November 2023
The global antibody therapy market size is evaluated at USD 351.09 billion in 2025 and is forecasted to hit around USD 973.60 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 12% from 2025 to 2034. The North America market size accounted for USD 119.12 billion in 2024 and is expanding at a CAGR of 12.15% during the forecast period. The market sizing and forecasts are revenue-based (USD Million/Billion), with 2024 as the base year.
The global antibody therapy market size was valued at USD 973.6 billion in 2024, and is calculated at USD 973.6 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach around USD 973.60 billion by 2034. The market is expanding at a solid CAGR of 12% over the forecast period 2025 to 2034. The North America antibody therapy market size reached USD 106.36 billion in 2023.
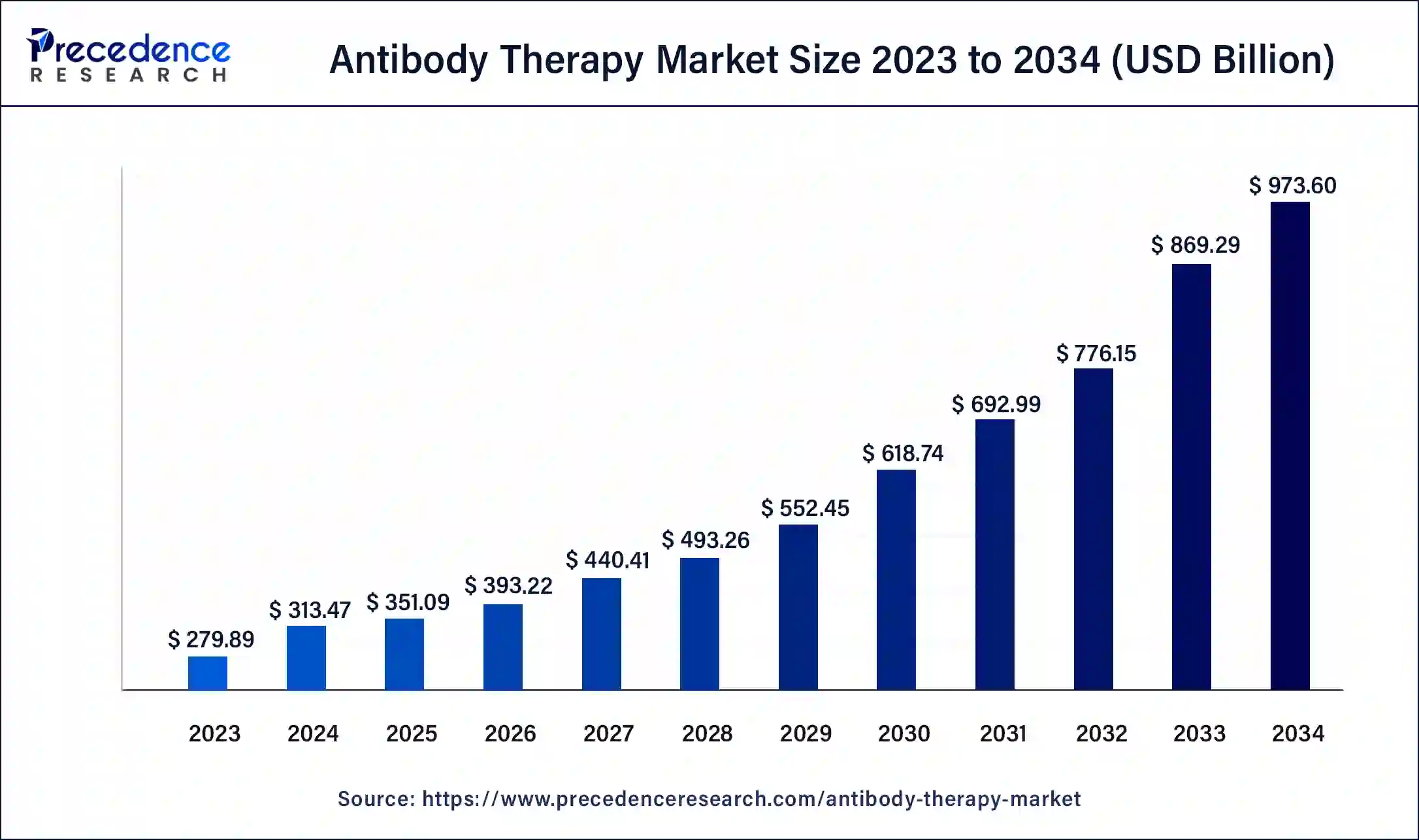
The U.S. antibody therapy market size was estimated at USD 83.71 billion in 2024 and is predicted to be worth around USD 265.03 billion by 2034, at a CAGR of 12.22% from 2025 to 2034.
