List of Contents
3D Printing Medical Devices MarketSize and Forecast 2025 to 2034
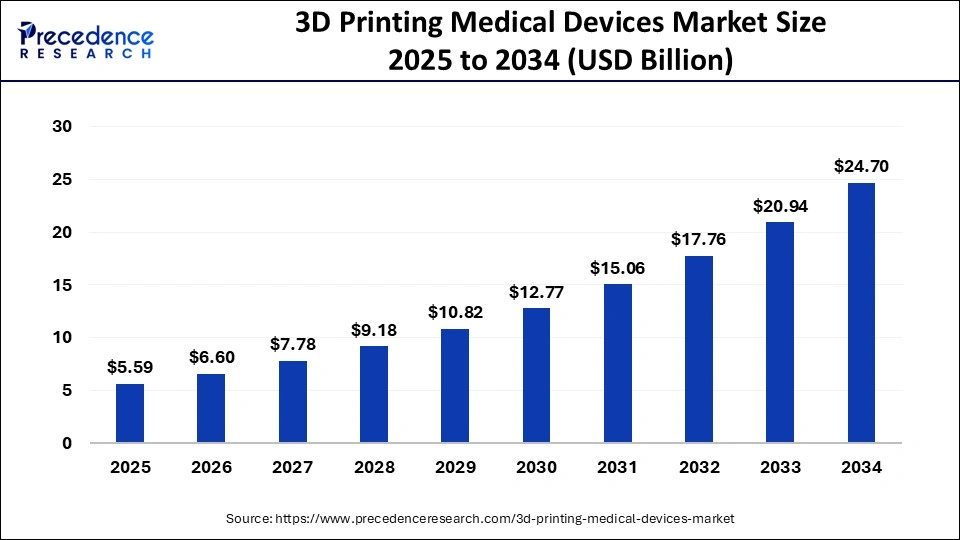
The global 3D printing medical devices market size was calculated at USD 4.74 billion in 2024 and is projected to surpass around USD 24.70 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 17.95% from 2025 to 2034.
3D Printing Medical Devices Market Key Takeaways
- North America led the global market with the highest market share in 2024.
- By products, the orthopedic products segment residential the biggest market share in 2024.
- By technology, the electron beam manufacturing (EBM) segment has held the highest market share in 2024.
- By application, the medical segment registered the maximum market share in 2024.
- By end user, the hospitals segment held a dominant presence in the 3d printing medical devices market in 2024.
Market Overview
3D printing medical devices refer to producing medical devices using 3D printing technology, also known as additive manufacturing. This technology creates three-dimensional objects by adding material layer by layer based on a digital model or design. The 3D printing medical devices market is the sector within the healthcare industry that involves the production and utilization of medical devices using 3D printing technology. 3D printing, or additive manufacturing, creates three-dimensional objects by adding material layer by layer based on a digital model or design.
The market is driven by several factors, such as the capability to produce customized devices that develops patient outcomes and satisfaction, which led to a growing demand for personalized healthcare solutions. In addition, 3D printing can decrease costs and production time related to traditional manufacturing processes, making it a great option for medical device manufacturers. Moreover, advancements in 3D printing technologies, such as the development of biocompatible materials, have extended the range of possibilities and applications for medical device production.
Furthermore, enhanced patient care and treatment, Regulatory Support and Guidelines, and quicker prototyping and time-to-market have improved the demand for the 3D printing medical devices market. 3D printing allows for rapid prototyping and iterative design improvements, significantly reducing the time required to develop new medical devices. This faster design and development cycle can accelerate the introduction of new devices to the market, facilitating innovation and improving patient access to advanced medical solutions.
However, quality control and standardization, material limitations, and limited skillset and training are anticipated to impede market growth. Ensuring consistent quality and performance of 3D-printed medical devices can be challenging due to materials, printing processes, and equipment variations. Maintaining quality control standards and establishing standardized protocols for 3D printing in the medical field is crucial to ensure device reliability and patient safety. Lack of standardized processes and quality control measures can hinder the widespread adoption and acceptance of 3D-printed medical devices.
