January 2025
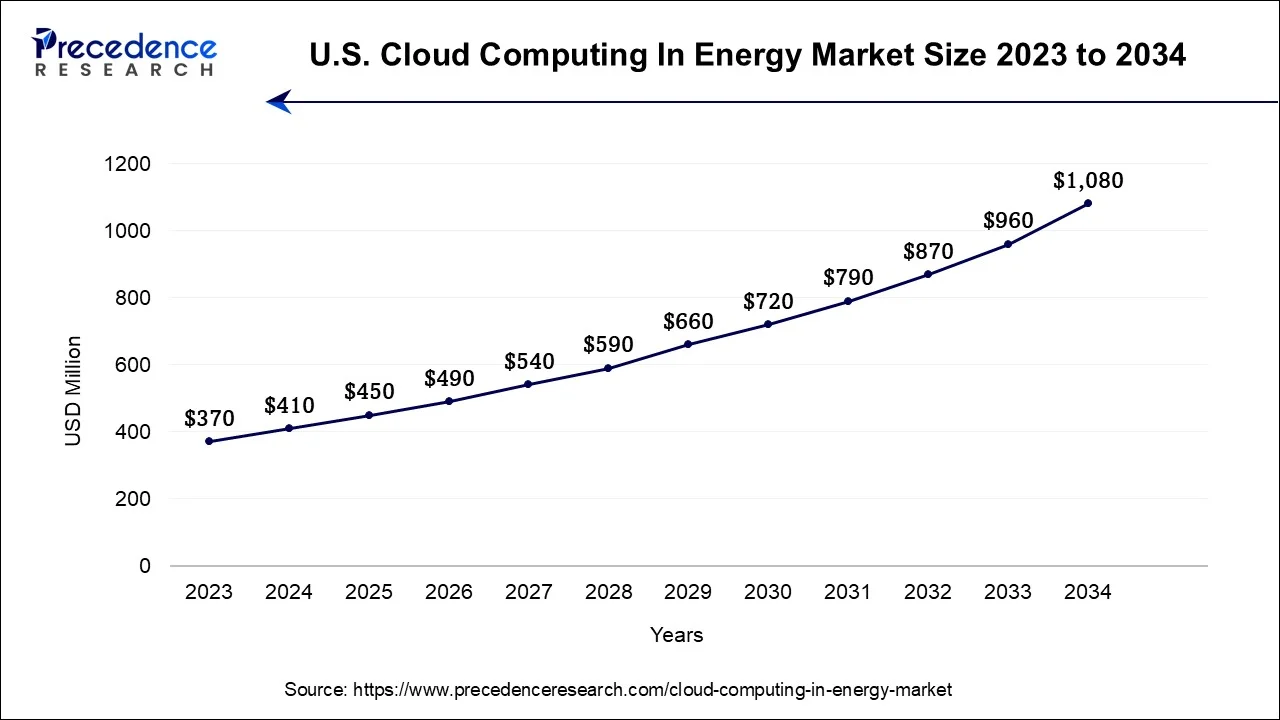
The global cloud computing in energy market size accounted for USD 1.32 billion in 2024, grew to USD 1.45 billion in 2025 and is projected to surpass around USD 3.42 billion by 2034, representing a healthy CAGR of 10% between 2024 and 2034.
The global cloud computing in energy market size accounted for USD 1.32 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 3.42 billion by 2034, representing a notworthy CAGR of 10% between 2024 and 2034.
