January 2025
The global genetic analysis market size is calculated at USD 8.42 billion in 2025 and is forecasted to reach around USD 21.67 billion by 2034, accelerating at a CAGR of 11.08% from 2025 to 2034. The North America genetic analysis market size surpassed USD 3.60 billion in 2024 and is expanding at a CAGR of 11.06% during the forecast period. The market sizing and forecasts are revenue-based (USD Million/Billion), with 2024 as the base year.
The global genetic analysis market size was USD 7.88 billion in 2024, estimated at USD 8.42 billion in 2025, and is anticipated to reach around USD 21.67 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 11.08% from 2025 to 2034. The genetic analysis market is driven by the global increase in the prevalence of chronic illnesses.
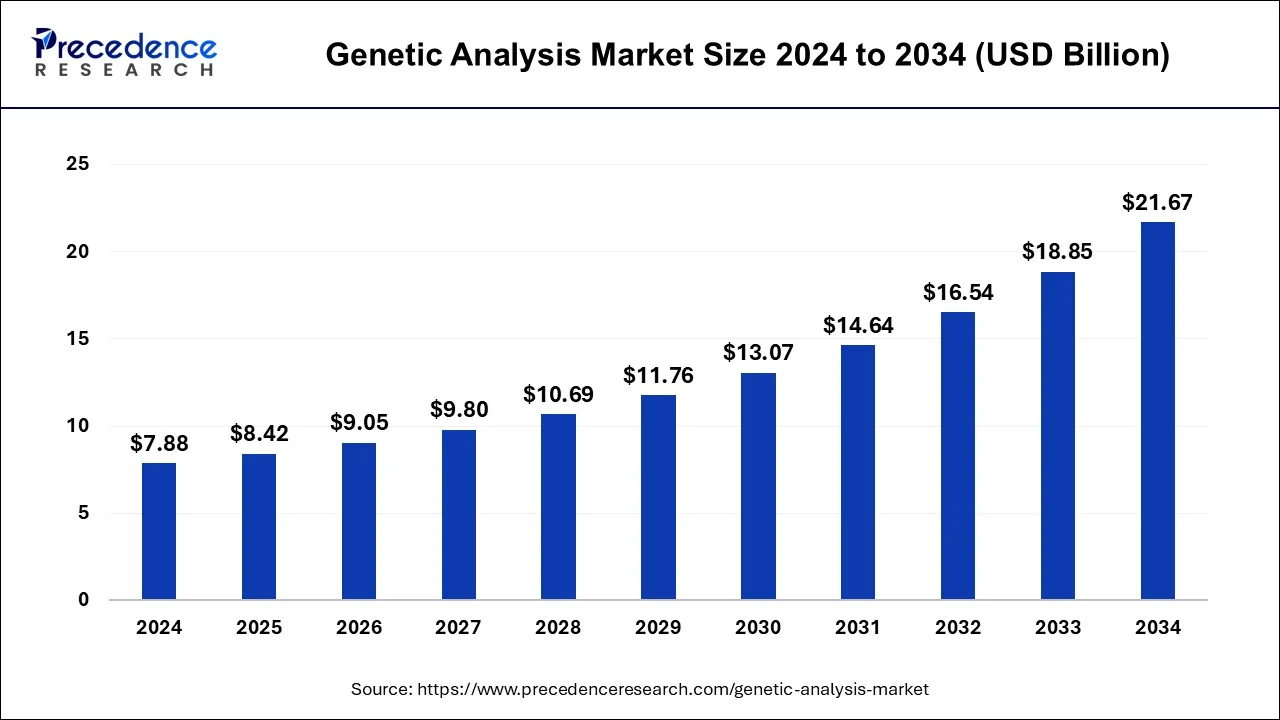
The global genetic analysis market size was USD 3.35 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 8.95 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 11.63% from 2025 to 2034.
