November 2023
The global antibody drug conjugates market size was USD 10.30 billion in 2023, estimated at USD 11.43 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 31.96 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 10.83% from 2024 to 2034.
The global antibody drug conjugates market size accounted for USD 11.43 billion in 2024 and is predicted to reach around USD 31.96 billion by 2034, rowing at a CAGR of 10.83% from 2024 to 2034.
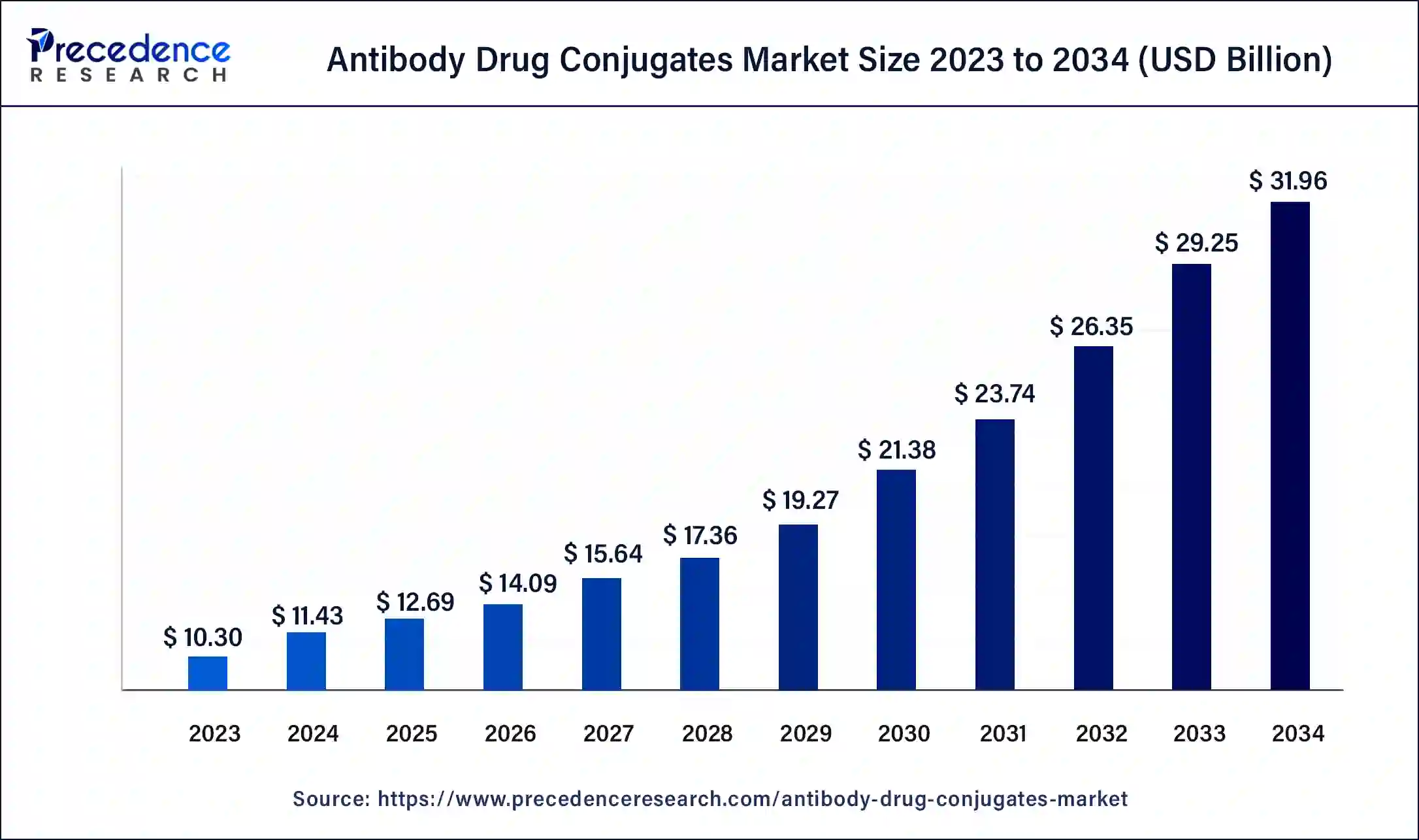
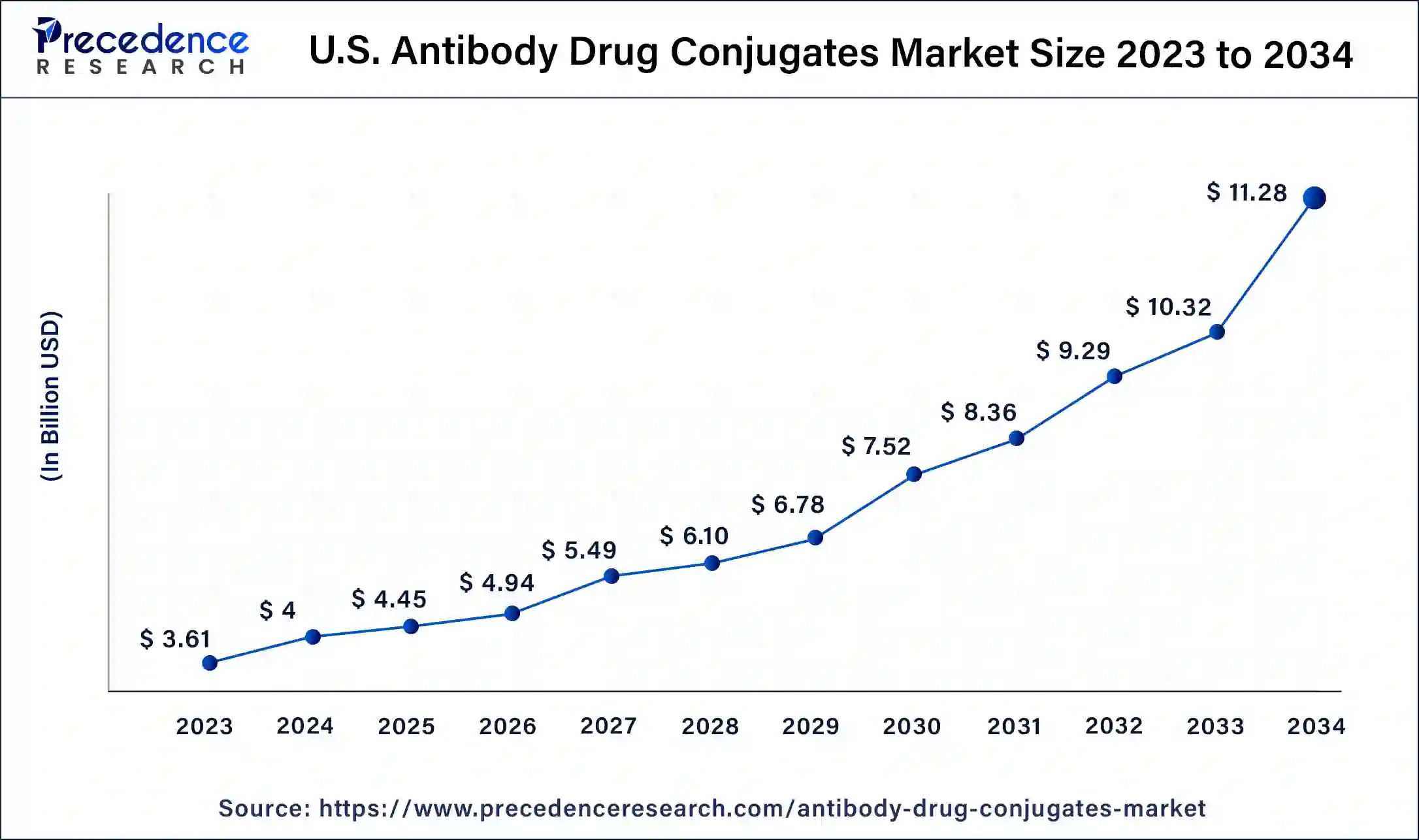
The U.S. antibody drug conjugates market size was estimated at USD 3.49 billion in 2023 and is predicted to be worth around USD 31.96 billion by 2034, at a CAGR of 11.5% from 2024 to 2034.
North America dominates the global antibody drug conjugates market, and the region is anticipated to maintain growth during the forecast period. Rising healthcare expenditures and new product development are significant factors to boost the growth of the antibody drug conjugates market in North America. Moreover, the rising cases of cancer patients will keep the requirement for antibody-drug conjugates highlighted during the projected timeframe.