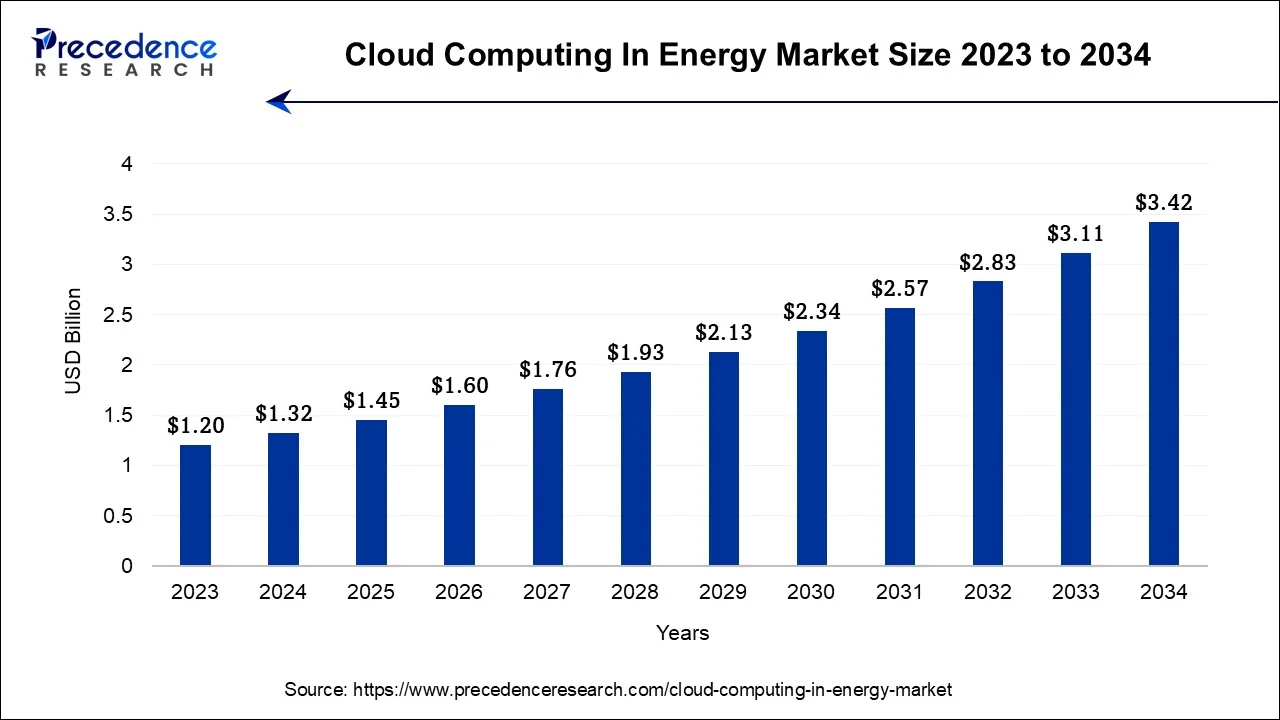
The U.S. cloud computing in energy market size was estimated at USD 410 million in 2024 and is estimated to surpass around USD 1,080 million by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 10.17% from 2024 to 2034.
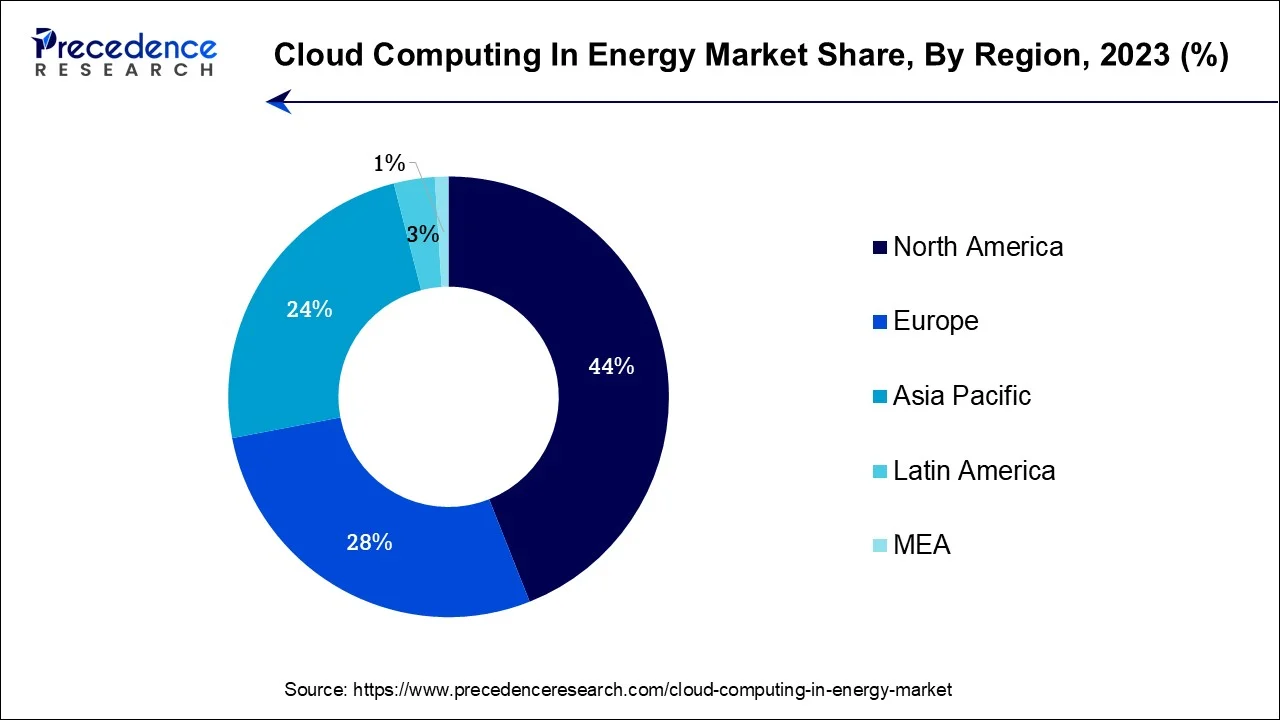
North America has held the largest revenue share 44% in 2023. North America dominates the cloud computing in the energy market due to several key factors. Firstly, the region boasts of advanced technological infrastructure, a robust cloud ecosystem, and a high level of digitalization within the energy sector. Additionally, North America is home to numerous innovative energy companies and tech giants investing heavily in cloud solutions. Stringent regulatory requirements and a strong emphasis on grid modernization drive the adoption of cloud-based analytics and remote monitoring. Furthermore, the region's commitment to renewable energy integration and a mature market for cloud services make North America a frontrunner in this transformative sector.
Asia-Pacific is estimated to observe the fastest expansion. The region's rapid industrialization and urbanization have led to increased energy demand, driving the need for advanced digital solutions. Moreover, Asia-Pacific boasts a growing renewable energy sector, necessitating cloud-based integration for grid management. Additionally, favorable government initiatives and investments in smart grid technology further accelerate adoption. The region's burgeoning tech-savvy population and robust IT infrastructure also contribute to its leadership in cloud adoption, making Asia-Pacific a hotbed for innovation and growth in the cloud computing in energy market.
Cloud computing within the energy sector involves harnessing distant servers and digital assets to optimize multiple facets of energy generation, distribution, and administration. It empowers the implementation of real-time data analysis, anticipatory maintenance, and the fine-tuning of smart grids. By storing and managing extensive data in cloud infrastructure, energy firms can boost operational effectiveness, minimize downtime, and arrive at better-informed conclusions. Furthermore, cloud computing facilitates the amalgamation of renewable energy sources, demand responsiveness systems, and electric vehicle charging networks, thus nurturing a more eco-friendly and resilient energy ecosystem while optimizing expenses and performance.
