February 2025
The global gene editing market size is accounted at USD 10.77 billion in 2025 and is forecasted to hit around USD 40.10 billion by 2034, representing a CAGR of 15.74% from 2025 to 2034. The North America market size was estimated at USD 4.56 billion in 2024 and is expanding at a CAGR of 15.73% during the forecast period. The market sizing and forecasts are revenue-based (USD Million/Billion), with 2024 as the base year.
The global gene editing market size was calculated at USD 9.30 billion in 2024 and is predicted to increase from USD 10.77 billion in 2025 to approximately USD 40.10 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 15.74% from 2025 to 2034.
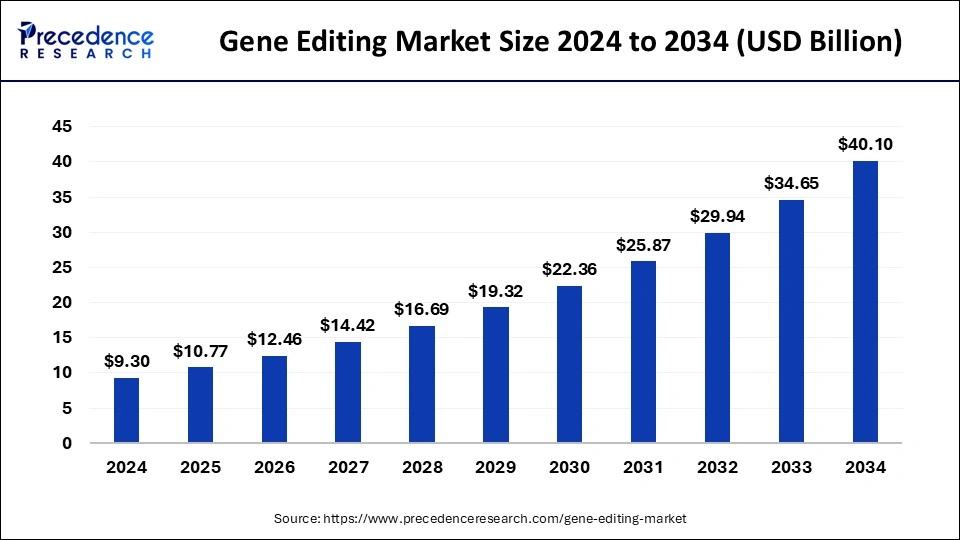
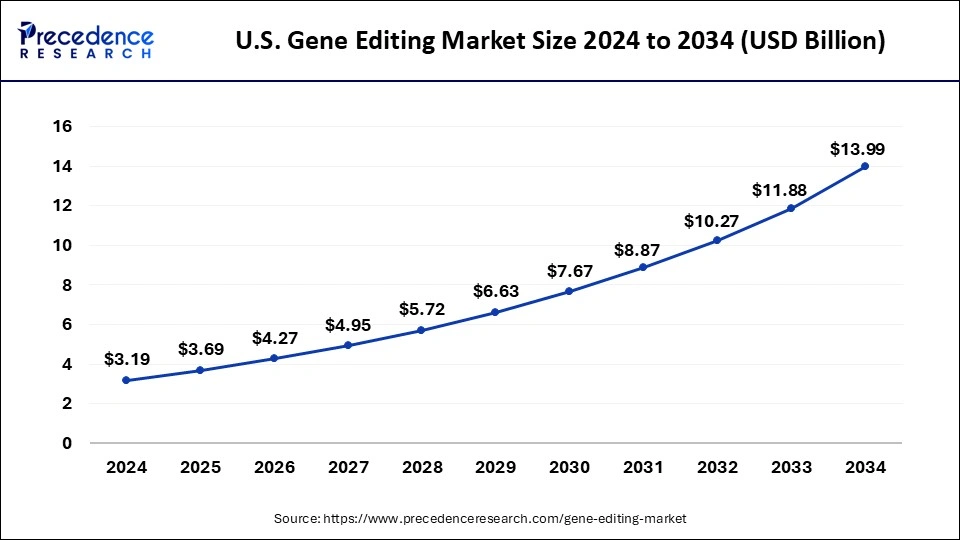
The U.S. gene editing market size was exhibited at USD 3.19 billion in 2024 and is projected to be worth around USD 13.99 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 15.93% from 2025 to 2034.