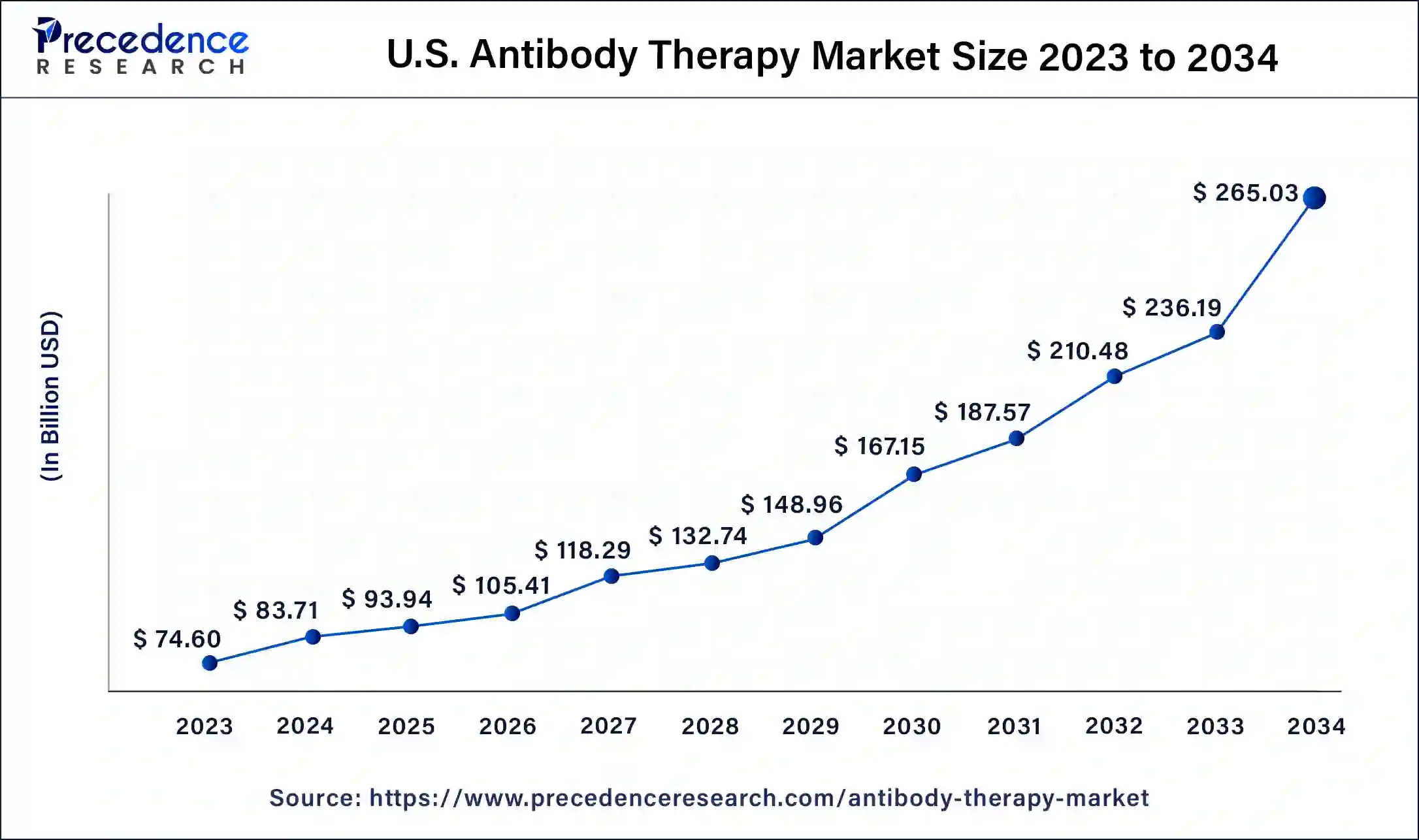
North America led the market with the biggest market share of 38% in 2024, particularly evident with 122 approvals of the 162 antibody therapies worldwide being granted in the U.S., according to Umabs-DB data. This dominance is attributed to the extensive investment in research and development by U.S.-based companies, resulting in their substantial market share
The U.S. leads in both research and clinical development within the antibody therapy field, further solidifying its leading position. In the context of COVID-19, vaccines utilized in the U.S. primarily target the spike (S) protein of the virus, with antibody detection against the receptor-binding domain (RBD) showing a higher correlation with neutralizing virus ability. Such insights are crucial for serologic studies, aiding in differentiating previous infection from vaccination.
