April 2025
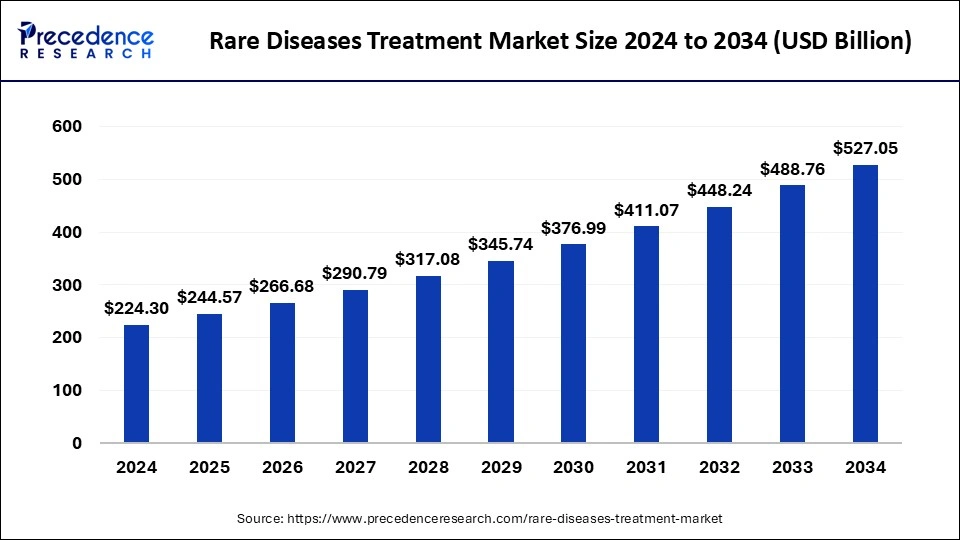
The global rare diseases treatment market size is calculated at USD 244.57 billion in 2025 and is forecasted to reach around USD 527.05 billion by 2034, accelerating at a CAGR of 8.92% from 2025 to 2034. The North America rare diseases treatment market size surpassed USD 109.91 billion in 2024 and is expanding at a CAGR of 8.95% during the forecast period. The market sizing and forecasts are revenue-based (USD Million/Billion), with 2024 as the base year.
The global rare diseases treatment market size was estimated at USD 224.30 billion in 2024 and is predicted to increase from USD 244.57 billion in 2025 to approximately USD 527.05 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 8.92% from 2025 to 2034. Pharmaceutical companies' strategic collaborations and acquisitions have driven the market.
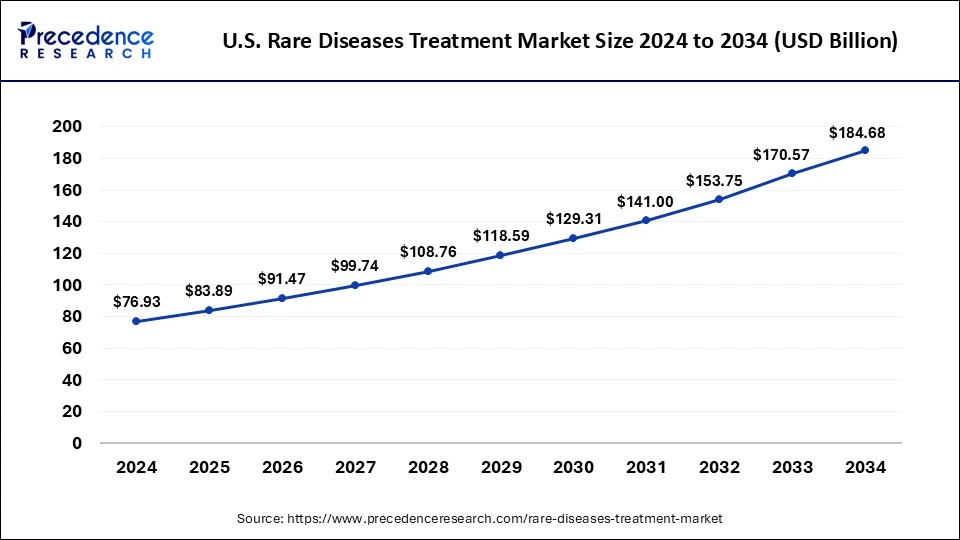
The U.S. rare diseases treatment market size was estimated at USD 76.93 billion in 2024 and is predicted to be worth around USD 184.68 billion by 2034 with a CAGR of 9.15% from 2025 to 2034.