Europe holds the second-largest market for antibody drug conjugates globally. Cancer causes over a quarter of all deaths in the United Kingdom in a year, and the rising prevalence of cancer in European countries is fueling the market’s growth in the region. Moreover, the high healthcare expenditure and an increasing number of research institutes in Germany are observed to propel the development of the antibody drug conjugates market during the forecast period.
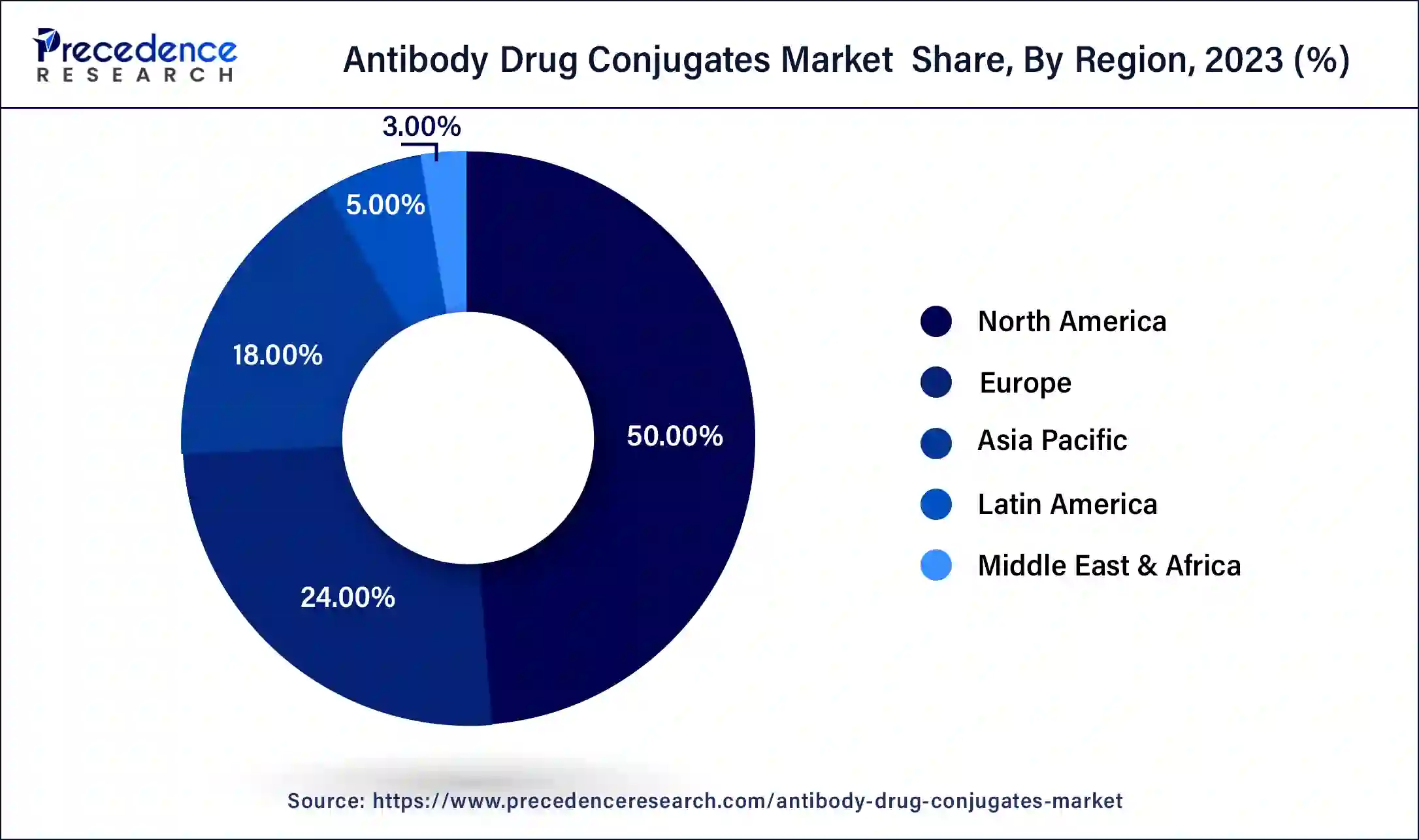
The antibody drug conjugates market in Asia Pacific is expected to grow at a CAGR of 19% during the forecast period. The rising cases of cancer and increasing geriatric population in the region are observed to boost the growth of the antibody drug conjugates market in the Asia Pacific. Moreover, the rising cases of lung, ovarian and stomach cancer in China and India have forced researchers to develop advanced cancer treatment options to reduce the mortality rate. In recent years, the healthcare sector in Asia Pacific has adopted the antibody-drug conjugate as an effective treatment for cancer. The demand for antibody drug conjugates in Asia Pacific is expected to be maintained during the forecast period.