Therapeutic monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) represent a groundbreaking advancement in medical treatment, harnessing the power of the immune system to combat diseases such as cancer, infections, and autoimmune disorders. These antibodies, either derived from the body's own immune system or synthesized in laboratories, target specific markers on cells or tissues, aiding in the eradication of harmful agents.
Monoclonal antibodies bind to antigens, prompting the immune system to develop tailored defenses against similar threats. This mimics the natural immune response, offering targeted treatment with reduced side effects compared to traditional therapies. The growing significance of therapeutic approaches has fueled several initiatives by pharmaceutical companies and is responsible for the market's current growth.
The antibody therapy market has witnessed remarkable expansion, driven by the approval of new drugs catering to diverse ailments, including cancers, autoimmune disorders, metabolic conditions, and infectious diseases. Over the past 25 years, mAbs have emerged as the primary treatment modality for various illnesses, reflecting substantial advancements in discovery and development processes.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Global Market Size by 2034 | USD 973.60 Billion |
| Global Market Size in 2025 | USD 351.09 Billion |
| Global Market Size in 2024 | USD 313.47 Billion |
| Growth Rate from 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 12% |
| Dominated Region | North America |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | Type, End User and Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Expanding applications of monoclonal antibody therapy
Advances in understanding the role of growth factors and their receptors in hematopoietic and neoplastic diseases have catalyzed the development of humanized chimeric monoclonal antibodies. These innovations offer a new perspective for treating leukemia, lymphoma, breast cancer, autoimmune diseases, and ischemic complications.
Monoclonal antibodies are instrumental in cancer diagnosis and therapy, immune response modulation for autoimmune diseases and graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), and prevention of allograft rejection. Additionally, their application in treating bacterial infections and reducing tissue damage in conditions like bacterial meningitis and myocardial reperfusion injury further fuels the growth of the antibody therapy market.
Increasing prevalence of chronic diseases driving demand for antibody therapy
The rising prevalence of chronic diseases has significantly contributed to the expanding use of antibody therapy. Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are increasingly applied in the treatment of severe, nonmalignant conditions such as atopic dermatitis, asthma, hypercholesterolemia, osteoporosis, migraine headaches, and bacterial infections. As a result, antibody drugs have become some of the most sought-after products in the pharmaceutical market.
Notably, among the top 50 drugs based on sales in 2021, 22 are antibody drugs, with adalimumab (Humira) emerging as the leading antibody drug with annual sales exceeding $20 billion. This robust demand for antibody therapy, driven by the prevalence of chronic diseases, continues to propel growth in the antibody therapy market.
High development costs
The formidable development costs associated with antibody therapy pose a significant obstacle to market expansion. With the average annual price of a monoclonal antibody (mAb) exceeding $96,731 and surpassing $100,000 for 34 mAb-indication combinations, affordability becomes a pressing concern for patients, healthcare providers, and payers alike. Particularly in oncology and hematology, where mAbs represent 40% of approved indications but account for over 85% of treatments priced at $100,000 or higher, the financial burden is pronounced.
Adjusting for production cost factors, oncology or hematology mAbs command substantially higher annual prices compared to those used in other therapeutic areas such as cardiovascular or metabolic disorders, immunology, infectious diseases or allergies, and ophthalmology. This disparity in pricing across therapeutic categories creates barriers to access and limits the potential growth of the antibody therapy market, underscoring the need for strategies to address cost concerns and enhance affordability.
