July 2024
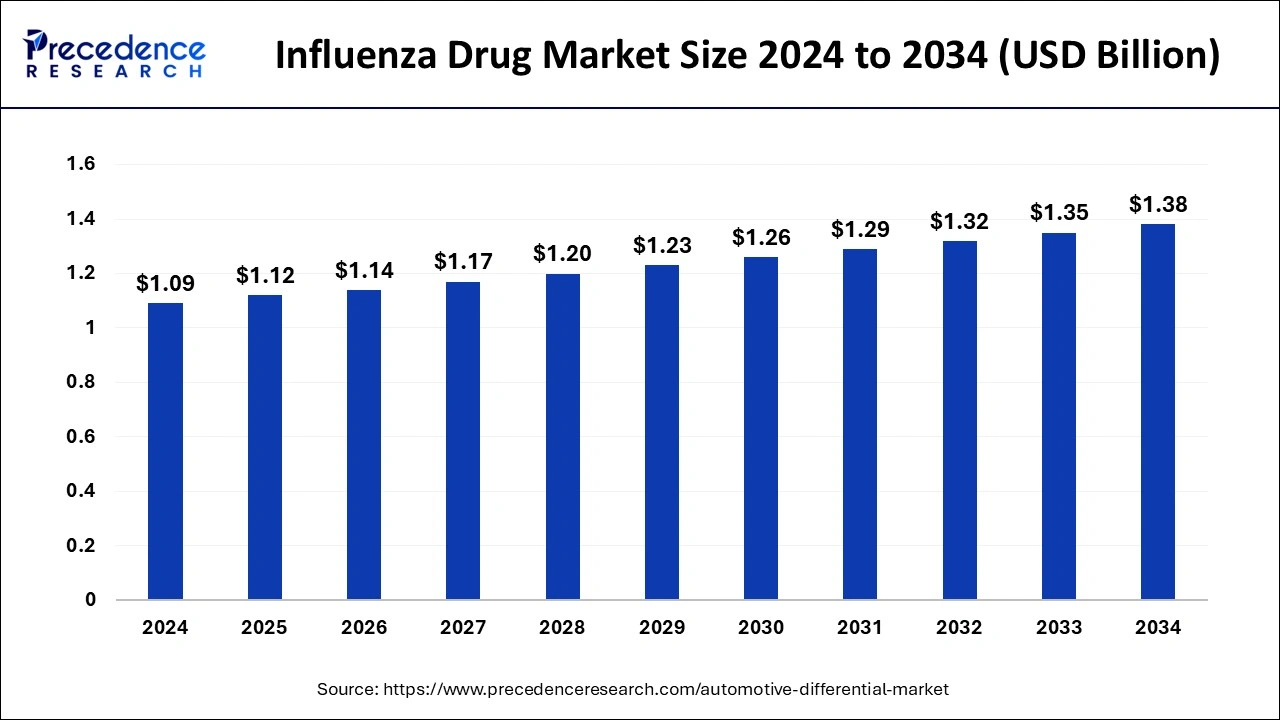
The global influenza drug market size is calculated at USD 1.12 billion in 2025 and is forecasted to reach around USD 1.38 billion by 2034, accelerating at a CAGR of 2.39% from 2025 to 2034. The market sizing and forecasts are revenue-based (USD Million/Billion), with 2024 as the base year.
The global influenza drug market size was estimated at USD 1.09 billion in 2024 and is predicted to increase from USD 1.12 billion in 2025 to approximately USD 1.38 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 2.39% from 2025 to 2034. As advancements in genomic sequencing and precision medicine continue, there’s a burgeoning interest in tailoring influenza treatment strategies to individual patients based on their genetic makeup, immune response, and susceptibility to viral strains.
Influenza treatment encompasses various strategies aimed at alleviating symptoms, shortening the duration of illness, and preventing complications associated with the influenza virus. The primary approach involves supportive care, which includes rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications to relieve symptoms such as fever, cough, and body aches. Antiviral medications, such as oseltamivir (Tamiflu) and zanamivir (Relenza), are also prescribed in certain cases, particularly for individuals at high risk of complications or those experiencing severe symptoms. These medications work by inhibiting the replication of the influenza virus, thereby reducing the severity and duration of illness when taken early in the course of infection.