North America is expected to sustain its dominance throughout the forecast period. The demand for gene editing medicines is driven by increased public and private funding, significant vital actors, the region's sophisticated healthcare system, and the high prevalence of genetic diseases. Patients and healthcare professionals have expressed great interest in the possibility of treating these illnesses. The area has a robust research infrastructure with a concentration of internationally renowned universities, research centers, and biotechnology firms specializing in genetic research and technology development. It has a thriving investment scene, with significant capital going to businesses in biotechnology and gene editing.
Government grants, private equity, and venture capital firms contribute to the funding required for gene editing technology research, development, and commercialization. It has a supportive regulatory framework that encourages innovation and the advancement of technology for gene editing. Explicit criteria for gene editing research and applications have been created by regulatory bodies, such as the FDA in the US, giving businesses a predictable path through the approval process. Collaboration between North American academic institutions, companies, and healthcare facilities supports a thriving ecosystem for transferring knowledge and technology. This collaborative setting speeds up the conversion of scientific discoveries into usable applications and treatments.
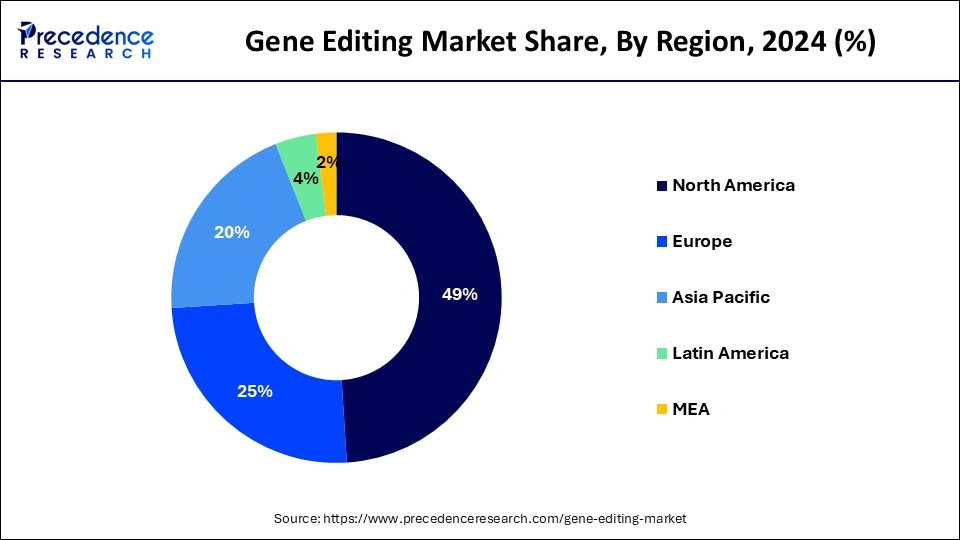
Asia Pacific is expected to be the fastest-growing in the gene editing market during the forecasted timeframe. With significant R&D investments from nations like China, Japan, and South Korea, Asia Pacific area boasts a thriving biotechnology and pharmaceutical industry. Numerous academic institutions and biotech businesses at the cutting edge of gene editing technology are based in these nations. Its vast and varied population is a big plus for clinical trials and the evaluation of gene-editing medicines. This diversity enables the study of numerous genetic variations, increasing the likelihood that gene editing therapies may be effective.
Moreover, gene editing research and development have been drawn to various Asia Pacific nations due to their relatively lax regulatory environments. This has resulted in quicker authorization for clinical trials and investigations compared to other locations. In addition, agreements between government, business, and academic institutions have aided the development of gene editing technology. Funding, resources, and experience devoted to advancing gene editing research in the area have expanded to public and commercial partnerships. The capacity to alter genes for focused therapies effectively fits the expanding trend toward individualized medical treatments.
The gene editing market offers a set of processes of modifying the DNA within an organism’s genome. This can involve adding, removing or altering specific segments of DNA. Gene editing technology has emerged as the most effective way to examine gene function, investigate the pathophysiology of hereditary disorders, create new gene therapeutic targets, breed varieties of crops, and perform other life science-related tasks due to the field's rapid growth. The discovery and development of contemporary gene-editing techniques have made it extremely simple to manipulate production hosts.
