October 2024
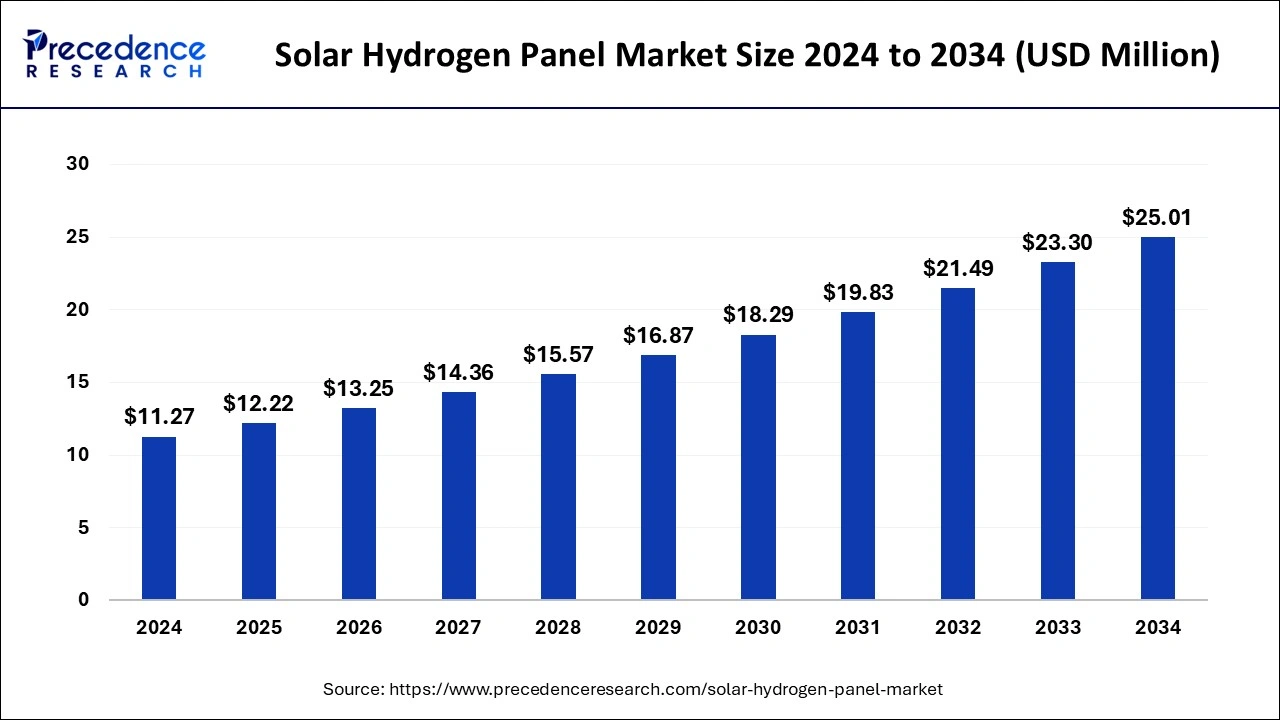
The global solar hydrogen panel market size is evaluated at USD 12.22 million in 2025 and is forecasted to hit around USD 25.01 million by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 8.30% from 2025 to 2034. The Europe market size was accounted at USD 4.51 million in 2024 and is expanding at a CAGR of 8.43% during the forecast period. The market sizing and forecasts are revenue-based (USD Million/Billion), with 2024 as the base year.
The global solar hydrogen panel market size accounted for USD 11.27 million in 2024 and is predicted to increase from USD 12.22 million in 2025 to approximately USD 25.01 million by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 8.30% from 2025 to 2034.
