January 2025
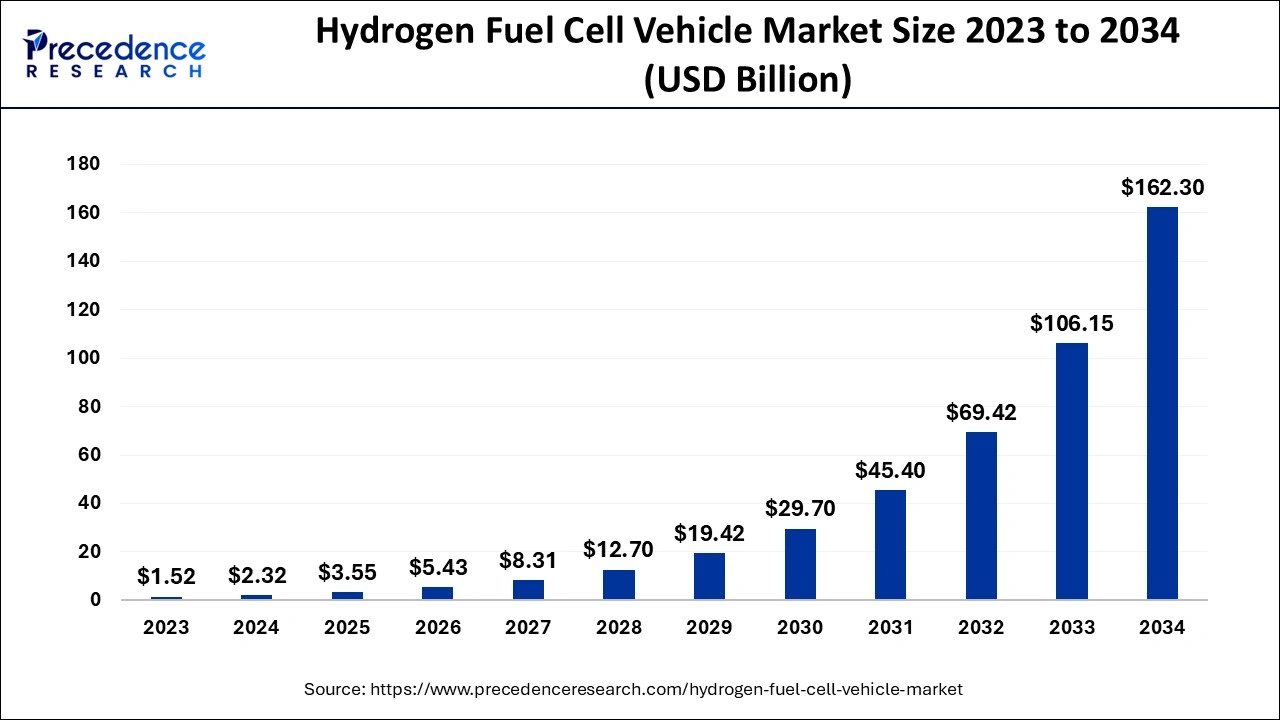
The global hydrogen fuel cell vehicle market size accounted for USD 2.32 billion in 2024, grew to USD 3.55 billion in 2025 and is predicted to surpass around USD 162.30 billion by 2034, representing a healthy CAGR of 52.90% between 2024 and 2034.
The global hydrogen fuel cell vehicle market size is estimated at USD 2.32 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 162.30 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 52.90% from 2024 to 2034.
