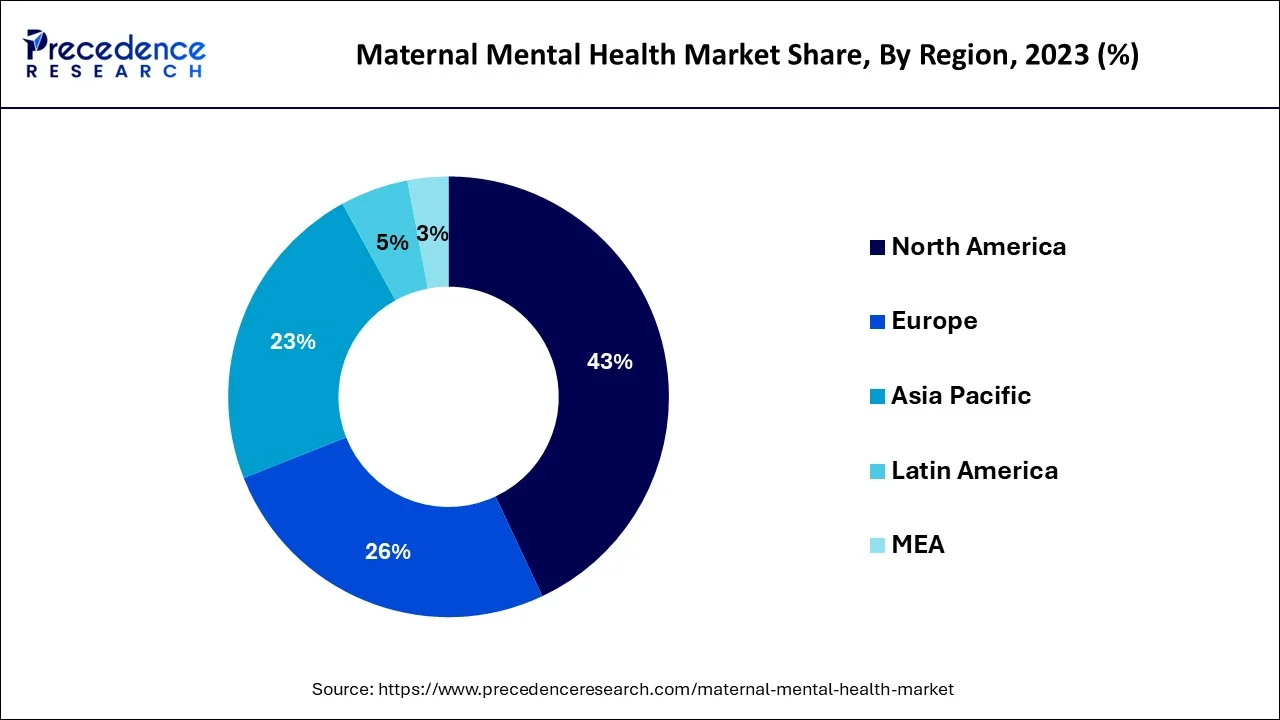
The maternal mental health care industry has been dominated by North America, which includes the United States and Canada. The area has benefited from increasing awareness, easier access to medical treatment, and government programs that place a high priority on maternal mental health. European countries maintain a substantial market share due to their well-established healthcare systems that make mental health therapies more easily accessible to pregnant moms and new mothers. The maternal mental health sector has had a notable increase in the Asia-Pacific area as a result of growing awareness and better healthcare infrastructure in countries like India, China, and Japan. In contrast, expenditures on and understanding of maternal mental health have gradually increased in other countries, such as Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa.
Concerningly, many women worldwide are affected by diseases such as prenatal depression, anxiety, and postpartum depression, which are common maternal mental health disorders. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that 10% of pregnant women and 13% of new mothers suffer from a mental condition, most often depression. Risk factors that contribute to the development of these diseases include a history of mental illness, a lack of social support, financial stress, a poor pregnancy or birth experience, and hormonal changes. Untreated maternal mental health problems can have a serious influence on breastfeeding, bonding with the infant, and the general health and development of the child.
One of the key factors contributing to this growth is the increasing awareness of maternal mental health issues. Women are seeking support and assistance as a result of increased awareness of the incidence and effects of mental health issues during pregnancy and the postpartum period. Healthcare providers, policymakers, and the general public are actively recognizing the importance of early detection and intervention, which is positively influencing the market's development. Technological advancements have played a crucial role in revolutionizing access to mental health services for pregnant women and new mothers. Innovations such as telehealth, digital health, and mobile applications have made counselling, resources, and support readily accessible, even in remote or underserved areas.
This enhanced accessibility has contributed significantly to the market's expansion. Healthcare systems are now integrating mental health services into maternity care settings. This comprehensive approach provides holistic support throughout the pregnancy and postpartum journey, making mental health services more available and easily accessible. The focus on personalized treatment approaches tailored to individual needs has also improved the effectiveness of interventions, positively impacting treatment outcomes and stimulating market growth.
