February 2025
The global graphite electrode market size accounted for USD 16.13 billion in 2024, grew to USD 16.84 billion in 2025, and is expected to be worth around USD 24.81 billion by 2034, registering a healthy CAGR of 4.4% between 2024 and 2034. The Asia Pacific graphite electrode market size is predicted to increase from USD 7.42 billion in 2024 and is estimated to grow at the fastest CAGR of 4.51% during the forecast year.
The global graphite electrode market size is expected to be valued at USD 16.13 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 24.81 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 4.4% over the forecast period from 2024 to 2034.
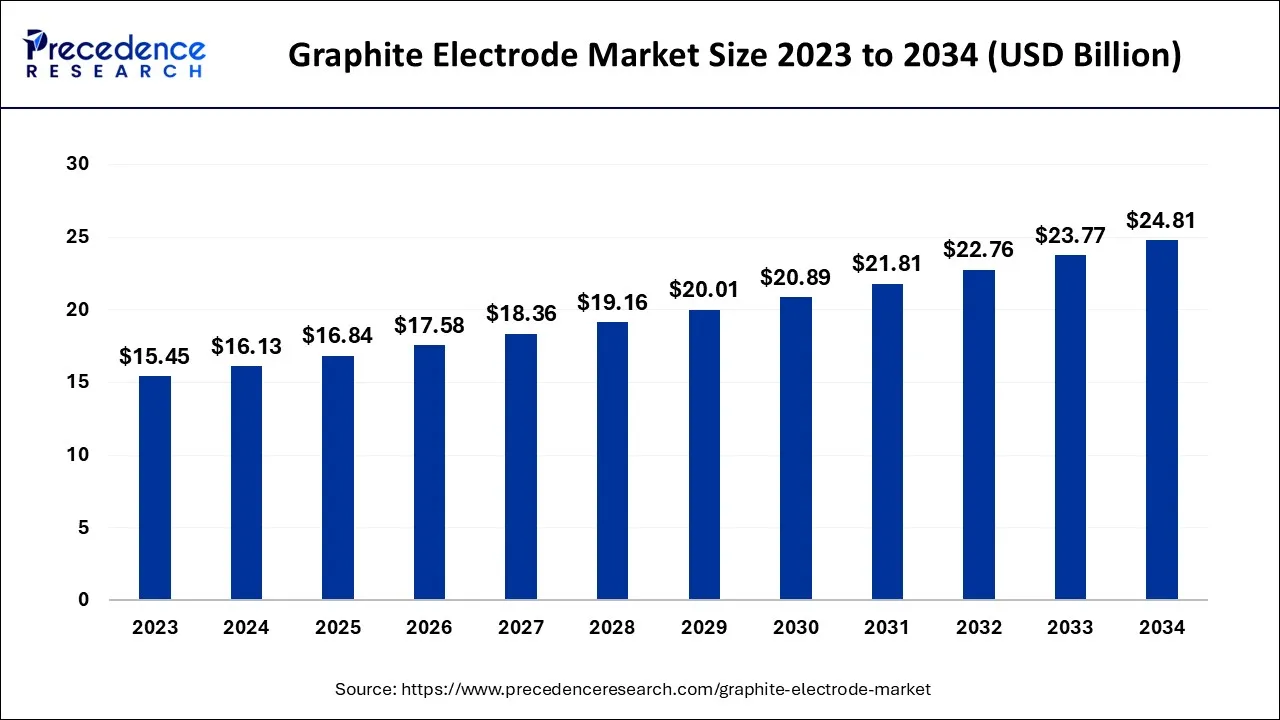
The Asia Pacific graphite electrode market size is exhibited at USD 7.42 billion in 2024 and is projected to be worth around USD 11.54 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 4.51% from 2024 to 2034.