Challenges in developing antibodies for complex membrane proteins
The complexities associated with developing antibodies for intricate membrane proteins like G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), ion channels, transporters, and membrane-bound enzymes present significant barriers to market growth in antibody therapy. Despite potential solutions such as antigen design, antibody-generation strategies, lead optimization technologies, and diverse antibody modalities, the inherent challenges persist.
Therapeutic antibody discovery and development technologies are evolving, but the limitations in effectively targeting difficult membrane proteins continue to hinder progress. This restriction impedes the expansion of the antibody therapy market by limiting the development of novel treatments for diseases and conditions reliant on these intricate targets. Until these challenges are effectively addressed, the full potential of antibody-based therapies in addressing a wide range of medical needs will remain unrealized, thereby constraining market growth in this sector.
Advancements in antibody therapeutics
Antibody-based therapeutics have emerged as a cornerstone in the treatment of diverse diseases, ranging from cancers to immune disorders and infectious diseases. Recent breakthroughs in antibody discovery and development present promising opportunities for the antibody therapy market. As antibody discovery progresses to preclinical development, the consideration of biophysical properties becomes paramount in determining the drug's efficacy. Notably, advancements in computer-aided methods have led to the identification of variants demonstrating superior attributes.
For instance, one variant showcased enhanced affinity, reduced aggregation propensity, lower isoelectric point (pI), improved stability, more elevated purification yield, and exceptional in vivo anti-tumor efficacy. This transformative discovery presents a promising candidate antibody for preclinical development, showcasing the potential of tailored antibodies to address unmet medical needs.
Such advancements not only enhance the efficacy and safety profile of antibody therapeutics but also expand the scope of applications across various disease categories. As a result, the antibody therapy market is poised for significant growth, fueled by the continuous innovation and optimization of antibody-based treatments to meet evolving healthcare demands. Leveraging these opportunities can lead to the development of novel therapies and improved patient outcomes, thereby driving further expansion and innovation in the market.
Advancements in antibody engineering techniques
The evolution of antibody engineering has become instrumental in the development of next-generation therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, with over 300 candidates currently undergoing clinical trials across diverse therapeutic areas. This surge in innovative therapies underscores the transformative potential of antibody engineering in revolutionizing healthcare.
Therapeutic antibody engineering encompasses a comprehensive analysis of genetic engineering approaches to optimize monoclonal antibodies for enhanced efficacy and safety. Key technologies such as single B cell antibody technology, humanization of phage display, human antibody mouse, monoclonal antibodies, and affinity maturation are at the forefront of this paradigm shift.
By leveraging these preeminent antibody engineering technologies, the antibody therapy market stands poised for substantial growth. These advancements facilitate the development of targeted and tailored therapies, addressing unmet medical needs across a spectrum of diseases. Moreover, the continuous refinement of antibody engineering techniques ensures the continual innovation and improvement of therapeutic antibody drugs, driving further expansion and adoption within the market.
The monoclonal antibodies (MABs) segment registered the maximum market share in 2024, offering targeted drug therapy by recognizing specific proteins in cancer cells. MAB therapies, engineered to mimic natural antibodies, are produced in laboratories to substitute, enhance, modify, or mimic the immune system's attack on undesired cells like cancer cells.
Monoclonal antibody therapy is increasingly prevalent, with numerous approvals for treating various cancer types and ongoing clinical trials exploring new drugs and applications. Administered mostly intravenously, MABs provide a more precise treatment option compared to others, contributing to the growth of the antibody therapy market.