Cloud computing has emerged as a transformative force within the energy market, ushering in a wave of innovation while confronting certain industry obstacles. It is now a catalyst for growth and evolution in the energy sector.
Cloud computing's ascent in the energy realm is marked by prominent trends. Firstly, the exponential surge in data from smart grids, IoT devices, and renewable energy sources necessitates efficient data handling and analysis, areas where cloud platforms excel. Secondly, the growing emphasis on eco-friendly and renewable energy sources demands agile, data-centric operations, which cloud solutions facilitate. Additionally, the accelerated adoption of remote work and digital collaboration, spurred by the pandemic, is propelling cloud usage, allowing energy firms to function seamlessly across geographically dispersed teams.
The expansion of cloud computing in the energy sphere is underpinned by various factors. Cloud solutions offer scalability, adaptability, and cost-efficiency, enabling energy companies to adjust their operations as required and optimize expenses. Furthermore, cloud-based analytics and machine learning capabilities offer predictive insights that bolster grid stability, minimize downtime, and enable proactive maintenance, ultimately enhancing overall operational efficiency. These dynamics present substantial business openings for energy companies to enhance their services, cut operational expenses, and introduce innovative solutions, bolstering their competitive standing.
While the advantages of cloud computing in energy are considerable, hurdles must be surmounted. Security and data privacy concerns loom large, particularly given the sensitivity of energy sector data and its critical infrastructure. Safeguarding cloud infrastructure from cyber threats and disruptions is paramount. Additionally, the shift to cloud-based systems necessitates significant investments in technology and workforce development. Managing this transformation carefully is essential to minimize disruptions and ensure a seamless transition.