Vaccinations are a vital part of the influenza drug market. They aid in preventing influenza infection and reducing its spread within communities. Annual influenza vaccination is recommended for individuals six months and older, with particular emphasis on groups at higher risk of complications, including young children, elderly individuals, pregnant women, and those with underlying health conditions. Vaccination not only protects vaccinated individuals but also contributes to herd immunity, indirectly safeguarding those who may be more vulnerable to severe illness.
Overall, within the influenza drug market, the management of influenza involves a combination of supportive care, antiviral medications, and vaccination. Prompt initiation of treatment, especially with antiviral medications, can significantly impact the course of illness and reduce the risk of complications, highlighting the importance of early detection and intervention during influenza outbreaks. Public health measures, including the promotion of vaccination and adherence to infection control practices, remain essential in mitigating the burden of influenza on both individuals and communities.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 1.12 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 1.38 Billion |
| Growth Rate from 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 2.39% |
| Largest Market | North America |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | By Type, By Mechanism of Action, By Route of Administration, and By End-user |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Advances in targeted antiviral therapies
In recent years, significant strides have been made in developing targeted antiviral therapies for influenza, driven by the need to combat evolving viral strains and emerging resistance to existing treatments. One notable advancement is the approval of baloxavir marboxil, a first-in-class cap-dependent endonuclease inhibitor, by regulatory agencies in several countries. Baloxavir marboxil offers a novel mechanism of action that disrupts viral replication early in the infection cycle, leading to rapid symptom relief and shorter duration of illness compared to standard antiviral agents. Its single-dose oral formulation presents a convenient treatment option, particularly for high-risk populations and individuals with limited access to healthcare facilities.
Moreover, ongoing research efforts are focused on developing next-generation antiviral compounds with enhanced potency, broader spectrum activity, and improved resistance profiles. Innovative strategies, including the identification of host-targeted therapies and combination therapies targeting multiple stages of the viral life cycle, hold promise for overcoming existing treatment challenges and addressing the evolving landscape of influenza viruses. These advancements underscore the importance of continued investment in antiviral research and development to meet the evolving needs of influenza treatment.
Emergence of universal influenza vaccines
Another significant driver in influenza treatment market is the pursuit of universal influenza vaccines capable of providing long-lasting and broad-spectrum protection against diverse influenza strains, including seasonal and pandemic viruses. Traditional influenza vaccines target the highly variable surface proteins of the virus, necessitating annual updates to match circulating strains. However, the emergence of antigenically distinct strains and the limitations of strain-specific vaccines highlight the need for more effective immunization strategies.
Recent advancements in vaccine technology, such as the development of mosaic vaccines, nanoparticle-based formulations, and adjuvanted vaccines, aim to induce broader and more durable immune responses by targeting conserved regions of the influenza virus. These next-generation vaccine candidates are designed to provide cross-reactive immunity against multiple influenza strains, potentially reducing the need for annual vaccine updates and improving pandemic preparedness. The pursuit of universal influenza vaccines represents a paradigm shift in influenza prevention, offering the potential to transform the way we control and mitigate the impact of influenza outbreaks globally.
Challenges in developing broad-spectrum antiviral therapies for influenza
In the realm of influenza treatment, a significant recent restraint revolves around the challenges encountered in developing broad-spectrum antiviral therapies. Despite advancements in antiviral research, the emergence of resistance to existing treatments and the need for effective options against diverse influenza strains present formidable obstacles. One of the primary reasons for this restraint is the high mutability of the influenza virus, particularly its surface proteins hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA). These proteins undergo frequent genetic changes, leading to antigenic drift and the emergence of new viral variants that can evade immune responses and antiviral interventions.