North America dominated the rare disease treatment rare disease treatment market in 2024. North America has a highly developed healthcare infrastructure with cutting-edge medical facilities and technology, especially in the United States. This makes it possible to diagnose, treat, and manage uncommon diseases more effectively. One of the main drivers is a substantial expenditure on research and development (R&D). In North America, financing from both the public and commercial sectors is significant, which encourages the creation of novel cures and treatments for uncommon illnesses. North America is home to several of the top pharmaceutical and biotechnology corporations in the world. These businesses are deeply engaged in the discovery, creation, and marketing of therapies for uncommon diseases. The regulatory landscape in North America, particularly in the U.S., is favorable to the development of drugs for uncommon diseases. Initiatives like the Orphan Drug Act offer grants, tax rebates, and market exclusivity as incentives.
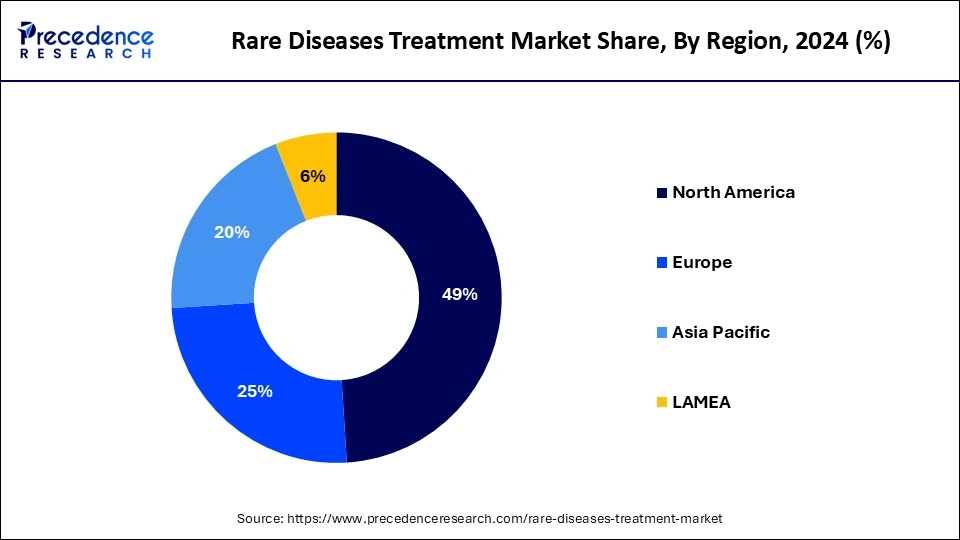
Asia Pacific is expected to grow at the highest CAGR in the rare disease treatment market during the forecast period. The area is seeing rapid economic expansion in several of its nations, which has led to higher healthcare costs. Infrastructure and services for healthcare, especially those for rare illnesses, are receiving increased funding from the public and commercial sectors. In Asia Pacific, people are becoming more aware of uncommon diseases. More instances are being found and treated as a result of enhanced diagnostic skills and raised health knowledge. Raising awareness is also being aided by patient advocacy organizations and public health efforts. Due to infrastructural upgrades and increased accessibility to medical services in rural and previously underserved areas, the region's healthcare access is growing. The detection and treatment of uncommon illnesses are made easier by this increased accessibility. Many countries in the region are implementing incentives and programs.
The rare disease treatment market refers to the industry involved in the development of treatment options for orphan diseases, commonly referred to as rare diseases. These diseases are illnesses that only affect a tiny portion of the population.
rare disease treatment market include the treatment of conditions such as cystic fibrosis, Huntington’s disease, gaucher disease, hemophila, dchenne muscular dystrophy. The cystic fibrosis affect the lungs and digestive systems, Huntington’s disease breakdown the nerve cells, gaucher disease buildup fatty substances, hemophila disorder impair the blood’s ability to clot, duchenne muscular dystrophy degenerate the muscles.
The rare disease treatment market is fragmented with multiple small-scale and large-scale players, such as F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., Pfizer, Inc., PTC Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, Novartis AG, Novo Nordisk, Bayer AG, AbbVie Inc., Merck & Co. Inc., Bristol Myers Squibb.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 244.57 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 527.05 Billion |
| Growth Rate from 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 8.92% |
| Largest Market | North America |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | Drug Type, Therapeutic Area, Patient, Route of Administration, Distribution Channel, and Regions |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Rapid FDA approvals
The rapid FDA approvals of rare disease treatment can boost the rare disease treatment market. The rapid FDA approvals significantly reduced the time and expense involved in introducing new drugs to the rare disease treatment market. Pharmaceutical companies can discover it more appealing to invest in rare disease treatments as a result of the lower financial risk and quicker potential return realization. Additionally, the FDA often prescribes orphan drugs, which are drugs that treat rare diseases.
Expensive trials due to lack of patient number
The expensive trials due to a lack of patient numbers may slow down the rare disease treatment market. The rare diseases impact a small percentage of the population. Due to this, finding enough volunteers for clinical trials is challenging and time consuming, which causes delays in the start and finish of these investigation.