In summary, cloud computing is reshaping the energy market by confronting industry challenges and harnessing key growth drivers. As the energy sector continues to navigate its digital evolution, cloud solutions offer a robust toolbox for enhancing operational efficiency, integrating renewable energy sources, and delivering more sustainable and resilient energy ecosystems. Nonetheless, businesses must address security apprehensions and make prudent investments in technology and workforce advancement to fully unlock cloud computing's potential within the energy industry.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Growth Rate from 2024 to 2034 | CAGR of 10% |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 1.32 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 1.45 Billion |
| Largest Market | North America |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | Service, Platforms, Infrastructure, and Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Integration of renewable energy
The seamless integration of renewable energy sources is a dynamic force propelling market expansion within the energy sector. This phenomenon finds its impetus in a convergence of influential factors. Foremost, the global imperative to curtail carbon emissions and confront the specter of climate change has instigated a widespread transition toward clean energy resources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power. Governments and regulatory bodies worldwide are actively incentivizing and mandating the incorporation of these sustainable energy alternatives, fostering a fertile landscape for market growth.
Additionally, noteworthy advancements in renewable energy technologies have rendered them increasingly competitive and dependable. With the diminishing costs of solar panels and wind turbines, complemented by enhancements in energy storage solutions, the feasibility of incorporating renewable sources into the energy matrix has surged. This transition also bolsters energy security by diversifying the energy supply, reducing reliance on fossil fuels, and mitigating vulnerabilities to supply disruptions.
Furthermore, given the inherent variability of renewable resources, the synergy between cloud computing and data analytics assumes paramount significance. These cutting-edge technologies empower grid operators to adeptly manage the intermittent nature of renewables, thereby ensuring grid stability and unwavering reliability. In summation, the integration of renewable energy sources not only harmonizes with environmental imperatives but also ushers in a wealth of economic opportunities, technological progress, and enhanced energy security, thus fueling substantial market growth within the energy sector.
Reliability and downtime
Reliability and downtime concerns present significant restraints on the growth of cloud computing in the energy market. Firstly, the energy sector is characterized by mission-critical operations, where even brief interruptions or downtime can have far-reaching consequences, impacting grid stability, operational efficiency, and customer satisfaction. Relying on cloud service providers introduces an element of vulnerability, as energy companies have limited control over the provider's infrastructure and maintenance schedules.
Secondly, as the energy industry transitions to more data-driven and automated processes, uninterrupted access to data and applications becomes paramount. Any cloud service outage can disrupt essential functions like real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and energy distribution, potentially causing financial losses and safety concerns. Furthermore, energy companies often operate in remote or challenging environments, such as offshore oil rigs or remote substations, where reliable internet connectivity may not always be guaranteed.
This dependency on network availability further exacerbates concerns about cloud reliability. Overall, while cloud computing offers numerous benefits, addressing these reliability and downtime challenges is crucial to gaining the trust of energy companies and ensuring the seamless integration of cloud technology in the sector. Robust service-level agreements (SLAs), redundancy measures, and disaster recovery plans are essential components of mitigating these restraints.
Remote monitoring and management
Remote monitoring and management (RMM) is emerging as a game-changer in the energy market, creating a myriad of opportunities. By leveraging cloud computing and IoT technologies, RMM enables energy companies to remotely oversee and optimize their assets, from power plants to distribution networks, regardless of geographic distance. This presents opportunities for enhanced operational efficiency as on-site visits become less necessary, reducing costs and risks associated with physical inspections and maintenance. Moreover, RMM empowers companies to proactively identify and address issues, minimizing downtime and improving grid reliability.
Additionally, the ability to collect real-time data and insights from remote assets enables better decision-making, predictive maintenance, and asset performance optimization, fostering a more sustainable and resilient energy ecosystem. As the energy sector continues to digitize, RMM is poised to unlock new avenues for cost savings, innovation, and improved service delivery, driving market growth and competitiveness.
Impact of COVID-19
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of cloud computing in the energy market. As remote work and collaboration became essential, cloud solutions enabled seamless operations and data access. Energy companies increasingly relied on cloud-based analytics for grid management, remote monitoring, and predictive maintenance, ensuring continuity while minimizing on-site staff. The pandemic also highlighted the importance of cloud-driven digital transformation in enabling energy resilience.