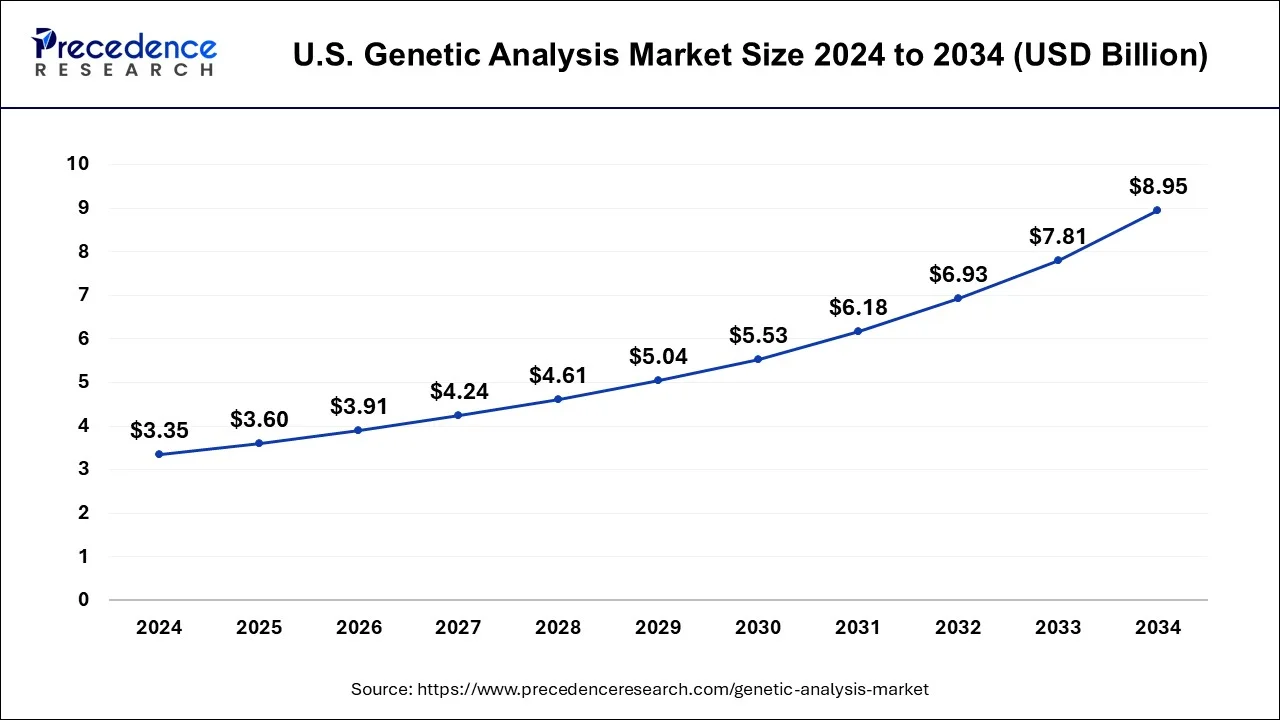
North America dominated the genetic analysis market in 2024. When it comes to the development of cutting-edge genetic analysis technologies, North America has been in the vanguard. This covers developments in CRISPR-based gene editing methods, microarray analysis, polymerase chain reaction (PCR), and next-generation sequencing (NGS). The market is expanding because of these developments, which have made it possible for academics and medical practitioners to conduct genetic studies more quickly, accurately, and affordably.
Because of its outstanding colleges, research centers, and biotechnology businesses, it draws talent from worldwide. Genetics, genomics, bioinformatics, and related subjects are among the many fields in which the region has a vast pool of highly qualified scientists, researchers, and healthcare professionals. This talent pool spurs creativity and makes it easier for advanced genetic analysis methods to be used in clinical and research contexts.