Personalized medicine
The personalized medicine of rare treatment can be the opportunity to grow the rare disease treatment market. The individual’s genetic and molecular profiles are taken into account while creating personalized medications, which can result in more focused and effective therapy. Personalized medicines have the potential to yield significant health benefits for rare diseases for which standard treatments are often ineffective. This could spur increased demand and the rare disease treatment market.
The biologics segment dominated the rare disease treatment market in 2024. The targeting disease pathways with great specificity and biologics encompass a broad spectrum of items such as recombinant proteins, gene treatments, and monoclonal antibodies. With many rare illnesses having distinct and intricate pathophysiologies that are better treated with biologics than with conventional small-molecule medications, this accuracy is especially crucial.
The creation and manufacturing of biologics, which may target genetic and molecular abnormalities on the basis of several uncommon illnesses, has been made possible by recent developments in biotechnology. Innovative therapies that were not achievable with traditional medications are now possible to advance to technologies like CRISPR and other gene-editing techniques. The biologics intended to treat rare illnesses now have easier access to approval in advance to the efforts of governments and regulatory agencies like the FDA and EMA.
The non-biologic segment is expected to grow rapidly in the rare disease treatment market during the forecast period. The development of drugs is a fast-changing profession, and important advancements in small-molecule medications are improving their efficacy -in treating uncommon disorders. The improved methods for finding drugs and modeling molecules are making it possible to develop non-biologic treatments that are more effective and precisely targeted.
Comparing non-biologic drugs, which are usually tiny molecules, with biologics, which frequently need injections or infusions, the former frequently have the benefit of oral bio-availability, which makes them easier to give. Higher patient compliance and improved overall treatment of uncommon illnesses can result from this convenience. Manufacturing expenses for non-biologic medication production are often lower than those for biologic drug production. Pharmaceutical corporations may find non-biologics more appealing due to their cost-effectiveness, which might lead to increased patient accessibility and affordability.
The cancer segment dominated the rare disease treatment market in 2024. Even though the number of individuals affected by each rare disease is very modest, there are a significant number of patients overall who have rare cancers. A considerable proportion of patients with uncommon diseases are affected by rare malignancies, including several forms of lymphomas, sarcomas, and leukemias. Over the past several years, there have been major breakthroughs in oncology therapies and cancer research. Targeted therapies and personalized medicine techniques have been developed in response to advances in understanding the genetic and molecular underpinnings of different uncommon malignancies. These treatments have proven especially beneficial for these illnesses. There is a significant unmet medical need since patients with uncommon malignancies frequently have poor prognoses and few therapy choices. The clinical research and market demand are driven by the need to identify effective therapies for these patients as soon as possible.
The blood-related disorder segment is expected to grow at a significant CAGR in the rare disease treatment market during the forecast period. Blood-related illnesses are a major area of interest for research and development since many of these diseases have obvious hereditary roots. Novel therapeutic targets and cutting-edge therapies are being developed as a result of this effort. Because there are generally few effective therapies for blood-related illnesses, there is a high unmet medical demand.
The health conditions such as sickle cell disease and hemophilia need lifetime care, and current therapies can be rather demanding. The creation of novel treatments that enhance quality of life and have greater efficacy is very appealing to patients as well as medical professionals. The regulatory agencies offer substantial encouragement and financial assistance for the development of therapies for uncommon blood diseases. Pharmaceutical firms are encouraged to engage in this market by regulatory incentives such as fast-track approvals, orphan medication designations, and others.
The injectable segment dominated the rare disease treatment market in 2024. When it comes to injectables, bio-availability is frequently higher than with oral or other modes of delivery. This indicates that a larger percentage of the medication enters the bloodstream, which is essential for the efficacy of several medical interventions, especially biologics like gene therapy, enzyme replacement therapy, and monoclonal antibodies. Complex biological medications, such as proteins, peptides, and gene therapies, are frequently used to treat uncommon disorders. However, these medications are frequently unstable or poorly absorbed when given orally. For these treatments, injectables are the best option since they provide stability, appropriate absorption, and therapeutic efficacy.
The oral segment is expected to grow at the highest CAGR in the rare disease treatment market during the forecast period. In general, oral drugs are easier to give and more convenient than injectables or other modes of delivery. This simplicity of use can greatly increase patient compliance, especially when it comes to the long-term therapies needed to manage a variety of rare diseases. The advances in drug delivery technologies, such as nanoparticle delivery systems, sustained-release formulations, and prodrug approaches, are enhancing the bio-availability and therapeutic efficacy of oral drugs. With the help of these advancements, oral administration is overcoming long-standing obstacles, including poor absorption and digestive system breakdown.
By Drug Type
By Therapeutic Area
By Patient
By Route of Administration
By Distribution Channel
By Geography
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
April 2025
January 2025
May 2024
February 2025