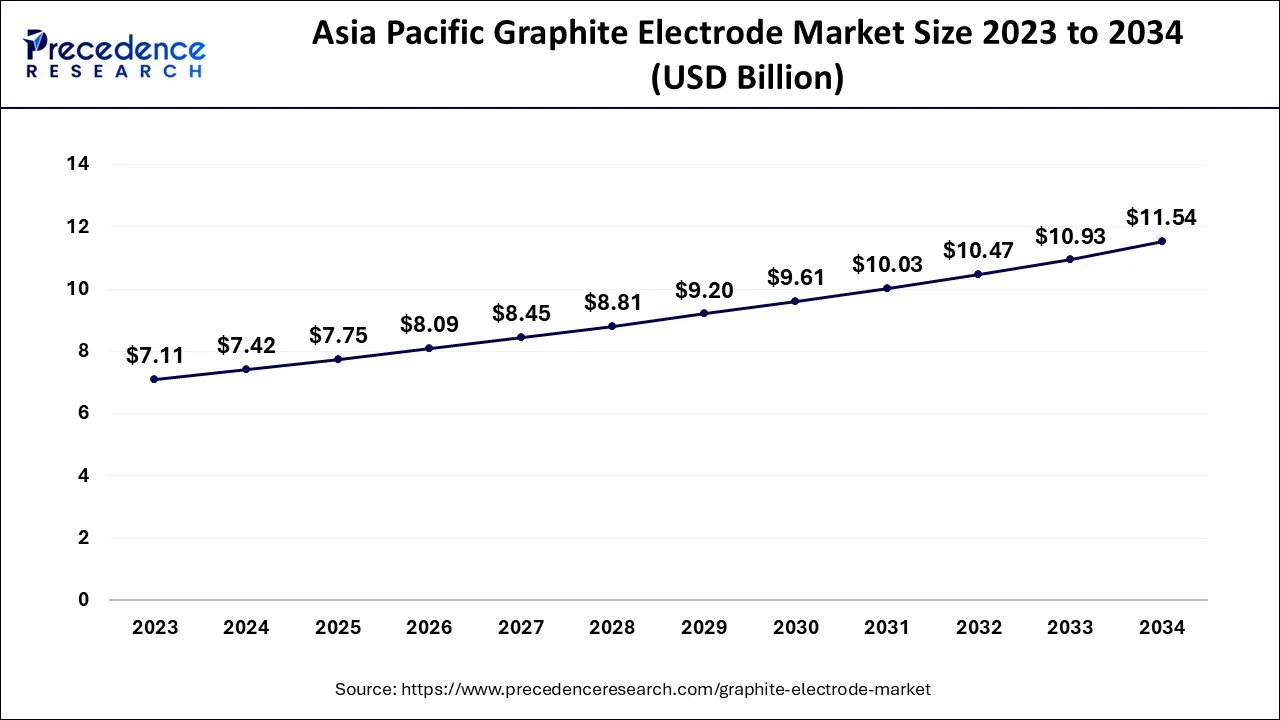
Asia Pacific is expected to dominate the market during the forecast period. The growth in the region is attributed to the increasing steel industry in the countries like China and India. Electrodes made of graphite are a crucial part of the manufacturing process for steel. They serve as the primary source of heat in the electric arc furnaces used to smelt down scrap metal and produce new steel. The rapid infrastructure development in these nations is increasing the need for steel, which will ultimately fuel market expansion over the projection period. For example, the secondary research indicates that China set a quota of RMB 3.65 trillion (US$573 billion) in SPBs for local governments in 2021, of which 97% had been issued by December 15, 2021.
According to a newsletter (link in Chinese) published on the website of the central government, all of the funds obtained through the issuing of SPBs were applied to "key areas determined by the Party Central Committee and the State Council". The infrastructure sectors for transportation, local government, and industrial parks received roughly half of the cash raised. Another 30% went to social programs including affordable housing, health and sanitation, education, senior care, culture, and tourism, while another 20% went to industries like forestry, agriculture, irrigation, energy, and rural-urban cold chain logistics. Thus, the aforementioned facts support the market growth during the forecast period.