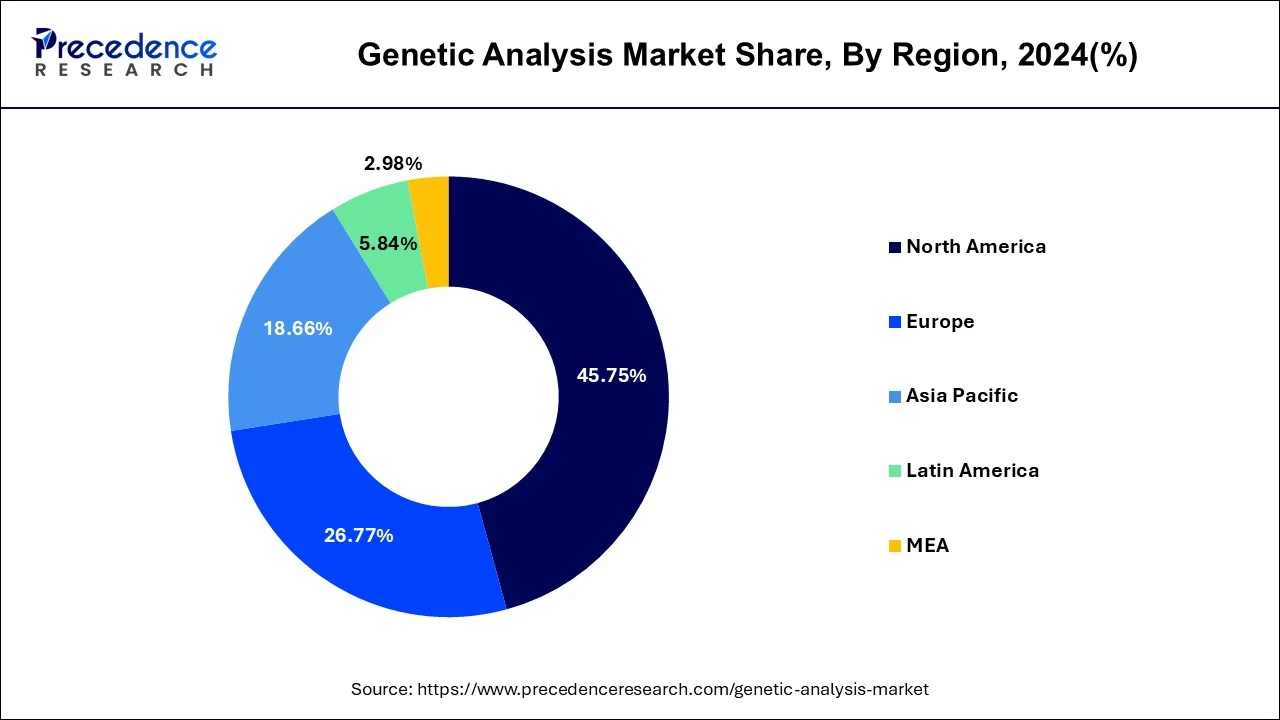
Europe holds the second largest share in the genetic analysis market during the forecast period. Europe has state-of-the-art research facilities and healthcare infrastructure, especially in nations like Germany, the UK, France, and Switzerland. These countries' well-established pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors encourage creativity and genetic analysis research. Genetic analysis is becoming more widely accepted and adopted in Europe due to increased public and professional understanding of its advantages.
The demand for genetic analysis services is driven by patient advocacy groups, educational programs, and media coverage that highlight the significance of genetic testing for illness prevention, diagnosis, and treatment.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest growing in the genetic analysis market during the forecast period. The region's rising healthcare spending has been a major factor in the expansion of the market. People are spending more money on healthcare, particularly genetic testing and analysis, as the economies in the area grow. The need for genetic analysis has increased in Asia-Pacific due to the trend toward personalized medicine, which uses genetic data to customize treatment regimens for specific patients. To maximize positive treatment outcomes and reduce adverse side effects, healthcare providers are progressively incorporating genetic testing into clinical practice.
Gene expression analysis, sequencing, genotyping, and bioinformatics are only a few techniques and resources utilized in genetic analysis to investigate genetic variants. These methods allow researchers and medical practitioners to read the genetic code, spot mutations, examine gene expression patterns, and comprehend how genetics affect health and illness.
Pharmacogenomics studies individual genetic differences to optimize pharmacological therapy by forecasting an individual's response to medication. Due to this individualized approach to medicine, healthcare professionals may provide the safest and most effective medications with the least amount of side effects. In forensic science, genetic analysis is used to identify people and determine biological ties using DNA profiling. By matching DNA samples from crime scenes with suspects' or databases', forensic investigators can solve crimes, identify victims, and clear innocent parties.
