June 2024
The global biosimilar monoclonal antibody market size is predicted to increase from USD 13 billion in 2024, grew to USD 16.01 billion in 2025 and is anticipated to reach around USD 104.71 billion by 2034, poised to grow at a CAGR of 23.20% between 2024 and 2034. The North America biosimilar monoclonal antibody market size is calculated at USD 4.55 billion in 2024 and is estimated to grow at a fastest CAGR of 23.37% during the forecast year.
The global biosimilar monoclonal antibody market size accounted for USD 13 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 104.71 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 23.20% between 2024 and 2034.
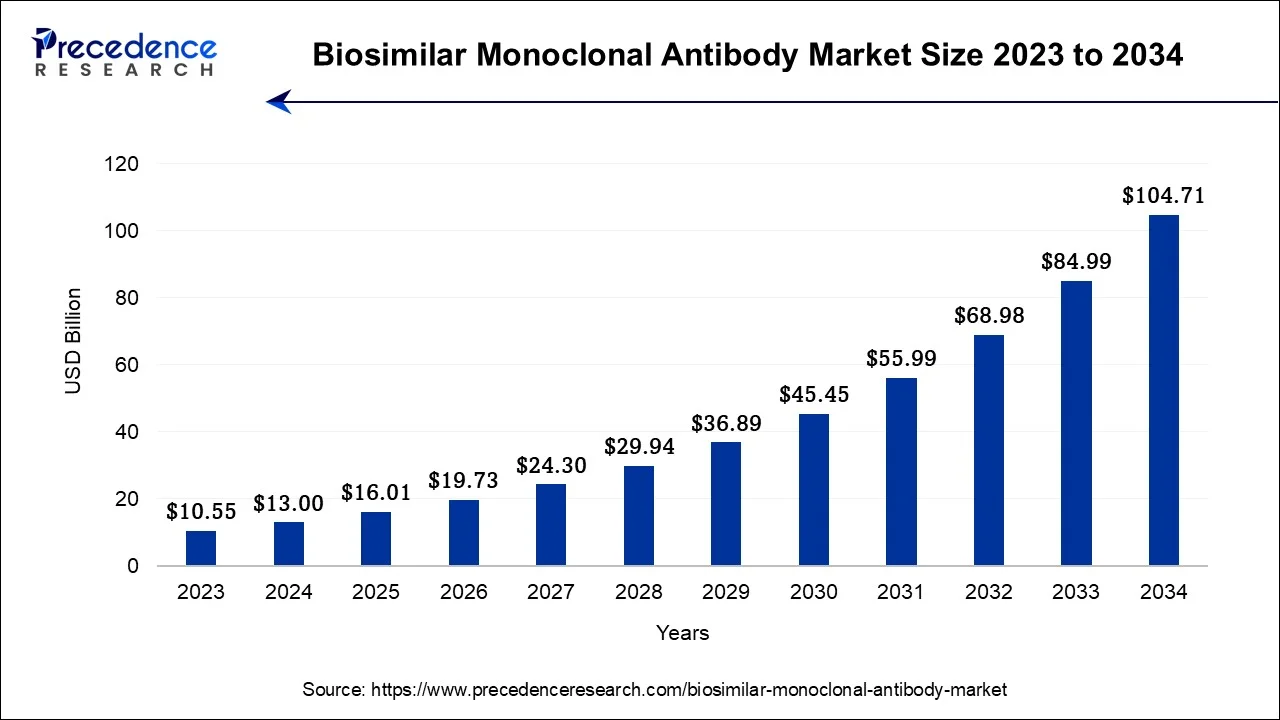
The U.S. biosimilar monoclonal antibody market size was valued at USD 3.19 billion in 2024 and is estimated to be worth around USD 26.21 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 23.44% from 2024 to 2034.