Developing antiviral drugs that can effectively target multiple strains and subtypes while overcoming viral escape mechanisms is a complex endeavor requiring a deep understanding of viral pathogenesis and host-virus interactions. The lengthy and costly process of drug development, coupled with regulatory requirements for safety and efficacy, poses additional challenges for bringing novel antiviral therapies to the influenza drug market. Despite promising preclinical data, many candidate drugs fail to demonstrate sufficient clinical benefit or face barriers to regulatory approval, limiting the availability of new treatment options for influenza.
Harnessing the potential of host-targeted therapies
Recent advancements in the influenza drug market have unveiled promising opportunities in the realm of host-targeted therapies. Unlike traditional antiviral drugs that directly target viral components, host-targeted therapies focus on modulating host factors and cellular pathways involved in the viral replication cycle. One promising avenue in host-targeted therapy involves targeting host proteins and cellular mechanisms essential for viral replication and propagation. Additionally, modulating host immune responses through immunomodulatory agents and cytokine inhibitors holds promise for attenuating influenza-associated inflammation and tissue damage, thereby improving clinical outcomes and reducing disease severity.
Recent advances in understanding the host-virus interaction landscape, facilitated by omics technologies and systems biology approaches, have identified novel host factors and signaling pathways critical for influenza pathogenesis. Exploiting these insights could lead to the development of targeted therapies that disrupt specific host-virus interactions while minimizing off-target effects and preserving host immune function. These create lucrative opportunities for businesses in the influenza drug market.
Revolutionizing vaccine design with mRNA technology
Another transformative opportunity for the influenza drug market is the application of mRNA technology to vaccine development. mRNA vaccines have gained prominence in recent years, particularly in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, owing to their rapid development timelines, scalability, and potential for inducing robust immune responses.
Within the market, mRNA vaccines offer several distinct advantages over traditional vaccine platforms. Their inherent flexibility allows for the rapid design and production of vaccines tailored to target specific influenza strains or conserved viral antigens. This adaptability is particularly relevant in the face of antigenic drift and shift, enabling timely updates to vaccine formulations to match circulating strains and improve vaccine efficacy.
mRNA vaccines have demonstrated the ability to induce potent and durable immune responses, including both humoral and cellular immunity, which are essential for conferring protection against influenza infection and reducing disease transmission. By leveraging mRNA technology, researchers can overcome longstanding challenges associated with egg-based and cell-based vaccine production, streamline the vaccine development process, and accelerate the deployment of novel influenza vaccines to address evolving public health needs.
The two most prominently utilized segments in the influenza drug market are antiviral medications and vaccines. The antiviral medication segment dominated the market in 2023. Antiviral medications, such as baloxavir marboxil and oseltamivir, are widely employed because they directly inhibit viral replication and alleviate symptoms, especially when administered early in the course of illness. Their usage is crucial in managing severe cases and preventing complications, particularly in high-risk populations. Advances in antiviral technology have led to the development of innovative compounds targeting various stages of the viral life cycle, enhancing efficacy and reducing the emergence of resistance.
The vaccine segment is expected to show significant growth during the forecast period. Vaccines play a pivotal role in influenza prevention and control by stimulating the immune system to produce protective antibodies against specific viral strains. Recent advancements in vaccine technology, notably the adoption of mRNA-based platforms, have revolutionized vaccine development and deployment. mRNA vaccines offer advantages such as rapid production, scalability, and flexibility in vaccine design, allowing for the timely adaptation to circulating strains and potential pandemic threats. Their use has been instrumental in improving vaccine efficacy, shortening production timelines, and addressing supply chain challenges, thereby enhancing global pandemic preparedness and response efforts.
The cap-dependent endonuclease inhibitors segment dominated the influenza drug market in 2024. Cap-dependent endonuclease inhibitors represent a promising class of antiviral agents that target a critical enzyme involved in viral RNA transcription. These inhibitors disrupt the viral replication process by blocking the activity of the endonuclease enzyme, which is essential for cleaving host mRNA caps and initiating viral RNA synthesis. Baloxavir marboxil is a notable example of a cap-dependent endonuclease inhibitor that has been recently approved for the treatment of influenza. Its unique mechanism of action offers rapid and potent antiviral activity against a broad spectrum of influenza viruses, including strains resistant to other antiviral drugs.