Genetic analysis plays a critical role in cancer research and treatment by discovering oncogenes, tumor suppressor genes, and other genetic abnormalities causing cancer formation. Based on the genetic makeup of tumors, it assists oncologists in selecting targeted medicines and creating individualized treatment regimens.
Genetic Analysis Market Data and Statistics
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Global Market Size in 2025 | USD 8.42 Billion |
| Global Market Size by 2034 | USD 21.67 Billion |
| Growth Rate from 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 11.08% |
| Largest Market | North America |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| 4Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | Product, Test, Technology, Application, End-use, and Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Drivers
Increased prevalence of chronic diseases and genetic disorders
Genetic analysis facilitates timely interventions and individualized treatment strategies by aiding in the early detection and diagnosis of various genetic abnormalities and chronic diseases. There is an increasing emphasis on genetic research to comprehend the underlying mechanisms of genetic illnesses and chronic diseases. Genetic analysis technologies are essential to these research projects and fuel market demand. Precision medicine, a medical specialty in which a patient's treatment is customized based on their genetic composition, has been made possible by developments in genetic analysis. This individualized approach is essential for hereditary disorders and chronic illnesses. Thereby, the increased prevalence of chronic diseases is observed to act as a driver for the genetic analysis market.
Advancements in genetic testing technologies
With NGS technologies, whole genomes may be sequenced quickly and affordably, allowing scientists and medical professionals to examine genetic variants thoroughly. As a result, whole-genome sequencing has replaced targeted gene panels as the primary genetic testing method. Bioinformatics advances have made it easier to evaluate genetic data, enabling researchers to glean valuable insights from large volumes of genomic data. Incorporating machine learning algorithms further improves the precision of genetic analyses and illness risk prediction.
Thousands of genetic variants, such as copy number variations (CNVs) and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), can be analyzed simultaneously thanks to microarray technology. This high-throughput method has transformed personalized medicine and the research of complicated genetic illnesses.
Restraint
Ethical concerns surrounding the use of genetic information
Genetic data is highly delicate and personal. People may choose not to share their data for research reasons or take part in genetic testing due to worries about abuse or illegal access to this information. Due to genetic predispositions to specific diseases or disorders, there are concerns about genetic discrimination in insurance, employment, and other contexts. People may decide not to get genetic testing done at all because of this anxiety. Genetic testing may provide details about a person or their family that could cause bias or social stigma. People may be discouraged from getting tested or disclosing their results if they fear stigma.
High cost of genetic testing and analysis
Many of the population cannot afford genetic testing and analysis, which limits the technology's potential effect and uptake. Genetic testing may or may not be covered by insurance, and since these tests can be expensive, insurance companies may refuse to pay them, or their coverage may be restricted, further limiting accessibility. Research and development activities in the sector may be impeded by the high cost of genetic analysis, which could hinder the understanding of hereditary illnesses and the development of effective remedies. High-cost acts as a major restraint for the genetic analysis market.
Opportunity
Growing demand for non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT)
NIPT is a safe and highly accurate way to identify genetic abnormalities in fetuses without requiring invasive procedures like chorionic villus sampling (CVS) or amniocentesis. By doing this, the mother's and the fetus's risk of problems is decreased. The need for NIPT tests is growing as more pregnant parents and medical professionals become aware of its advantages. The growing understanding of genetic problems and technological developments drives this trend. Numerous nations are modernizing their regulatory frameworks to allow for NIPT as they become more aware of the clinical utility of these tests. Further propelling market expansion are advantageous reimbursement rules for NIPT in some areas, which make it more reasonable and accessible for pregnant parents.
The reagents & kits segment dominated the genetic analysis market with the largest share in 2024. The fundamental components of genetic analysis procedures are reagents and kits. These are the materials and equipment required for conducting laboratory operations and experiments. Numerous products are included in them, including buffers, enzymes, primers, probes, PCR reagents, sequencing kits, DNA extraction kits, and other consumables. Demand for specialized reagents and kits catered to specific research goals is rising as research gets more and more specialized. Businesses in this market sector provide customization services, enabling researchers to get goods tailored to their needs. This modification can entail changing the concentrations, creating new kits, or changing the buffer composition to satisfy experimental needs.