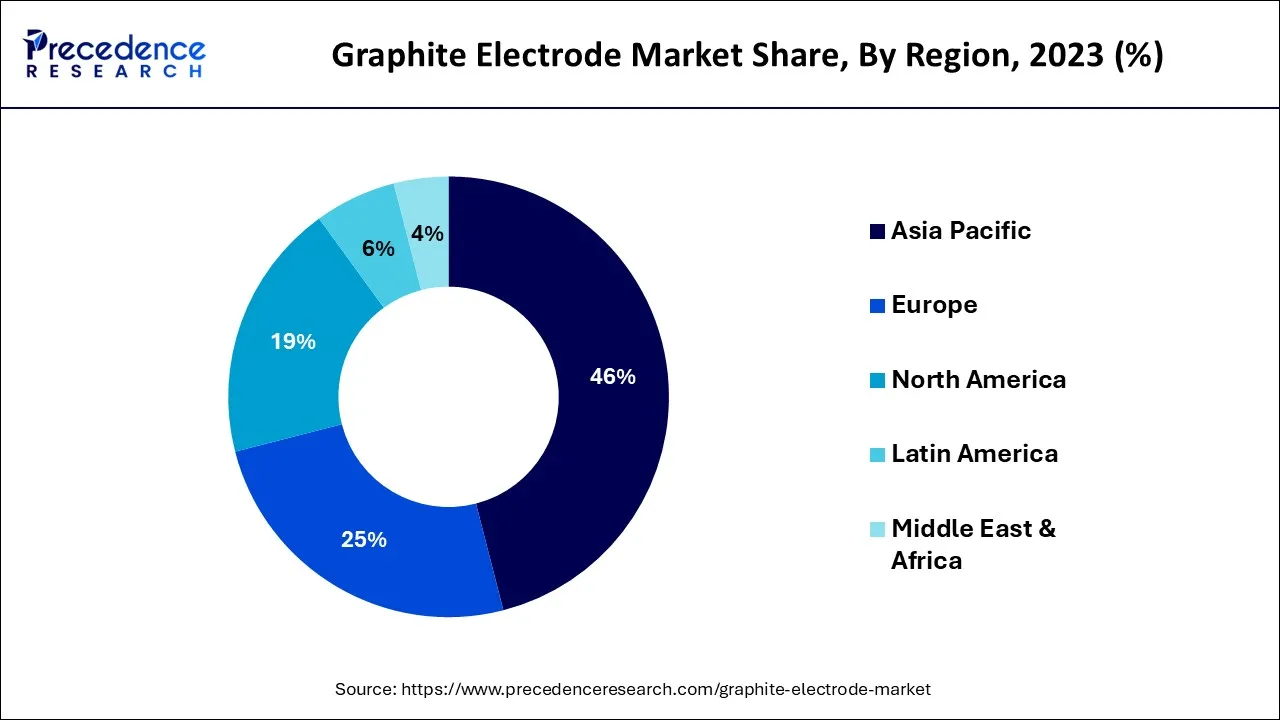
North America is expected to grow significantly during the forecast period. The regional growth is owing to the increasing steel production. According to the estimate, the American iron and steel industry contributed more than $520 billion in revenue and nearly two million jobs to the U.S. economy in 2017. In terms of pay and benefits, these workers made almost $130 billion. Federal, state, and municipal taxes collected by the sector totaled $56 billion.
The two ends of an electric current's input or output are made of a conductive material called a graphite electrode. And the material used to create this kind of conductive media is graphite. In order to create the thermally melting steel during the electric furnace steelmaking process, electricity must be converted into heat. Copper electrodes were the only conductive materials employed in the past. As technology advanced, copper electrodes were increasingly replaced by graphite electrodes. The graphite electrode has a higher high-temperature resistance than the copper electrode, which is necessary for inserting it into the furnace, by a factor of three to four.
A type of material with the characteristics of electrical conductivity, high-temperature resistance, and corrosion resistance and it is simple to produce is graphite electrode. In the fields of metallurgy, electrochemistry, the chemical industry, etc., graphite electrode is frequently utilized. It is a kind of conductive substance that electric furnaces utilize to make steel. The primary ingredients are petroleum coke and pitch coke, with coal tar pitch serving as the binder. These components are then combined in a certain ratio. Graphite electrode, also known as artificial graphite electrode, is a type of conductive material made of high temperature resistant graphite that is manufactured through calcination, batching, graphitization, and mechanical processing. Natural graphite electrodes do exist, although they are quite uncommon.
According to the National Bureau of Statistics, China produced 94.85 million tons of crude steel in August 2020, an increase of 8.4% from the same month in 2019.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 16.13 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 24.81 Billion |
| Growth Rate from 2024 to 2034 | CAGR of 4.4% |
| Largest Market | Asia Pacific |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | By Electrode Grade, By Raw Material, and By Application |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America and Middle East & Africa |
Increasing global steel production
Despite the COVID-19 pandemic, steel output is increasing at a healthy rate worldwide. Due to its significant demand across a variety of end-use industries, including construction, automotive, appliances, etc., steel production is progressing throughout multiple locations despite being one of the pandemic's most severely affected industries. The Asia-Pacific region produced the crudest steel in 2020, totaling 1388.7 million tonnes, accounting for 1878 million tonnes worldwide, according to the World Steel Association's 2021 Stainless Steel Figures report. In 2020, the Middle East and Europe respectively produced 139.2 million tonnes and 45.4 million tonnes of crude oil. According to the World Steel Association's 2021 research, the global steel production market is already displaying a good trend. This will lead to a high demand for graphite electrodes, which will propel the graphite electrodes market over the forecast period.