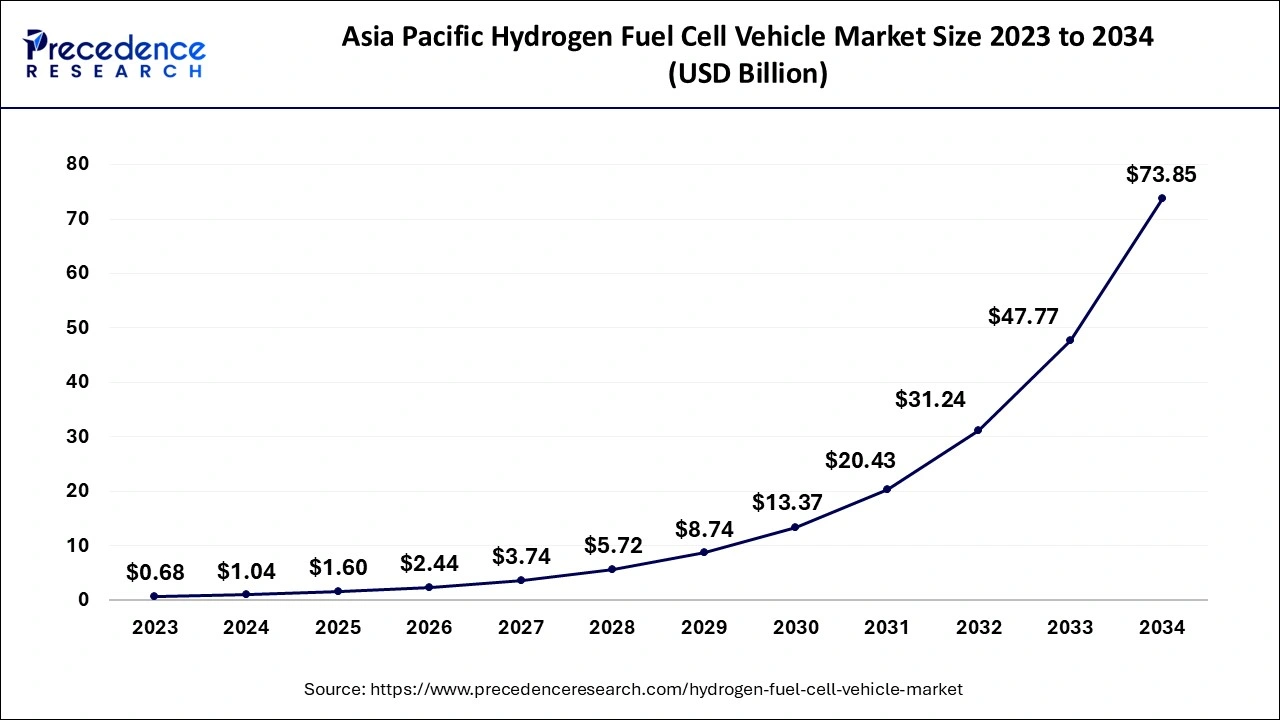
The Asia Pacific hydrogen fuel cell vehicle market size is evaluated at USD 1.04 billion in 2024 and is predicted to be worth around USD 73.85 billion by 2034, rising at a CAGR of 53.14% from 2024 to 2034.
The market for autonomous fuel cells in the Asia Pacific is anticipated to be the largest over the projected period, followed by Europe and North America. The market is being driven by the strong demand for fuel cell vehicles for both public and private transportation as well as the large share of passenger vans in overall vehicle manufacturing.
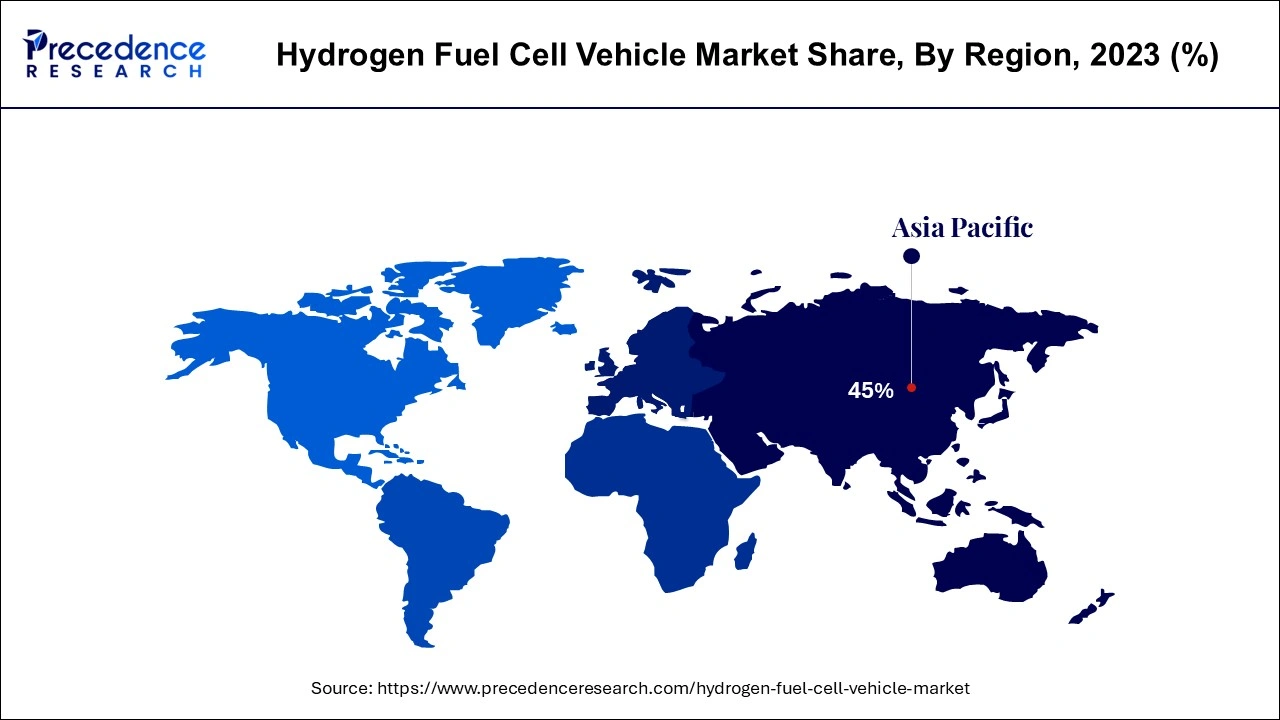
Additionally, Asia Pacific is the greatest market for green technology in the world, with Japan, China, and South Korea now having the largest markets there for fuel cells. Several companies intend to make significant investments to increase their production capacity and market fuel cell vehicles. For instance, Hyundai intends to spend USD 6.7 billion to boost fuel cell output and multiply its manufacturing capacity by more than 200 by 2033.