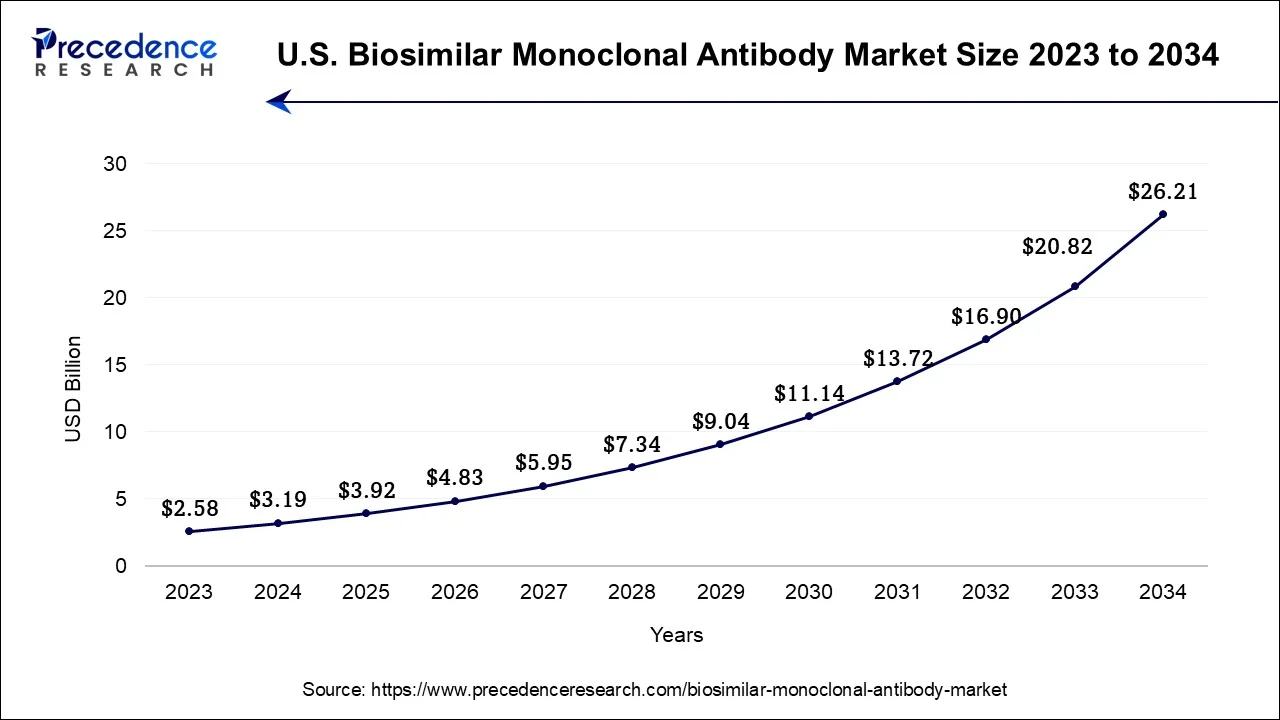
North America has held largest revenue share 35% in 2023. The dominant position of North America in the biosimilar monoclonal antibody market can be attributed to several compelling factors. The region benefits from its advanced healthcare infrastructure, a mature regulatory framework, and substantial healthcare expenditure, all of which facilitate the development and widespread adoption of biosimilars.
Moreover, a thriving research and development ecosystem, a robust presence of the pharmaceutical industry, and a growing demand for economical biologic therapies collectively bolster North America's leadership in this market. Notably, the United States, a pivotal component of the North American region, has taken proactive measures to promote biosimilar competition, reinforcing the region's prominent standing in the biosimilar monoclonal antibody market.
Asia-Pacific is estimated to observe the fastest expansion with the highest CAGR of 8.3% during the forecast period. Asia-Pacific commands a substantial growth in the biosimilar monoclonal antibody market due to several factors. The region's large population and increasing healthcare expenditures drive the demand for affordable therapeutic options, making biosimilars an attractive choice. Additionally, supportive regulatory frameworks in countries like India and South Korea facilitate biosimilar development and approval.
The presence of prominent pharmaceutical companies and a growing emphasis on biotechnology further bolster the market. Moreover, the region's rising prevalence of chronic diseases, such as cancer, creates a substantial market for biosimilar monoclonal antibodies, cementing Asia-Pacific's significant growth in this sector.
The biosimilar monoclonal antibody sector encompasses the realm of the pharmaceutical industry dedicated to the production and distribution of biosimilar monoclonal antibodies. Monoclonal antibodies serve as therapeutic proteins widely utilized in the management of various medical conditions, including cancer and autoimmune ailments. Biosimilars represent almost identical versions of already-approved monoclonal antibodies, meticulously crafted to present more economically advantageous options.