The development of novel cap-dependent endonuclease inhibitors continues to be an active area of research, with efforts focused on optimizing drug potency, pharmacokinetics, and resistance profiles to enhance their clinical utility and address emerging challenges in influenza management.
The host cell protease inhibitors segment is expected to grow significantly during the forecast period. Host cell protease inhibitors represent another innovative approach to influenza treatment by targeting cellular enzymes essential for viral entry and replication. These inhibitors interfere with the proteolytic cleavage of viral surface proteins required for viral fusion and entry into host cells, thereby preventing viral infection and propagation.
Recent advancements in understanding the role of host cell proteases, such as TMPRSS2 and furin, in influenza virus pathogenesis have spurred the development of selective protease inhibitors as potential antiviral agents. These inhibitors offer the advantage of targeting host factors that are conserved across multiple influenza strains, potentially reducing the risk of drug resistance. Clinical trials evaluating the efficacy and safety of host cell protease inhibitors in influenza treatment areunderway, with promising results indicating their potential as a novel therapeutic strategy for combating influenza infections.
The intranasal segment dominated the influenza drug market in 2024. The intranasal administration route offers a non-invasive and convenient delivery method, allowing for the direct targeting of the respiratory mucosa, which the influenza virus primarily infects. Intranasal formulations, such as nasal sprays or drops, provide rapid absorption and distribution of antiviral drugs or vaccines, making them effective for both treatment and prevention.
The subcutaneous segment is expected to show significant growth in the influenza drug market. Subcutaneous administration or subcutaneous injections involve delivering medications into the fatty tissue layer beneath the skin. This route offers advantages such as sustained drug release and ease of administration, making it a preferred option for certain antiviral medications or long-acting formulations used in influenza treatment. Additionally, subcutaneous delivery can help bypass gastrointestinal degradation and achieve predictable pharmacokinetics, ensuring optimal therapeutic outcomes.
The pharmacies segment dominated the influenza drug market in 2024. Pharmacies play a crucial role in providing access to influenza antiviral medications, over-the-counter remedies, and influenza vaccines. With the expansion of pharmacist-administered vaccination programs, pharmacies have become convenient hubs for both treatment and prevention of influenza.
The corporate health programs segment is expected to grow significantly in the forecast period. Many companies are implementing comprehensive health programs that include influenza vaccination campaigns, wellness initiatives, and education on preventive measures. Corporate health programs aim to protect employees from influenza, reduce absenteeism, and promote overall well-being in the workplace.
North America has dominated the influenza drug market due to several factors in 2024. The region benefits from robust healthcare infrastructure, advanced research capabilities, and high awareness levels regarding influenza prevention and treatment. Moreover, stringent regulatory frameworks ensure the availability of safe and effective influenza vaccines and antiviral medications.
The United States, in particular, accounts for a significant share of the global influenza drug market, driven by extensive vaccination campaigns, proactive public health measures, and strong investment in research and development. As of recent data, the United States remains a key player in influenza treatment, with a comprehensive influenza vaccination program and widespread availability of antiviral medications in healthcare settings and pharmacies.
Asia Pacific is emerging as a significant market for influenza treatment, driven by population growth, increasing healthcare expenditure, and growing awareness of the importance of influenza prevention and management. Countries such as China, Japan, and India are witnessing rapid advancements in healthcare infrastructure, coupled with rising investment in influenza research and development. Additionally, the threat of influenza outbreaks and the potential for pandemic influenza strains have spurred governments in the region to prioritize influenza preparedness and strengthen healthcare systems.
China, as a prominent player in Asia Pacific, has made substantial strides in influenza treatment and prevention. With a large population and growing healthcare infrastructure, China has implemented comprehensive influenza vaccination programs and invested in the development of domestic antiviral medications. Recent data from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention (China CDC) indicates a steady increase in influenza vaccine coverage rates, with efforts focused on expanding access to vaccination in both urban and rural areas.
By Type
By Mechanism of Action
By Route of Administration
By End-user
By Geography
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
July 2024
July 2024
August 2024
June 2023