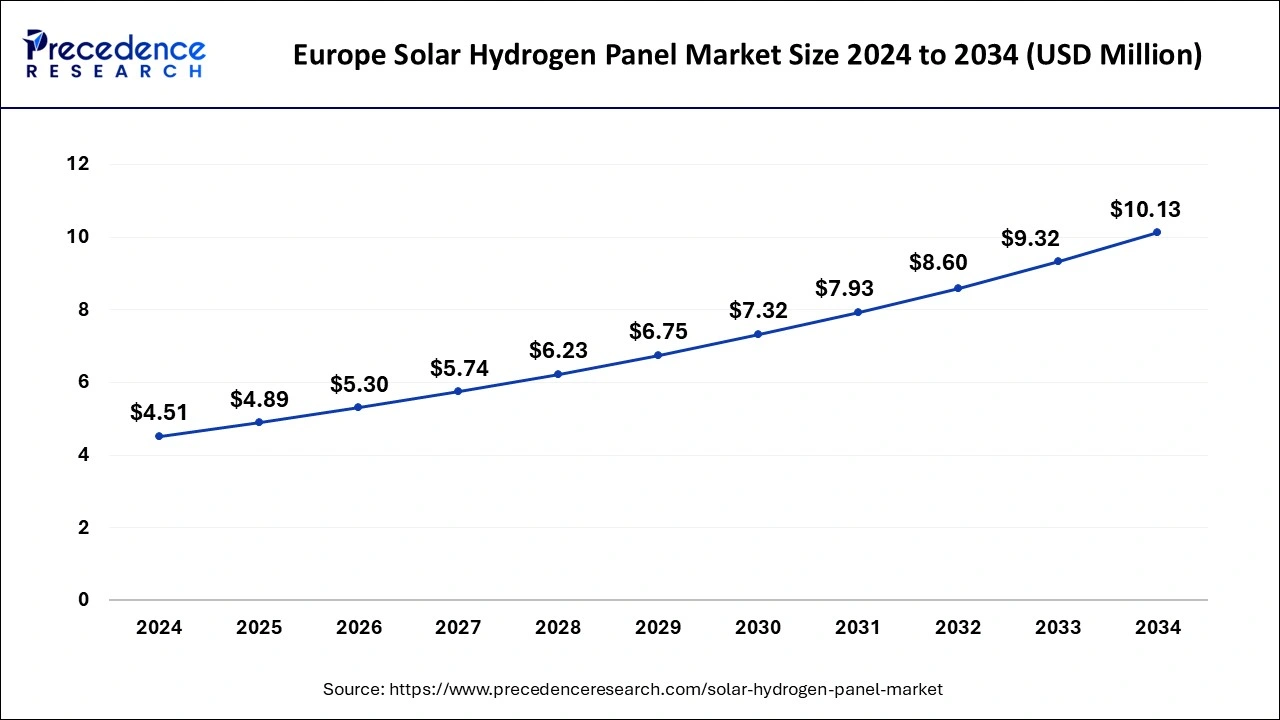
The Europe solar hydrogen panel market size was exhibited at USD 4.51 million in 2024 and is projected to be worth around USD 10.13 million by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 8.43% from 2025 to 2034.
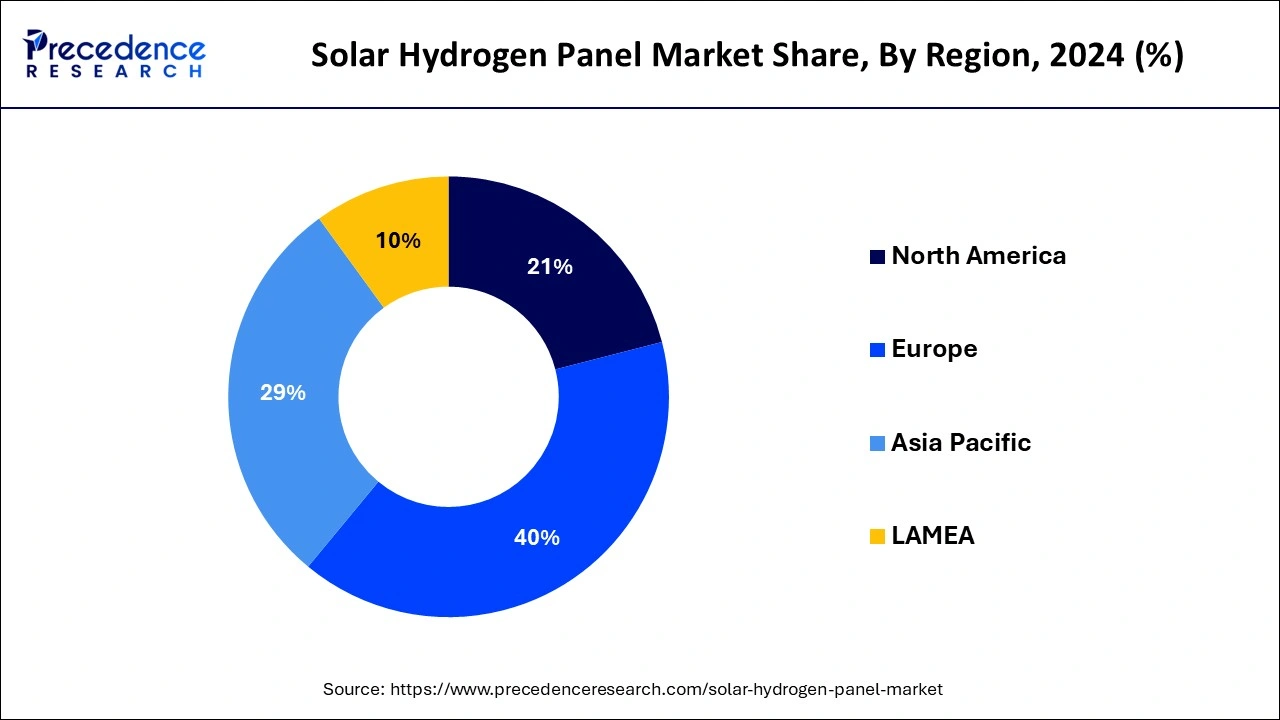
Europe held the largest share of the solar hydrogen panel market in 2024 and is expected to continue doing so throughout the forecast period. Europe has been leading the way in the usage of renewable energy and has set high standards for lowering greenhouse gas emissions. The move to sustainable energy is thought to depend heavily on hydrogen, and interest in solar hydrogen panel technology has grown. European nations have been investing in hydrogen technology research and development, particularly solar hydrogen panel development, in conjunction with the European Union (EU).
Government regulations and incentives significantly shape the solar hydrogen panel market. A number of European nations have enacted legislation to encourage the advancement and application of hydrogen technology. Governments, businesses, and academic institutions in Europe have been working together to develop hydrogen technologies. The purpose of these partnerships is to pool resources, make use of experience, and hasten the commercialization of solar hydrogen panels and associated technology.
North America is expected to gain a considerable share of the solar hydrogen panel market during the forecast period. Demand for renewable energy solutions is rising as awareness of climate change and the need to cut greenhouse gas emissions grows. Solar hydrogen panels provide a sustainable method of producing hydrogen, which can be utilized as a clean fuel for a variety of uses, such as energy storage and transportation.
Solar hydrogen panels are becoming more efficient and economical due to developments in electrolysis technology, hydrogen storage technologies, and solar panel technology. In North America, investments in renewable energy projects—including solar hydrogen initiatives—have increased significantly. The surge in cash is propelling research and development endeavors, resulting in technological breakthroughs and advances in the solar hydrogen panel market.
As awareness of climate change grows, so does the need to cut greenhouse gas emissions. Consequently, investments in renewable energy technology have surged. The need for energy security and independence is driving investments in locally produced renewable energy technology like solar hydrogen panels. The efficiency and affordability of solar hydrogen panels have increased due to developments in photovoltaic technology and electrolysis procedures, making them more appealing for use in residential and commercial settings.
Homeowners who want to produce clean energy for their dwellings and possibly store extra energy as hydrogen for use in fuel cells or other applications are becoming more and more interested in installing solar hydrogen panels. Businesses are looking into solar hydrogen panels as a way to lower their energy expenses and carbon impact while improving their ecological credentials. Renewable energy projects, such as solar hydrogen panel installations, are receiving regulatory backing, incentives, and subsidies from numerous governments worldwide.