The lockdown measures implemented by various governments in anticipation of the COVID-19 pandemic have disrupted supply chains and manufacturing processes, leading to shortages in the availability of raw materials and components necessary for 3D printing medical devices. Furthermore, the COVID-19 pandemic created a surge in demand for PPE, including face shields, masks, and respirators. 3D printing played a crucial role in addressing the PPE shortage by enabling these devices' rapid production. Many individuals, companies, and organizations turned to 3D printing to produce face shields and other protective equipment to support frontline healthcare workers. According to the Pew research center in 2020 between February and June, companies with 3D printing capability, hospitals, and even 3D printing enthusiasts printed about 38 million face shield parts, 12 million nasal swabs used in tests, 2.5 million ear savers for masks, 241,000 mask parts, and 116,000 ventilator parts.
Technological Advancement
The technological advancement in the 3D printing medical devices market features bioprinting, surgical guides and models, materials development, 3D printed drugs, and customized medical devices. Technology in healthcare is encouraging the healthcare sector to adopt more technology for convenient study and growth in the healthcare market. The growth of technology in healthcare is due to the increased number of diseases and the growing demand for custom-made devices.
The materials of 3D printing are important to increase the range of prosthetics, surgical instruments, and medical applications. Bioprinting allows the formation of complex biological tissues and organs. The automation in 3D printing processes includes quality control, design manufacturing. 3D printing is also used to provide accurate surgical models and guides. The 3D-printed drugs in pharmaceutical manufacturing enable the creation of customized drug formulations for patient needs.
The 3D printing medical devices market is highly developed in technological advancement. The future of technological advancement is focusing on new applications, automation and integration, and biocompatibility. Furthermore, improving the advancement of the market secures health, safety, and quick responses in the healthcare sector. Also, it will accelerate integration to achieve efficient and effective growth of the market.
Market Scope
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 4.74 Billion |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 5.59 billion |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 24.70 Billion |
| Growth Rate from 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 17.95% |
| Largest Market | North America |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | By Products, By Technology, By Application, and By End User |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America and Middle East & Africa |
Market Dynamics
Key Market Drivers
Improved patient care and treatment to brighten the market prospect
The ability of 3D printing to support highly customized and patient-specific medical devices is one of the key factors driving market demand. Traditional manufacturing methods may produce standardized devices that may not perfectly match an individual patient's anatomy. However, 3D printing enables the formation of personalized devices designed for each patient's unique necessities. Whether it's a prosthetic limb, orthopedic implant, or dental restoration, 3D printing enables the precise customization and adaptation of medical devices to fit the patient's specific anatomy. This customization improves patients' comfort, functionality, and overall outcomes, leading to a higher demand for 3D-printed medical devices.
Moreover, 3D printing enables the production of complex and intricate designs that are not easily achievable through traditional manufacturing methods. This capability opens up new possibilities for developing advanced medical devices that enhance patient care and treatment. For instance, in orthopedic surgery, 3D printing allows for the creation of patient-specific implants with optimized geometries and porous structures that promote better integration with the surrounding bone tissue. This promotes faster healing, reduces the risk of complications, and improves the long-term success of the implant.
In addition to customization and complex designs, 3D printing facilitates rapid prototyping and iterative design improvement process. This accelerates the development of new medical devices, allowing for quicker implementation and evaluation of innovative solutions. The ability to iterate and refine designs based on feedback and testing results in devices better suited to meet patient needs and deliver improved outcomes. Furthermore, 3D printing enables the production of anatomical models and surgical guides that assist in surgical planning and procedures. Surgeons can use patient-specific 3D printed models to practice complex surgeries, assess potential complications, and optimize surgical approaches. This preoperative planning enhances surgical precision, reduces operating time, and minimizes patient risks. Thus, these factors drive demand for the 3D printing medical devices market.
Regulatory support and guidelines
Establishing clear and comprehensive regulatory frameworks provides confidence to medical device manufacturers, healthcare providers, and patients, fostering the adoption and growth of 3D printing technology in the medical field. Regulatory support ensures safety and efficacy in developing and using 3D-printed medical devices. Regulatory authorities, such as the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), have recognized the importance of 3D printing in healthcare and have issued specific drafts, guidelines and regulations for these devices.