With the rising number of cancer patients across the globe, antibody drug conjugates have become a sword for the oncology sector. An antibody drug conjugate is a highly targeted type of cancer therapeutic created by grafting monoclonal antibodies to a cytotoxic payload. Antibody drug conjugates are one of the most evolving methods of novel cancer therapy.
An ideal antibody drug conjugate contains a potent cytotoxic agent, a highly selective monoclonal antibody and a stable linker. Antibody drug conjugates successfully and selectively seek out cancer cells by limiting the damage to healthy cells. These antibody drug conjugates are directly delivered into the cancer cells in a targeted manner.
Antibody drug conjugates offer an innovative and practical therapeutic application that combines the potent cell-killing activity of highly cytotoxic small molecule drugs with unique anti-tumor activity. Conventional prolonged chemotherapy, however, fails to recognize the carcinogenic cells and healthy cells which are prone to adversely affect human health; in contrast, the antibody drug conjugates reduce systematic toxicity.
The sudden rise in research and development (R&D) activities has resulted in a capacity to generate advanced and next-generation antibody drug conjugates. The recent innovations in the global antibody drug conjugates market have focused on the development of effective, less time-consuming and cost-effective therapies for the treatment of cancer.
The global antibody drug conjugates market is expected to witness a significant increase during the forecast period due to rising cancer cases across the world. The most cancer types across the globe are ovarian, lung, breast and colon; the rising circumstances have forced researchers to develop advanced and cost-effective treatment methods. The growth of antibody-drug conjugates is attributed to the increasing clinical trials in the global pharmaceutical industry.
The rising investment in research and development (R&D) activities are supplementing the growth of the global antibody drug conjugates market. The antibody drug conjugates have minimal side effects; this factor makes them an ideal cancer treatment. Additionally, the antibody-drug conjugates offer a combination of conventional and advanced therapies that assure effective outcomes; this factor is highlighting the importance of antibody-drug conjugates worldwide.
The World Health Organization recently collaborated with the International Agency for Research on Cancer to control the occurrence of non-communicable diseases, including types of cancer. This is expected to boost interest in developing advanced treatments. Moreover, the rising awareness about self-health care is supporting the market’s growth by increasing the number of cancer diagnoses. However, the high cost associated with research and development and the failure of products hinders the market’s growth.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2023 | USD 10.30 Billion |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 11.43 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 31.96 Billion |
| Growth Rate from 2024 to 2034 | CAGR of 10.83% |
| Largest Market | North America |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | Application, Technology, and Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America and Middle East & Africa |
Increased clinical trials for antibody drug conjugates
As antibody drug conjugates are becoming an essential class for cancer treatment, the clinical trials for advanced and next-generation antibody drug conjugates are experiencing a rise. With the rising incidence of cancer globally, researchers are inclined towards evaluating the outcomes for next-generation antibody drug conjugates through clinical trials.
Clinical trials often help in determining the efficacy of a newly designed drug or vaccine. As of June 2022, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved twelve antibody drug conjugates for clinical use. The rising clinical trials act as a driving factor for the market’s growth by offering next-generation antibody drug conjugates to the world healthcare sector.
High production costs and other limitations of antibody drug conjugates
Antibody drug conjugates have high production costs; the price of raw materials, deployed technology, time-consuming production and required skilled and professional workforce dominate the cost of production for antibody drug conjugates. Moreover, fluctuations in the prices of raw materials affect production costs. Biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies invest a considerable amount in research and development activities.
Further, the procedures until the antibody drug conjugates get into the market require a specific budget. Considering the amount needed in the process, the high production costs for antibody drug conjugates hinder the market’s growth by limiting the involvement of small-scale pharmaceuticals and biotech companies.