The market has witnessed substantial expansion, primarily driven by the escalating demand for economically efficient biologic therapies. Despite grappling with regulatory complexities and fierce market rivalry, the expiration of patents is anticipated to herald an influx of additional biosimilars, augmenting patient accessibility to essential treatments, encouraging competition, and potentially curbing healthcare expenditure.
The biosimilar monoclonal antibody market represents a thriving and swiftly evolving segment in the pharmaceutical domain. This niche specializes in the production and distribution of biosimilar versions of monoclonal antibodies, which serve as crucial therapeutic proteins for treating diverse medical conditions, including cancer and autoimmune disorders. Numerous noteworthy trends and catalysts for growth are shaping the industry's landscape.
One prominent growth factor propelling the biosimilar monoclonal antibody market forward is the escalating demand for economically viable biologic therapies. As healthcare costs continue their upward trajectory, biosimilars emerge as a financially sound alternative to their costly originator counterparts. The imperative is to expand patient access to essential treatments while simultaneously curbing the mounting healthcare expenses.
Observable industry trends indicate a persistent expansion in the biosimilar monoclonal antibody market, stemming from the expiration of patents for original monoclonal antibodies. This creates substantial avenues for pharmaceutical enterprises to conceptualize and introduce biosimilar alternatives. Moreover, the regulatory framework is adapting to simplify the approval process for biosimilars, thereby providing added impetus for market growth.
However, the biosimilar monoclonal antibody market is not devoid of its hurdles. The development of biosimilars necessitates substantial investments in research and development, and companies must surmount technical challenges to attain a high degree of likeness to the original monoclonal antibodies. Complexities surrounding regulations and intellectual property can prove formidable obstacles for market entry, as do the demanding clinical trials essential for approval.
In summary, the biosimilar monoclonal antibody market thrives due to the burgeoning need for economical biologic therapies and the openings created by patent expirations. While the industry continues its expansion, businesses encounter formidable challenges in navigating intricate regulatory terrain and successfully crafting top-tier biosimilars. Notwithstanding these impediments, the market is poised for sustained growth and offers promising business prospects for those equipped to confront and surmount these barriers.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Growth Rate from 2024 to 2034 | CAGR of 23.2% |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 13 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 104.71 Billion |
| Largest Market | North America |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | By Type, By Indication, and By End User |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Expired patents
The termination of patents plays a pivotal role in propelling the growth of the biosimilar monoclonal antibody market. As original monoclonal antibody patents expire, it paves the way for pharmaceutical firms to venture into the development of biosimilar alternatives. This creates a lucrative business opportunity, as biosimilar manufacturers can enter the arena, introducing competition that yields a range of essential advantages.
To begin, it intensifies market rivalry, naturally leading to reduced prices for monoclonal antibody therapies. This heightened competition exerts pressure on originator drug manufacturers to reevaluate their pricing strategies, rendering these life-saving treatments more cost-effective and accessible to both patients and healthcare systems. Secondly, the availability of biosimilars expands the choices for healthcare providers and patients alike. It empowers them to opt for treatments that are equally efficacious but more economically viable.
This augmented array of options and affordability amplifies patient access to critical therapies. In sum, the termination of patents is a fundamental driver for the growth of the biosimilar monoclonal antibody market. It facilitates heightened competition, cost-effectiveness, and accessibility, concurrently fostering innovation and advancement within the pharmaceutical sector.
Clinical trial requirements
Clinical trial prerequisites stand as a notable impediment to the expansion of the biosimilar monoclonal antibody market. Regulatory authorities mandate rigorous clinical trials for biosimilar development to confirm product safety and efficacy. These trials entail substantial resource allocation, time consumption, and financial investments. Moreover, the demanding clinical trial requirements not only extend the product development timeframe but also pose financial burdens that might deter potential manufacturers from entering the biosimilar market.
The stringent criteria can also lead to challenges in patient recruitment, as biosimilar clinical trials often necessitate larger participant pools, creating delays and recruitment difficulties. In essence, the clinical trial demands represent a formidable barrier, constraining the growth of the biosimilar monoclonal antibody market. They impose substantial costs, protracted development timelines, and can discourage new industry players from venturing into this pharmaceutical segment.