One of the most widely used fuels in the world right now is hydrogen, and many individuals are anticipating that it will accompany electric cars. With the restricted manufacturing of medium commercial vans from Peugeot, Citroen, and Opel, Stellantis has launched in the era of hydrogen-powered vans. Electricity is generated by using hydrogen to operate a hydrogen fuel cell. Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle possess high potential to reduce emissions related to the transportation sector. They do not produce any greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions during vehicle operation.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and National Highway Traffic Safety Administration collaboratively created the US GHG emissions and fuel efficiency standards for heavy-and medium-duty vehicles in North America (NHTSA). The Energy Independence and Security Act (EISA) of 2007 gave the NHTSA the authority to establish fuel consumption guidelines, while the Clean Air Act gave the EPA the power to establish a GHG emissions program. The GHG program contains guidelines to regulate hydrofluorocarbon leaks from air conditioning systems, as well as CO2 emission requirements, and N2O and CH4 emission standards.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 2.32 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 162.30 Billion |
| Growth Rate from 2024 to 2034 | CAGR of 52.90% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | Vehicle Type, Technology, and Geography |
Accessibility to technologically advanced and user-friendly products
Government initiatives for the development of hydrogen fuel infrastructure
Highly reactive and flammable gas
The rise in environmental concerns
An expensive initial investment in infrastructure
COVID-19 Impact on the Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle Market
The COVID-19 pandemic disrupted the whole environment, which led to a worldwide halt in new automobile sales and manufacturing. Original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) had to wait until the lockdowns were removed which alter the amount of production. The automobile sector relies heavily on capital investment and regular finance to maintain operations. Due to this, production during the pandemic's early months halts, and this result in a decline in demand. This has a statistically significant impact on Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEV) producers and automobile fuel cell manufacturers.
The market suffered tremendously from a shortage of raw material supplies, a lack of workforce for manufacturing sites, and a lack of a good business strategy execution process as a result of the global lockdown and closure of manufacturing facilities. However, the industry is anticipated to expand steadily in the post-pandemic period due to rising petrol prices and growing demand for environmentally friendly automobiles.
Based on the vehicle, the Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle market is segmented into passenger vehicles and commercial vehicles. Four-wheeled vehicles that are used to transport products are known as Commercial vehicles. Road vehicles classified as commercial vehicles are either used to transport passengers, cargo, or both. Buses, trucks, vans, and other similar vehicles fall under this category. Commercial vehicles are an essential component of every economy since they are crucial for the movement of both people and goods.
A passenger vehicle is basically a road vehicle such as a car, truck, or van, designed to carry people instead of goods. Passenger vehicle Manufacturers have created a niche for targeting the country's middle-class population with reasonable prices, quality features, tiny sizes, and simple financing options. For instance, Global automotive production declined by 16% globally to less than 78 million vehicles, equivalent to sales levels in 2010, according to the International Organization of Motor Vehicle Manufacturers (OICA).
Based on Technology, the hydrogen fuel cell vehicle market is segmented into proton exchange membrane fuel cell, phosphoric acid fuel cells, and others. The majority of market share advancements for fuel cell technology in 2023 were contributed by proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFC), and this trend is anticipated to continue over the projected period. Polymer electrolyte is used in PEMFC to conduct protons. Perfluorosulfonic acid (PFSA) polymer, like Nafion®, is a typical PEMFC electrolyte that has excellent proton conductivity, high chemical stability, good mechanical strength, and great flexibility.
Liquid phosphoric acid is used in phosphoric acid fuel cells (PAFCs) as the electrolyte, while platinum catalyst-enhanced porous carbon electrodes serve as the electrode material. Solid oxide fuel cells don't require expensive catalysts like ruthenium because they can operate at high temperatures. The most typical use for solid oxide fuel cells is in stationary applications.
By Vehicle Type
By Technology
By Geography
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
January 2025
January 2025
January 2025
January 2025