Moreover, the antibody drug conjugates have a few limitations and challenges, including low penetration capacity and failed outcomes. A few other limitations and difficulties with antibody drug conjugates, such as immunogenicity, lack of stable linkage in blood circulation, drug resistance, uncertain toxicity, poor mechanism of penetration and unusual size of mAbs, can give adverse outcomes of the therapy to the cancer patient. However, researchers across the globe are focused on developing next-generation antibody drug conjugates that can combat such limitations by improving the product's overall efficacy.
Improving the role of government and private sector in cancer prevention
Considering the public health concerns and the continuously rising prevalence of cancer across the globe, governments are inclined towards investing in cancer prevention research activities. Along with this, several governments in developing countries are focused on improving the healthcare infrastructure to offer effective treatment to cancer patients. The rising role of government in cancer prevention will boost the support for antibody drug conjugate production; this will supplement the market’s growth during the projected period.
The United States spends over $200 million on cancer care. Whereas the total amount invested in cancer research globally was estimated at $187 billion in 2021, the investments are increasing with the rising incidence of cancer. Moreover, several governments have deployed various schemes for the population to receive adequate treatment without any barrier; this increases the involvement of patients in cancer treatment.
For instance, the Indian government has deployed numerous central healthcare schemes such as National Health Protection Scheme, Prime Minister National Relief Fund and State Illness Assistance Funds that provide cost-effective treatment for cancer patients.
Covid-19 Impacts:
The sudden outbreak of Coronavirus across the globe negatively impacted almost every industry worldwide by disturbing operations. Similarly, the pandemic has adversely affected the global antibody drug conjugates market. Factors such as declined patient visits and reduced diagnosis rates due to strict lockdown restrictions negatively impacted the growth of the global antibody drug conjugates market. Moreover, a prolonged halt in research and development (R&D) activities affected the market’s development during the critical period of the Covid-19 pandemic. The trade market was disturbed during the period; the pandemic also affected the supply chain of GMP raw materials required in the manufacturing process.
The Covid-19 pandemic affected the global cancer care facilities, disturbing the antibody drug conjugates market. The strict lockdown restrictions during the pandemic period resulted in delayed or denied manufacturing practices and contracts associated with antibody drug conjugates. However, the global antibody drug conjugates market is expected to recover at a pace after the pandemic. On a positive note, the pandemic has forced people to choose advanced healthcare measures; this will result in an increased number of cancers diagnoses and, subsequently, will boost the requirement for antibody drug conjugates.
The breast cancer segment accounts for the most significant global antibody drug conjugates market share. Breast cancer is a non-transmissible disease that arises in the breast's glandular tissue. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), in 2020, approximately 2.3 million women were diagnosed with breast cancer. The rising number of approvals for antibody drug conjugates that can be utilized in treating breast cancer is fueling the segment’s growth.
The blood cancer segment is expected to hold a significant share during the forecast period. Being the fifth most common cancer, blood cancer affects the blood cells, and there are numerous types of blood cancer. At the same time, the prevalence of lymphoma and leukemia has increased in recent years. The rising prevalence of leukemia in children has shifted the focus of researchers to develop next-generation antibody drug conjugates for pediatric leukemia; this factor is expected to boost the segment’s growth during the forecast period.
The cleavable linker technology segment holds the most significant global antibody drug conjugates market share. The cleavable linker technology is the most popular method used in antibody drug conjugates therapy as it has the capacity to release cytotoxin from the antibody drug conjugates. Cleavable linkers play a vital role in the success of antibody-drug conjugates by utilizing the inherent properties of tumor cells; the unmatched advantages of cleavable linkers in cancer treatment supplement the segment’s growth. Moreover, the rising usage of Adcetris drug for cancer treatment, which uses cleavable linkers, highlights the potential of the cleavable linker segment in the global market.
The rapidly increasing utilization of Kadcyla is supporting the growth of the non-cleavable linker segment. Kadcyla is the antibody drug conjugate used in breast cancer treatment that uses non-cleavable linker technology. The non-cleavable linker segment is projected to increase significantly during the forecast period. Non-cleavable linkers have high stability and help kill antigen-negative cells.
Recent Developments
Segments Covered in the Report:
By Application
By Technology
By Geography
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
November 2023
October 2024
October 2024
July 2024