The rising prevalence of genetic abnormalities and hereditary diseases is continuously fueling the demand for gene editing technology. Gene editing can fix or alleviate the underlying genetic abnormalities in these illnesses, which have hitherto been challenging to treat. With the constant development of gene editing technologies like CRISPR-Cas9, TALENs, and zinc finger nucleases, gene editing has become more specialized, effective, and widely available. These technologies have created new opportunities for the treatment of genetic abnormalities and the creation of cutting-edge medicines. Gene editing is widely being applied in agriculture to develop crops with better qualities, such as disease resistance, increased nutritional value, and longer shelf life. These programs can increase crop yields and address issues with food security.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 40.10 Billion |
| Market Size by 2025 | USD 10.77 Billion |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 9.30 Billion |
| Growth Rate from 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 15.74% |
| Largest Market | North America |
| Fastest Growing Market | Asia-Pacific |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 To 2034 |
| Segments Covered | Product and Services, Technology, Application, End-user, and Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Advancements in medical understanding
The search for new drugs has become more active as medical understanding of illness mechanisms has improved. The development of novel pharmaceuticals is sped up by gene editing in creating disease models for testing. The transport of gene editing tools into cells has been improved due to viral vector technology developments. For gene therapies to be successful, this is essential.
The growth of gene editing applications has been fueled by medical discoveries that have produced safer and more effective viral vectors. Treatment for uncommon diseases, sometimes known as orphan diseases, has grown in popularity because of medical advancements. Targeted medicines for various conditions can be developed by gene editing, which encourages investment and market expansion.
Gene editing for therapeutic applications has been underlined by medical advancement. Researchers are looking at gene editing to cure hereditary diseases such as sickle cell anemia, cystic fibrosis, and muscular dystrophy. These breakthroughs raise the demand for tools and services related to gene editing. Regulatory organizations are more likely to support and expedite the approval process for gene therapies and modified treatments as medical knowledge of the potential benefits of gene editing increases.
Complex multigenic traits
Testing gene therapies that target complex multigenic features in clinical trials can be difficult. It is challenging to distinguish the effects of the altered genes from those of other genetic and environmental factors, which makes it harder to demonstrate effectiveness. Researching the genetics of complex features and how they interact takes a lot of effort. It takes longer to bring medicines to market because successful gene editing procedures for these qualities necessitate substantial trial and confirmation.
It can be difficult to pinpoint all the genetic elements contributing to complex traits like intellect or susceptibility to specific diseases because many of these attributes are not regulated by a single gene. This ignorance hampers the creation of accurate gene editing methods. It can be unethical to alter numerous genes to affect complex features.
Rising utilization for the healthcare sector
Gene editing can correct or replace mutated genes responsible for monogenic diseases (caused by a single gene mutation). This offers the potential to cure conditions like sickle cell anemia, cystic fibrosis, and certain types of muscular dystrophy. Gene editing can engineer immune cells to target and eliminate viral infections like HIV. This approach offers a potential cure for chronic viral diseases requiring lifelong management. Gene editing can facilitate the development of advanced gene therapies, where genes are added or modified to treat infections. This includes introducing therapeutic genes into patients' cells to produce missing proteins or correct dysfunctional pathways. The growth of healthcare and therapeutic applications will stimulate increased investment in research and development for gene editing technologies, likely leading to improved tools, techniques, and safety protocols, further accelerating the field's progress.
The reagents & consumables segment is expected to be dominant in the gene editing market during the predicted period. Consumables and reagents are critical as they facilitate the actual gene editing procedures. Cas9-like enzymes are required for precise DNA slicing, whereas primers and probes aid in target recognition and confirmation. These items are heavily used by researchers to precisely modify genes. Significant research in academia, medicine, agriculture, and other sectors drives the gene editing business. The need for reagents and consumables increases along with the growth of research activities, assuring the segment's sustained leadership.