Biosimilar penetration in oncology
The introduction of biosimilars into the field of oncology has ushered in compelling opportunities within the biosimilar monoclonal antibody market. Monoclonal antibodies are pivotal in cancer treatment, providing a substantial patient base and a thriving market for these biological therapies. Biosimilars, with their cost-effective appeal, present an enticing option for healthcare systems and cancer patients grappling with the formidable financial challenges of cancer treatment.
Within this landscape, biosimilar manufacturers have the chance to develop and offer biosimilar monoclonal antibodies that cater to specific cancer types or individual patient requirements. This tailored approach can address the escalating demand for economical cancer treatments, potentially alleviating the financial burden on patients and healthcare providers.
Moreover, regulatory bodies are increasingly acknowledging the significance of biosimilars in oncology, simplifying the approval pathways and endorsing their integration into cancer care. This accommodating regulatory environment creates a conducive setting for biosimilar manufacturers to explore novel avenues, ultimately advancing patient access to life-saving oncology therapies while fostering expansion in the biosimilar monoclonal antibody market.
Impact of COVID-19
The biosimilar monoclonal antibody market experienced a dual impact from the COVID-19 pandemic. Supply chain disruptions and regulatory delays posed challenges to the market, affecting manufacturing and distribution. Simultaneously, the pandemic underscored the importance of cost-effective biologic therapies, spurring increased interest in biosimilars. Healthcare systems, strained by the pandemic's financial fallout, sought affordable treatment options, driving the adoption of biosimilars. While the full, long-term ramifications remain uncertain, the pandemic has emphasized the need for resilient supply chains and reaffirmed the role of biosimilars in delivering economical healthcare solutions.
According to the type, the infliximab segment has held 32% revenue share in 2023. The infliximab segment holds a substantial share in the biosimilar monoclonal antibody market due to several key factors. Infliximab is a widely used monoclonal antibody for treating various autoimmune diseases, making it a significant part of the market. Additionally, patents for the originator infliximab have expired, creating a prime opportunity for biosimilar manufacturers. Its well-established efficacy and demand, coupled with cost-saving benefits, have driven healthcare providers and patients to favor infliximab biosimilars, thereby securing a significant market share within the biosimilar monoclonal antibody segment.
The adalimumab segment is anticipated to expand at a significantly CAGR of 24.7% during the projected period. The Adalimumab sector's commanding growth within the biosimilar monoclonal antibody market can be attributed to multiple compelling factors. Most notably, this specific monoclonal antibody, instrumental in addressing autoimmune maladies like rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease, has seen a series of patent expirations, prompting a surge in biosimilar development. Its substantial cost and widespread utilization in treatment regimens have fueled the demand for more budget-friendly biosimilar alternatives. Consequently, patients and healthcare systems alike are increasingly turning to Adalimumab biosimilars to alleviate the financial strains associated with treatment, thereby establishing this segment as a dominant growth leader in the biosimilar monoclonal antibody market.
In 2023, the oncology segment had the highest market share of 44% on the basis of the indication. The dominance of the oncology sector within the biosimilar monoclonal antibody market can be attributed to the extensive use of monoclonal antibodies in cancer therapy. Cancer, being a widespread and life-threatening disease, contributes to a substantial patient base seeking these treatments. The substantial expenses linked with oncology care have accentuated the attractiveness of biosimilars, as they provide substantial cost savings while upholding therapeutic effectiveness. Moreover, regulatory endorsement of biosimilars in the oncology field, combined with the potential to customize treatments for specific cancer types, has further elevated their significance in this market, establishing oncology as a pivotal driving force in the adoption of biosimilar monoclonal antibodies.