The instruments segment is the fastest-growing in the genetic analysis market. The industry for genetic analysis tools gains a lot from continuous technical development. Genetic analysis has been transformed by breakthroughs like polymerase chain reaction (PCR), next-generation sequencing (NGS), and microarray technologies, which enable quicker, more accurate, and more affordable testing. Researchers, doctors, and pharmaceutical businesses are drawn to these technological advances because they provide access to cutting-edge tools to improve their genetic research and applications. The popularity of genetic analysis tools has been fueled by the declining prices of genetic sequencing, which have made it more affordable for consumers, healthcare providers, and academics.
Companies in the instruments segment provide high-throughput sequencing systems that allow researchers to sequence entire genomes or specific sections quickly and cheaply. The market is expanding rapidly due to more labs and organizations investing in genetic analysis equipment as the cost barrier decreases.
Genetic Analysis Market Revenue (USD Million), By Product, 2022-2024
| Product | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 |
| Reagents & Kits | 4,019.9 | 4,256.9 | 4,526.3 |
| Instruments | 2,267.3 | 2,402.4 | 2,548.7 |
| Software | 717.2 | 760.0 | 803.2 |
The disease diagnostic testing segment dominated the genetic analysis market with the largest share in 2024. Genetic testing technology has advanced significantly, becoming more widely available, reasonably priced, and precise. Genetic analysis has been transformed using techniques such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR), microarray analysis, and next-generation sequencing (NGS). The need for precise and effective diagnostic testing is rising as genetic illnesses are becoming more commonplace globally.
Genetic analysis is used to monitor and diagnose conditions such as sickle cell anemia, Huntington's disease, cystic fibrosis, and several types of cancer.
The prenatal and newborn testing segment is the fastest growing in the genetic analysis market during the forecast period. Genetic analysis technological advancements have greatly improved the precision, effectiveness, and cost-effectiveness of prenatal and neonatal testing. For example, next-generation sequencing (NGS) has wholly changed genetic testing by making it possible to sequence entire genomes or regions of interest quickly. This has allowed researchers to gain a thorough understanding of genetic variants. Expectant parents and medical professionals are much more aware of the advantages of genetic testing throughout pregnancy and the first few months after giving birth.
Because of this, more people are choosing to have diagnostic testing and prenatal genetic screening to determine their risk of genetic abnormalities and to make well-informed decisions about becoming pregnant.
The real-time PCR system segment dominated the genetic analysis market in 2024. Nucleic acid detection and quantification can be done with precision and sensitivity using real-time PCR equipment. This is important for genetic analysis since even minute differences or mutations must be correctly identified. Multiplexing refers to the ability of several real-time PCR systems to simultaneously detect and quantify multiple target sequences inside a single reaction. This is perfect for high-throughput screening applications since it simplifies the analysis procedure, lowers the sample size needed, and boosts throughput.
Applications for real-time PCR can be found in many domains, such as forensic research, biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and environmental monitoring. Its superiority in the genetic analysis market is primarily due to its adaptability and versatility to various business and research demands.
The next-generation sequencing (NGS) segment is the fastest-growing in the genetic analysis market during the forecast period. Personalized medicine, pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and medical diagnostics are just a few industries where NGS is used. NGS is used in medical diagnostics to find genetic changes linked to various illnesses, such as infectious diseases, cancer, and uncommon genetic disorders. NGS is used in agriculture for trait mapping, crop development, and biodiversity research. Pharmaceutical companies use NGS for pharmacogenomics, target identification, and drug discovery. Furthermore, NGS makes customized treatment methods possible by detecting genetic variants that affect an individual's susceptibility to disease and how well a therapy works.
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) is a state-of-the-art technique that has been used to read Saudi human genomes in a way that is both economical and clinically effective. Over 65,000 samples have been sequenced due to the program, and 7,500 variations have been found. Of these variants, almost 3,000 are new causal mutations linked to more than 1,230 uncommon genetic illnesses.