The unwavering support from maternal health advocacy groups and nonprofits has been instrumental in raising awareness and reducing the stigma associated with seeking mental health support during pregnancy and the postpartum period. As more women feel empowered to seek help, the demand for maternal mental health services has increased, further boosting the market's growth. Government initiatives and policies in various countries have also played a significant role. Funding for mental health programmes, the integration of mental health services into maternal care, and healthcare professional training have all contributed to the expansion of the maternal mental health market. Ongoing research in the field has led to a better understanding of maternal mental health disorders, their prevalence, risk factors, and effective interventions. The continuous improvement of evidence-based practices and treatment options has instilled confidence in mental health services, encouraging more women to seek help and driving further market growth.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 14.03 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 179.71 Billion |
| Growth Rate from 2024 to 2034 | CAGR of 29.05% |
| Largest Market | North America |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024 To 2034 |
| Segments Covered | Disease Indication, Treatment, and Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Technological advancements
The maternal mental health market has completely changed how easily pregnant women and new mothers may obtain and receive mental health care. Mobile applications, telehealth, digital health, and other innovations have made it simple and remote to obtain help, information, and counselling. Women now have access to mental health care even in remote or undeveloped areas as a result of technology improvements. Technology integration has increased the efficacy and efficiency of therapies, improving the overall support for maternal mental health.
Socioeconomic factors
The maternal mental health market is significantly constrained by socioeconomic considerations. Financial limitations and economic problems can make it difficult for expectant mothers and new mothers to get mental health care. Women from low socioeconomic status may have trouble purchasing mental health treatments or may not have the resources to get the right care. For vulnerable communities, this difference may result in uneven assistance and exacerbate mental health issues. In order to promote the general wellness of all women throughout the perinatal period and to ensure equal access to services and support for maternal mental health, it is critical to remove these socioeconomic hurdles.
Research and development
Understanding the prevalence, risk factors, and efficient therapies for maternal mental health issues can be improved by investing in R&D. The special mental health requirements of expectant mothers and new mothers can be met with the use of evidence-based practices, personalized treatment approaches, and creative solutions that are made possible by ongoing research. R&D advancements can help reduce stigma and raise awareness while also enhancing the effectiveness and quality of mental health treatments. The market may better address the rising need for comprehensive and successful maternal mental health care by giving research top priority.
Workforce shortage
The maternal mental health market has a major difficulty due to a lack of qualified workers. The availability and accessibility of services for expectant mothers and new mothers may be constrained by the dearth of mental health specialists with specialized training and experience in maternal mental health. The need for perinatal mental health treatment is growing, though there may not be enough workers to meet the demand, which might lead to longer wait times and a reduced ability to deliver care quickly. In order to meet the expanding mental health needs of this vulnerable population and maximize the use of available resources, it is necessary to invest in training programs, encourage mental health professionals to focus on maternal mental health and promote collaborative care models.
In 2023, postpartum depression was noted as having the highest cases in the maternal mental health market. Postpartum depression is a prevalent mental health issue affecting women after childbirth, constituting a substantial segment of the maternal mental health market. Increasing awareness has led to more women seeking support and treatment. Early detection and intervention are prioritised by healthcare providers and advocacy groups. Telehealth and digital health solutions provide vital remote counseling and support. Integrating mental health services into maternity care settings enhances access to specialized care.
According to the maternal mental health market, dysthymia, also known as chronic depressive illness, poses difficulties. It is defined by milder, more persistent depressive symptoms that are sometimes disregarded or blamed on the pressures of parenting. Women might not seek help since it is persistent, which could result in a missed diagnosis and a lack of care. It is crucial for healthcare professionals to exercise caution when providing prenatal and postpartum care. Digital health and telehealth innovations can help with continuing assistance and early detection. To lessen stigma and guarantee proper care for dysthymia during the prenatal period, public awareness efforts and research activities are essential.
The most common treatment employed in the maternal mental health market in 2022 was interpersonal psychotherapy. Interpersonal psychotherapy, which focuses on enhancing relationships and resolving factors that contribute to disorders of maternal mental health, is a critical therapeutic strategy in the maternal mental health market. IPT helps expectant mothers and new mothers through the typical tensions, role transitions, and life changes that occur during the perinatal period. It improves coping mechanisms and communication, promoting emotional well-being. IPT, which provides organised and time-limited psychotherapy, is incredibly beneficial for women who are experiencing postpartum depression or anxiety.
Antidepressants are essential for treating moderate-to-severe instances of depression or anxiety both during and after pregnancy. They balance emotions, reduce symptoms, and improve general wellbeing. Considerable thinking is needed in order to weigh possible benefits and risks, particularly with regard to pregnancy and breastfeeding. The use of antidepressants is safe and acceptable when decisions are made in collaboration with healthcare professionals. Antidepressants will remain a key therapeutic in the maternal mental health market as knowledge of maternal mental health increases and psychopharmacology advances.
Segments Covered in the Report:
By Disease Indication
By Treatment
By Geography
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
February 2025
February 2025
January 2025
March 2025