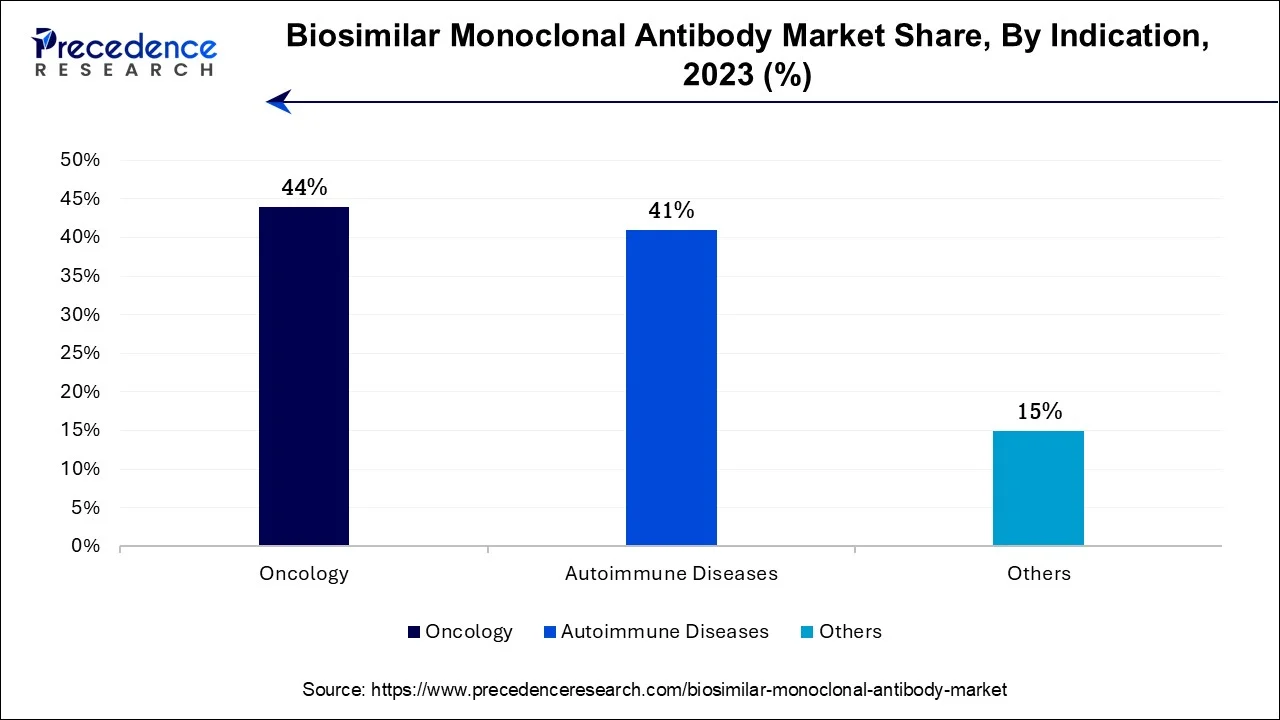
The autoimmune diseases segment is anticipated to expand at the fastest rate over the projected period. The dominant growth of the autoimmune diseases segment in the biosimilar monoclonal antibody market can be attributed to several pivotal factors. These conditions, marked by immune system irregularities, frequently necessitate monoclonal antibody therapies. Biosimilars are attractive in this context due to their cost-efficiency when compared to the high-priced original biologics. Given the rising incidence of autoimmune diseases and the imperative for more affordable treatment alternatives, the demand for biosimilar monoclonal antibodies in this therapeutic domain has experienced remarkable growth, establishing their significant growth in the market.
In 2023, the hospital segment had the highest market share of 49% on the basis of the end user. Hospitals dominate the biosimilar monoclonal antibody market due to several reasons. Firstly, hospitals are primary healthcare providers, with a substantial patient base requiring advanced treatments, including monoclonal antibodies. Secondly, they have the infrastructure and skilled medical personnel to administer these complex therapies.
Additionally, hospitals often have stronger negotiation power with drug suppliers, allowing them to access cost-effective biosimilars. The inclination towards centralized purchasing and administration in hospital settings further contributes to their significant market share, as they can efficiently manage and control the usage of biosimilar monoclonal antibodies.
The others segment is anticipated to expand at the fastest rate over the projected period. The "Others" segment holds a substantial share in the biosimilar monoclonal antibody market because it encompasses diverse end users such as research institutes, academic institutions, and small-scale healthcare providers, making it a broad category. These end users often favor biosimilars due to their cost-efficiency and accessibility.
Furthermore, smaller healthcare facilities and research entities typically have budget constraints that drive them to opt for cost-effective biosimilars. As a result, the "Others" segment, representing a wide range of users, collectively contributes significantly to the biosimilar monoclonal antibody market, emphasizing the versatility and economic appeal of these biologic therapies.
Segments Covered in the Report
By Type
By Indication
By End User
By Geography
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
June 2024
October 2024
September 2024
October 2024