It emphasized the value of cloud scalability and cost-efficiency amid economic uncertainties. Overall, COVID-19 underscored cloud computing's pivotal role in enhancing efficiency, resilience, and innovation within the energy sector, driving its continued growth.
According to the service, the infrastructure as a service (IaaS) sector has held a 43% revenue share in 2023. Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) holds a substantial share in the cloud computing market for energy due to its unique suitability for the sector's specific needs. Energy companies require scalable and flexible IT infrastructure to accommodate the variable demands of power generation and distribution. IaaS offers a cost-effective and agile solution, allowing them to scale resources up or down as needed, optimize operational efficiency, and efficiently integrate renewable energy sources. Moreover, it provides the foundation for data-intensive tasks like real-time monitoring and predictive analytics, which are crucial for grid stability and managing energy assets effectively.
The platform as a service (PaaS) sector is anticipated to expand at a significantly CAGR of 11.7% during the projected period. The dominance of the platform as a service (PaaS) segment in the cloud computing market for the energy sector is attributed to its capacity to expedite and refine application development and deployment processes. PaaS empowers energy firms to craft and tailor applications that cater precisely to their requirements, enhancing grid management, data analysis, and customer services. Moreover, PaaS delivers a scalable and cost-efficient solution, alleviating the complexities associated with infrastructure management. This adaptability and efficacy render PaaS the favored choice for energy enterprises seeking agility and innovation in response to the ever-evolving industry landscape, solidifying its substantial footprint within the market.
In 2023, the Amazon Web Services (AWS) segment had the highest market share of 34% on the basis of the Platform. Amazon Web Services (AWS) commands a significant share of the cloud computing market within the energy sector due to several key factors. AWS offers a comprehensive array of cloud services tailored to the specific demands of energy companies, delivering scalable infrastructure, cutting-edge analytics, and IoT capabilities. Furthermore, AWS maintains a vast global network infrastructure that ensures dependable, low-latency connectivity, ideal for remotely overseeing and managing energy assets. AWS's unwavering dedication to security and compliance aligns seamlessly with the rigorous standards governing the energy industry. Its established reputation, extensive client base, and strategic alliances further cement its dominant position in the energy-focused cloud computing landscape.
The Google cloud platform (GCP) is anticipated to expand at the fastest rate over the projected period. Google cloud platform (GCP) holds a substantial share in the cloud computing energy market due to its robust infrastructure, data analytics capabilities, and commitment to sustainability. GCP's secure and scalable cloud services enable energy companies to efficiently manage vast data volumes, optimize grid operations, and integrate renewable resources. Additionally, Google's extensive experience in data centers powered by renewable energy aligns with the energy sector's sustainability goals. GCP's ability to deliver innovative solutions and environmentally responsible services positions it as a trusted partner in the energy market's digital transformation, contributing to its market dominance.
The servers segment held the largest revenue share of 41% in 2023. The servers segment holds a significant share in the cloud computing in the energy market because it forms the basis of cloud infrastructure. Energy companies rely on powerful server clusters to store and process vast amounts of data generated by smart grids, IoT devices, and renewable energy sources. These servers facilitate real-time analytics, predictive maintenance, and grid optimization. As the energy sector increasingly embraces digital transformation and data-driven decision-making, the demand for robust and scalable server infrastructure continues to grow, making this segment a pivotal component in the cloud computing ecosystem for energy companies.
The networking equipment segment is anticipated to grow at a significantly faster rate, registering a CAGR of 12.9% over the predicted period. The networking equipment segment holds a significant share in the cloud computing in the energy market due to its pivotal role in enabling reliable and efficient data communication within the energy infrastructure. As the industry increasingly adopts cloud-based solutions, networking equipment becomes essential for connecting remote assets, such as smart grids and sensors, to cloud platforms. This connectivity is crucial for real-time data monitoring, analytics, and grid optimization. Furthermore, networking equipment enhances cybersecurity measures, ensuring the secure transmission of sensitive energy data to and from the cloud, making it a cornerstone of the sector's digital transformation.
Segments Covered in the Report
By Service
By Platforms
By Infrastructure
By Geography
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
January 2025
January 2025
January 2025
January 2025