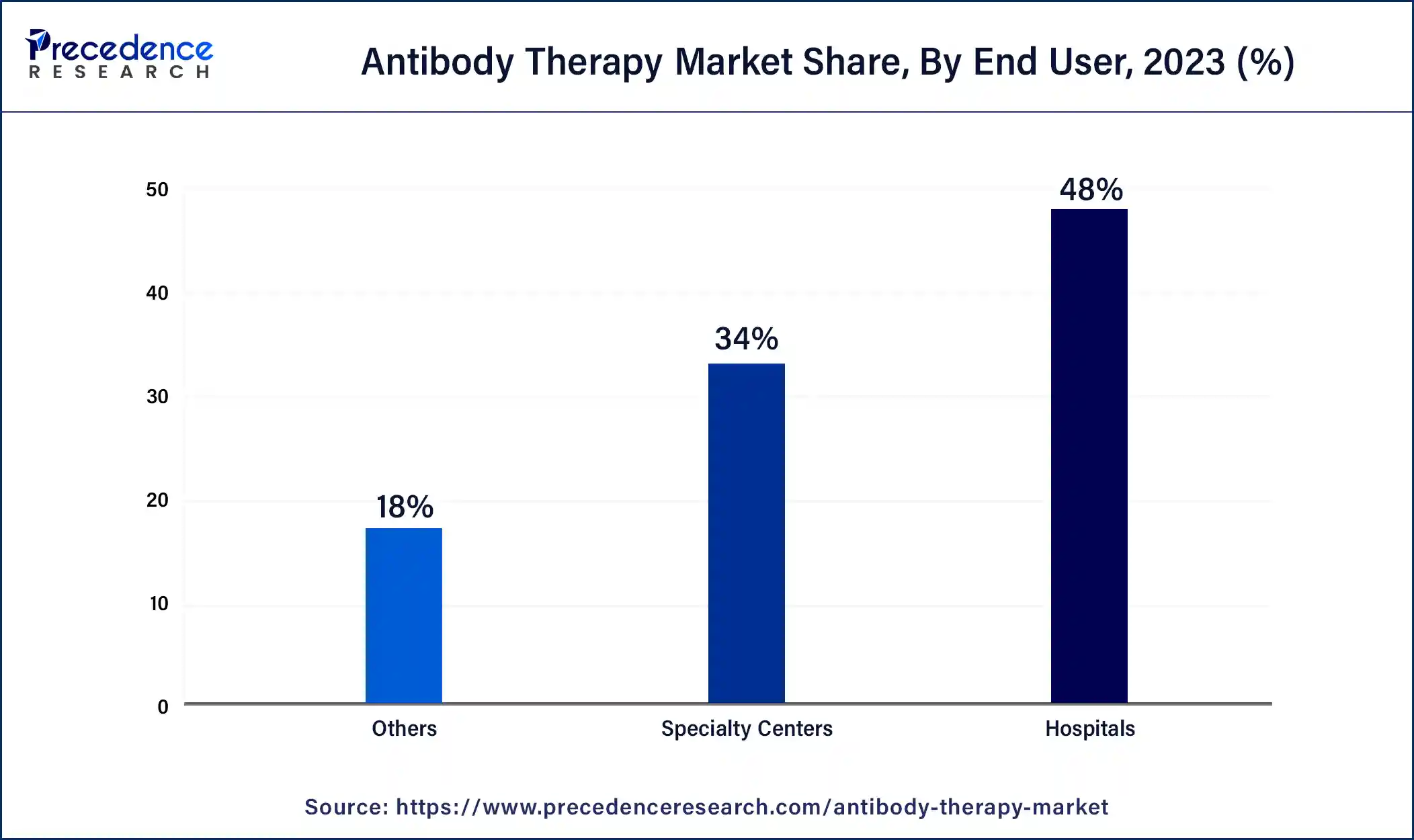
The hospital segment held the largest share within the antibody therapy market, in 2024, with fast-acting laboratory-made antibodies transitioning from seldom-used to widely adopted therapies. Doctors increasingly utilize monoclonal antibody treatment as a frontline option, particularly for eligible patients, potentially transforming treatment paradigms. Monoclonal antibodies hold the promise of averting hospitalizations among high-risk groups and curbing disease progression.
Hospital use may obviate the need for steroids and immunomodulation, thereby mitigating the risk of severe infections like mucormycosis and secondary bacterial and viral infections such as CMV. Monoclonal antibodies must possess essential biophysical properties, including high antigen binding activity, stability, and low immunogenicity, fostering growth in the antibody therapy market.
By Type
By End User
By Region
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
November 2023
September 2024
May 2025
October 2024