The use of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (HFCVs) as an emission-free substitute for conventional internal combustion engine vehicles is growing. The hydrogen required to power these cars might be produced in part by solar hydrogen panels. In comparison to conventional energy sources, solar hydrogen panels continue to be somewhat expensive, even with recent technological breakthroughs. However, over time, falling costs for electrolysis and solar photovoltaic technology may assist in mitigating this problem.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Growth Rate from 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 8.30% |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 12.22 Million |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 11.27 Million |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 25.01 Million |
| Largest Market | Europe |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | Technology and End-use |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Driver
Energy independence
Solar energy is a renewable and nearly infinite resource that solar hydrogen panels capture. These solar panels may generate hydrogen without depleting finite fossil fuel sources by using sunlight as their main energy source, hence promoting energy independence. By providing a sustainable substitute for fossil fuels, solar hydrogen panels help lessen reliance on natural gas and oil imports. This acts as a driver of the solar hydrogen panel market.
Energy security is improved by this shift away from fossil fuels because it reduces the geopolitical dangers that come with resource dependency. Decentralized energy production is made possible by solar hydrogen panels, which let local enterprises, communities, and people produce their own hydrogen. The solar hydrogen panel market provides options for off-grid applications, where access to conventional energy sources may be expensive or limited.
Intermittency and energy storage
Because solar power generation depends on sunshine, which changes throughout the day and is influenced by the weather, it is intermittent. This intermittency hampers the reliability of the energy supply and grid stability. Using extra electricity from solar panels, hydrogen can be created through electrolysis and stored for use as fuel in fuel cells to produce electricity or as fuel for other purposes, such as transportation. Solar hydrogen panels use a combination of electrolysis and photovoltaic (PV) technologies to create hydrogen from water and sunlight directly. They present a viable route for the generation and storage of renewable energy.
Integration of advanced solutions with existing infrastructure
It is possible to connect the solar hydrogen panel market with the current electricity networks. As part of this integration, appropriate grid connections must be established for the export or import of electricity, as well as compliance with grid standards and laws. Water is a necessary raw ingredient for the electrolysis process in solar hydrogen panels. Evaluating water availability, quality, and sourcing is a necessary step in integrating with the current water delivery system.
The solar hydrogen panel market has several industrial uses, including transportation, chemical synthesis, and refining. Integration with current industrial infrastructure entails finding ways to use hydrogen in place of fossil fuels and adapting current machinery or procedures to handle hydrogen use. This creates new avenues for the players of the solar hydrogen panel market to explore.
The amorphous silicon solar cell segment held the largest share in the solar hydrogen panel market and is expected to continue to do so during the forecast period. Applications for solar panels have made use of amorphous silicon (a-Si) solar cell technology, including solar hydrogen panels. Typically, these panels are made of photovoltaic cells, which use light from the sun to produce energy. This electricity is then used to electrolyze water molecules to separate them into hydrogen and oxygen.