Customization and unique solutions are frequently needed for gene editing investigations. To satisfy the particular requirements of researchers, manufacturers provide reagents and consumables that are specially crafted. Customers are drawn in, and this tailored approach further strengthens the market position of the segment. The testing and optimization stages of gene editing research sometimes involve several iterations.
The clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR) segment is expected to be dominant in the gene editing market during the forecast period. Researchers can swiftly produce cell and animal models using CRISPR genome editing, accelerating the study of diseases, including cancer and mental illness. Currently, CRISPR is being explored as a quick diagnostic tool. CRISPR-Cas systems have emerged as the most popular genome editing tool in molecular biology labs worldwide because of their benefits of simple design, low cost, high efficiency, robust reproducibility, and quick cycle.
Establishing genetically altered animal and cell-based models of numerous human diseases, including exogenous gene knock-in models, site-directed mutagenesis models, and gene knockout models, is the most critical application of CRISPR-Cas systems in the medical profession.
For instance, tailoring gene editing techniques to look for a particular CFTR mutation is possible. However, there are numerous CF-causing variants. In the lab, scientists are examining the efficacy and efficiency of several procedures that would enable the correction process to correct any number of mutations, from just one transformation to all. In addition, in medical trials for treating several blood disorders, including sickle cell anemia. Because blood cells can be removed from the human body and administered using gene editing tools in a laboratory, these illnesses make attractive candidates for gene editing. The blood cells can be put back into the body after the mutations have been fixed using gene editing techniques.
The transcription activator-like effector nuclease (TALEN) segment is expected to grow at the fastest rate during the forecast period. Targeting specific DNA sequences with TALENs is highly accurate. Because of their modular construction, the nucleases are adaptable tools for various gene editing applications that may be made to recognize almost any target sequence. In a variety of cell types, including both mammalian and non-mammalian cells, TALENs have been proven effective.
This adaptability allows scientists to investigate gene editing in various biological systems. The therapeutic uses of TALENs, including the treatment of genetic diseases, are extremely promising. They are suitable for reversing disease-causing mutations due to their precise DNA targeting. The market is expanding further due to the adoption of TALEN technology by various sectors to create GMOs with improved features.
The cell line engineering segment is expected to be dominant in the gene editing market during the forecast period. Stable and heritable cell changes, essential for drug research and bio-manufacturing applications, can be produced with the help of cell line engineering. It is recommended for sectors that need constant synthesis of compounds because of their dependability and uniformity.
Technological developments like CRISPR-Cas9 have transformed cell line engineering as they have made it more effective, affordable, and accessible. With these techniques, researchers may precisely target genomic areas, reducing off-target effects and raising the likelihood that desired alterations would be produced. Cell line engineering has become more prevalent in academics and business. The genetic engineering segment is expected to grow at the fastest rate during the forecast period. The invention of CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing technology has completely changed the game. Scientists can precisely target and change genes with previously unheard-of precision and efficacy. Due to its accessibility, gene editing has become more widely available, allowing for genetic engineering research across the globe.
The drug discovery & development segment is expected to witness a significant growth rate during the forecast period. With gene editing tools, researchers may precisely alter a gene's sequence, allowing them to pinpoint prospective therapeutic targets with previously unheard-of accuracy, facilitating knowledge of the underlying biological mechanisms of illnesses and expediting the validation of treatment targets.
The pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies segment is expected to be dominant in the gene editing market during the forecast period. These businesses have a wealth of molecular biology, genetics, and drug development expertise. They have the resources and scientific knowledge to advance gene editing techniques effectively. Numerous businesses engage in cross-disciplinary collaboration with academic institutions and research organizations to improve the development of gene editing technology. Such partnerships strengthen group knowledge and can result in ground-breaking breakthroughs.
The academic and research institutes is the fastest growing segment. Academic institutions house eminent academics and scientists with in-depth knowledge of genetics and molecular biology, making them centers of competence. They have created ground-breaking gene editing technologies due to their creative thinking and commitment to improving science. In contrast to what is usually pursued by industry, academic researchers frequently work on more experimental and high-risk topics. These projects may produce unanticipated discoveries and brand-new uses, broadening the potential services for gene editing.
By Product and Services
By Technology
By Application
By End-user
By Geography
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
February 2025
January 2025
February 2025
November 2024