Genetic Analysis Market Revenue (USD Million), By Technology, 2022-2024
| Technology | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 |
| Real-Time PCR System | 2,157.5 | 2,305.4 | 2,467.1 |
| Next-generation Sequencing (NGS) | 3,791.0 | 4,016.8 | 4,261.4 |
| Others | 1,055.9 | 1,097.0 | 1,149.7 |
The infectious diseases segment dominated the genetic analysis market in 2024. Globally, infectious illnesses continue to pose a severe threat to public health, contributing significantly to morbidity and mortality rates. Situations such as the COVID-19 pandemic have highlighted the significance of quick and efficient diagnosis methods for infectious diseases. Due to increased awareness, significant funds have been allocated to developing genetic analysis tools specifically designed for detecting and tracking infectious diseases. Genetic analysis is essential for surveillance, detection, and containment operations in emerging infectious disease epidemics. Epidemiologists can trace the distribution of infectious agents, pinpoint the transmission routes, and study the evolution of infections in real time thanks to the rapid sequencing and analysis of pathogen genomes.
The utilization of genetic epidemiology as a method improves response to outbreaks by offering helpful information for public health initiatives.
The genetic diseases segment is the fastest growing genetic analysis market during the forecast period. Healthcare providers and the public have a notably higher level of awareness regarding hereditary illnesses. Due to this increased knowledge, there has been increased demand for genetic testing and screening programs to detect people at risk of genetic diseases early on. More people are undergoing genetic analysis to understand their genetic predispositions better and take preventative action. Globally, the incidence of genetic illnesses is growing due to aging populations, consanguineous marriages, changing lifestyles, and environmental variables.
More genetic analysis is required to detect and treat several genetic diseases that are growing more common. Examples of these diseases include Duchenne muscular dystrophy, sickle cell anemia, and cystic fibrosis.
The research and development laboratories segment dominated the genetic analysis market in 2024. Since R&D laboratories prioritize innovation and research, they frequently have access to state-of-the-art technologies and apparatus. They invest significantly in cutting-edge genetic analysis instruments like microarray, polymerase chain reaction (PCR), next-generation sequencing (NGS), and bioinformatics platforms. They can perform precise and efficient high-throughput genomic tests due to this cutting-edge technology.
Innovative scientific efforts to understand the complexity of the human genome and other species are driven mainly by R&D laboratories. They are the driving forces behind innovative research that advances our knowledge of gene expression regulation, population genetics, evolutionary biology, and genetic disorders. R&D labs push the boundaries of scientific understanding and create the groundwork for creating cutting-edge genetic analysis methods and technology through their groundbreaking research.
The diagnostic centers segment shows a significant growth in the genetic analysis market during the forecast period. Growing awareness of the significance of genetic information in healthcare has increased demand for genetic testing services in recent years. A growing number of people are requesting genetic analyses due to their desire to learn more about their hereditary susceptibilities to certain diseases. Diagnosing genetic abnormalities is no longer the exclusive use of genetic testing. It is used in several fields, such as pharmacogenomics, ancestry testing, prenatal screening, and personalized medicine. Diagnostic facilities are finding innovative ways to serve a wide range of client demands as applications for genetic analysis continue to expand.
Genetic testing has become a valuable tool for early disease identification and risk assessment as the focus on preventative healthcare grows. Diagnostic centers offer comprehensive genetic testing services customized to each patient's risk profile, positioning them as significant participants in the preventative healthcare space.
Genetic Analysis Market Revenue (USD Million), By End Use, 2022-2024
| End-use | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 |
| Hospitals | 1,294.4 | 1,376.2 | 1,464.0 |
| Research & Development Laboratories | 3,048.7 | 3,249.3 | 3,457.6 |
| Diagnostic Centers | 1,607.0 | 1,678.4 | 1,777.9 |
| Others | 1,054.3 | 1,115.3 | 1,178.7 |
By Product
By Test
By Technology
By Application
By End-use
By Geography
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
January 2025
January 2025
July 2024
January 2025