These guidelines outline the requirements for design, manufacturing, and quality control processes to ensure that 3D-printed medical devices meet the necessary safety and performance standards. For instance, in July 2022, the FDA drafted an initial framework that outlined various potential manufacturing scenarios. This framework will determine the agency's regulatory approach to 3D printing for point-of-care devices and when it will exercise its enforcement discretion. These drafts and guidelines provide a clear roadmap for manufacturers to navigate the regulatory landscape, reducing ambiguity and uncertainty and promoting the responsible and compliant use of 3D printing in medical device production.
Regulatory support helps to build trust and confidence among healthcare professionals and patients. Rigorous regulatory oversight provides assurance that 3D printed medical devices undergo proper evaluation and meet the necessary quality and safety standards. This confidence is crucial in encouraging healthcare providers to adopt and integrate 3D printed devices into their practice. Patients, too, benefit from regulatory support as it ensures that the devices they receive have undergone thorough evaluation, reducing the risk of potential complications or failures. Moreover, regulatory support fosters innovation and investment in the 3D printing medical devices market. By providing a clear regulatory pathway, authorities enable manufacturers to bring innovative 3D printed devices to the market more efficiently. This encourages companies to invest in research and development, as they understand the requirements and expectations for regulatory approval. The presence of regulatory support signals a commitment to supporting advancements in 3D printing technology and its safe implementation in healthcare. Therefore, regulatory support and guidelines drive demand across the 3D printing medical devices market.
Key Market Challenges
High cost causing hindrances to the market
Medical devices must be compatible with the human body, minimizing the risk of adverse reactions or complications. While there are biocompatible materials available for 3D printing, there is a need for further research and development to expand the range of materials with suitable biocompatibility profiles. Enhancing biocompatibility will allow for the production of a wider variety of medical devices, including implants, prosthetics, and surgical tools, meeting the diverse needs of patients and healthcare providers.
Furthermore, the mechanical properties of 3D-printed medical devices are another concern. Devices must possess adequate strength, durability, and flexibility to withstand the stresses and demands of their intended use. Achieving the desired mechanical properties may be challenging, as 3D printing processes may introduce material defects, such as voids, layer delamination, or inconsistent material density. These defects may compromise the structural integrity and functional performance of the devices. Ongoing research and development efforts are necessary to optimize printing parameters, post-processing techniques, and material formulations to improve the mechanical properties of 3D printed medical devices.
Sterilization is a critical requirement for medical devices to ensure patient safety. However, not all 3D printing materials are compatible with common sterilization methods, such as steam autoclaving or gamma radiation. Some materials may degrade or change properties when exposed to sterilization processes, affecting the device's functionality and safety. Developing sterilizable materials suitable for 3D printing is essential to enable the production of devices that may undergo proper sterilization protocols without compromising their integrity or performance. Addressing material limitations requires ongoing research and collaboration between material scientists, 3D printing manufacturers, and healthcare professionals. Material science and formulation advancements are necessary to expand the range of biocompatible materials suitable for 3D printing. In addition, efforts to optimize printing processes and post-processing techniques may help improve the mechanical properties of printed devices. Close collaboration with regulatory bodies is also essential to ensure that new materials meet safety and quality standards. Thus, material limitations will be crucial for unlocking the full potential of 3D printing in medical devices.
Key Market Opportunities
- Growing research and development
- Technology advancements
Products Insights
On the basis of products, the 3D printing medical devices market is divided into dental products, cardiovascular products, neurological products, orthopedic products, craniomaxillofacial products, and others, with the orthopedic products segment accounting for most of the market. This is because 3D printing offers the advantages of patient-specific design and improved osseointegration for better functional outcomes. The orthopedic product segment comprises 3D printed orthopedic implants, prosthetics, surgical guides, and personalized instruments for joint replacements, bone fixation, spinal surgeries, and limb prosthetics.