Stringent regulations
China has consistently contributed to the market for graphite electrodes and has the greatest global steel production and consumption. However, the region's steel industry has expressed concern about the government laws surrounding industrial pollution. The government's industrial pollution control measures have forced China to close 300 million tonnes of out-of-date, highly polluting steel manufacturing capacity, slowing down steel production during the previous few years, according to Graphite India Limited's Corporate Presentation August 2020 report. As a result, China's environmental restrictions may continue to have an impact on the country's steel output, which would ultimately limit the use of graphite electrodes and the market's expansion in the years to come.
Increasing demand for electric vehicles
The massive global production of electric vehicles is anticipated to be a major factor in the growth of the market for graphite electrodes. More lithium-ion batteries will be required by more electric vehicles, which will ultimately increase the demand for more graphite electrodes. The main component of the anode in lithium-ion batteries is graphite material. In China, the market for electric and alternative energy vehicles is expanding quickly. The China Association of car Manufacturers (CAAM) has reported that the Chinese car industry would continue to grow, with the demand for NEVs (New Energy Vehicles) expected to increase over the next several years. Similar to this, it is projected that in the years to come, the region of Europe would see a good trend in the electrically chargeable vehicle (EV) and hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) categories.
According to estimates from the European Automobile Manufacturers Association (ACEA), the market share of electrically-chargeable vehicles increased from 3% in 2019 to 10.5% in 2020. In a comparable way, hybrid electric vehicle sales accounted for 11.9% of all automobile sales in 2020 as opposed to 5.7% in 2019. By increasing the manufacture of lithium-ion batteries, this development in the electric vehicle market will accelerate the growth of the graphite electrodes market throughout the projected period.
Based on the electrode grade, the global graphite electrode market is segmented into ultra-high power, high power and regular power. The ultra-high power electrode grade accounted for the largest market share in 2023 and is expected to continue the same pattern during the forecast period. Due to its frequent use in big electric arc furnaces for the production and refinement of steel, the ultra-high power graphite electrode is gaining popularity. These graphite electrodes are a better choice than other graphite electrodes because they have strong characteristics such high temperature resistance, crack resistance, durability, and superior quality.
Furthermore, due to its high production efficiency and capacity to lower overall production costs, this type of electrode is widely utilized in electric arc furnaces. Due to UHP graphite electrodes' excellent properties, steel producers all over the world are turning to them to produce long-lasting, high-quality steel and ultimately make a greater profit. For instance, the largest provider of ultra-high-powered graphite electrodes in the world, Showa Denko, stated in a 2020 report that its global graphite electrode business totaled a staggering yen 300 billion (USD 2.73), of which the ultra-high power graphite electrode segment has generated 30% share. The corporation wants to grow all of its top businesses, which include those that make graphite electrodes, by the year 2025. This will increase the market share of ultra-high power graphite electrodes. Thus, this is expected to drive the segment growth over the forecast period.
Based on the application, the global graphite electrode market is divided into electric arc furnace, ladle furnace and others. The electric arc furnace is expected to dominate the market during the forecast period. Steel is made by melting steel scrap, directly reduced iron (DRI), hot briquetted iron (HBI), or solid pig iron in an electric arc furnace (EAF). Electricity provides the necessary force to melt the feedstock on the EAF path. In order to melt steel scrap, graphite electrodes are generally utilized in the electric arc furnace (EAF) steelmaking process. Graphite is used to make electrodes because of its resistance to high temperatures.
In EAF, the electrode tip can reach 3,000o F, which is just half as hot as the surface of the sun. Electrodes can be anywhere between 75 mm and 750 mm in diameter and up to 2,800 mm in length. UHP electrodes (generally 350 mm and larger) and HP and UHP electrodes (typically 400 mm and smaller) are frequently used in electric arc furnaces (EAF) in steel mills and iron and steel foundries, respectively. Thus, this is expected to drive the segment growth during the forecast period.
Market Segmentation:
By Electrode Grade
By Raw Material
By Application
By Geography
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
February 2025
January 2025