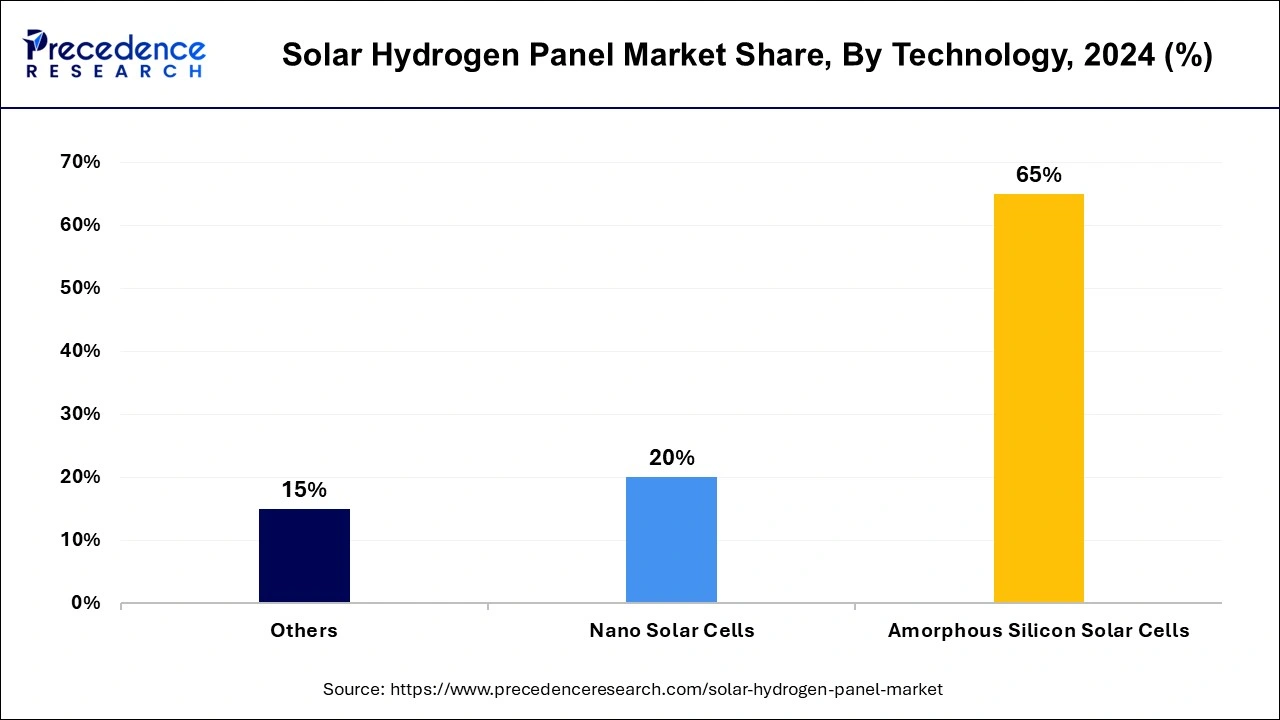
Depositing amorphous silicon onto flexible substrates can make lightweight and flexible solar panels. This flexibility can be useful in some cases, like with curved surfaces or portable solar panels. When it comes to low-light performance, amorphous silicon solar cells outperform crystalline silicon solar cells. The particular requirements of the application, such as financial limits, spatial constraints, and the optimal efficiency of hydrogen production, will determine the choice of solar cell technology, including whether to employ amorphous silicon.
Even though amorphous silicon solar cells aren't as efficient as crystalline silicon solar cells, they can still be made for less money, especially when you take into account the materials and manufacturing method. In comparison to crystalline silicon solar cells, amorphous silicon solar cells typically have lower efficiency and deteriorate more quickly over time. Therefore, a number of criteria, such as cost, required efficiency, and environmental issues, influence the choice of solar cell technology.
The industrial segment holds the largest share in the solar hydrogen panel market and is expected to hold the largest share during the forecast period. Businesses use solar hydrogen panels as a power source to electrolyze hydrogen during production. After that, this hydrogen can be feedstock for a variety of industrial processes or utilized as a clean fuel.
By enabling enterprises to create hydrogen locally, solar hydrogen panels help them become less dependent on fossil fuels and the power grid. Industrial establishments may benefit from increased energy independence and security as a result. The carbon footprint of industrial processes can be greatly decreased by using solar energy to create hydrogen. Green hydrogen, which is hydrogen generated from renewable energy sources like solar power, is better for the environment than hydrogen made from fossil fuels.
Even though using solar hydrogen panels may need a large initial investment, businesses can save money over time by lowering energy costs and lowering the risk of energy price fluctuations. Without needing significant changes to current procedures, solar hydrogen panels can frequently be combined with existing industrial infrastructure, allowing for a reasonably smooth shift to cleaner energy sources.
Research and development initiatives to increase the effectiveness and affordability of solar hydrogen panel technologies especially suited for industrial applications are also driven by the solar hydrogen panel market’s industrial segment. The industrial sector's adoption of solar hydrogen panels can also be influenced by government policies, rules, and incentives that support the generation of hydrogen and the use of renewable energy.
By Technology
By End-use
By Geography
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
October 2024
August 2024
January 2025
August 2024