Technology Insights
On the basis of technology, the 3D printing medical devices market is divided into fused deposition modeling (FDM), bioprinting, selective laser sintering (SLS), electron beam manufacturing (EBM), stereo-lithography, binder jetting, and others, with electron beam manufacturing (EBM) segment accounting for most of the market. EBM technology utilizes an electron beam to selectively melt metal powders and create solid objects layer by layer. EBM is commonly used in producing orthopedic implants and dental components due to its ability to produce complex and porous structures.
Application Insights
On the basis of the application, the 3D printing medical devices market is divided into medical, pharmaceutical, and others, with the medical segment accounting for most of the market. This is because the medical sector comprises many applications where 3D printing is utilized to manufacture medical devices and components. This includes the production of implants, prosthetics, surgical instruments, anatomical models, patient-specific guides, and orthotics. 3D printing enables customization, precision, and patient-specific solutions in the medical field.
End User Insights
On the basis of the end user, the 3D printing medical devices market is divided into hospitals, research centers, pharmaceutical & biotechnology companies, and others, with the hospital's segment accounting for most of the market. Hospitals utilize 3D printing technology to create patient-specific medical devices, such as surgical guides, implants, and prosthetics. 3D printing enables hospitals to tailor medical devices to individual patients, improving treatment outcomes and patient satisfaction. Additionally, hospitals may utilize 3D printing for anatomical models and surgical planning, enhancing preoperative preparation and surgical precision.
Regional Insights
North America dominates the market, primarily driven by several factors, including strong technological capabilities, robust healthcare infrastructure, supportive regulatory environment, high healthcare expenditure, collaborative ecosystem, and the demand for personalized medicine. Furthermore, North America has a well-established and advanced healthcare infrastructure, providing a conducive environment for adopting3D printing in medical applications. The presence of leading hospitals, research institutions, and medical device manufacturers fosters collaboration and drives the development and adoption of 3D-printed medical devices.
Currently, North America is dominating the 3D printing medical devices market. The progress in investment in research and development, and the advanced healthcare infrastructure, places the region in first place. Customization in 3D printing personalizes surgical tools, implants, and devices. The innovation in healthcare supporting advancement leads the region in the market, along with the government initiatives.
Europe is a significant market for 3D printing medical devices, with Germany, the United Kingdom, and France being the major contributors to the market's growth. This is due to Europe's well-developed healthcare infrastructure with advanced hospitals, research institutions, and healthcare facilities. This infrastructure provides a fertile ground for adopting and integrating 3D printing technology in medical devices. The presence of skilled healthcare professionals and collaboration between academia and industry further drives the growth of the market.
The region in Asia-Pacific is anticipated to have the greatest CAGR. This is because the Asia-Pacific region has a rapidly expanding healthcare industry driven by increasing population, rising healthcare expenditure, and improving healthcare infrastructure. This growth creates a favorable environment for adopting 3D printing technology in medical devices as healthcare providers seek innovative solutions to enhance patient care.
3D Printing Medical Devices Market Companies
- 3T RPD Ltd.
- Renishaw plc.
- Concept Laser GmbH
- GENERAL ELECTRIC
- Arcam AB
- EOS GmbH Electro Optical Systems
- Materialise
- ENVISIONTEC, INC.
- 3D Systems, Inc.
- Stratasys Ltd.
- Cyfuse Biomedical K.K.
- ORGANOVO HOLDINGS, INC.
Recent Developments
- In February 2025, TrabTech and AddPark target to 3D print 200,000 medical devices annually. Turkey has emerged as a key player in this field, with companies like BTech, TrabTech, and Addpark now driving innovation.
- In April 2025, Restor3d, a U.S.-based 3D implant company, secured USD 38 million for patient-specific musculoskeletal implants. 3D printing is beginning to play an increasing role in the US surgical landscape in the creation of custom surgical guides for patients' anatomy.
Segments Covered in the Report
By Products
- Dental Products
- Cardiovascular Products
- Neurological Products
- Orthopedic Products
- Cranio-maxillofacial Products
- Others
By Technology
- Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM)
- Bioprinting
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
- Electron Beam Manufacturing (EBM)
- Stereo-lithography
- Binder Jetting
- Others
By Application
- Medical
- Pharmaceutical
- Others
By End User
- Hospitals
- Research Centers
- Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology Companies
- Others
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Ask For Sample
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client