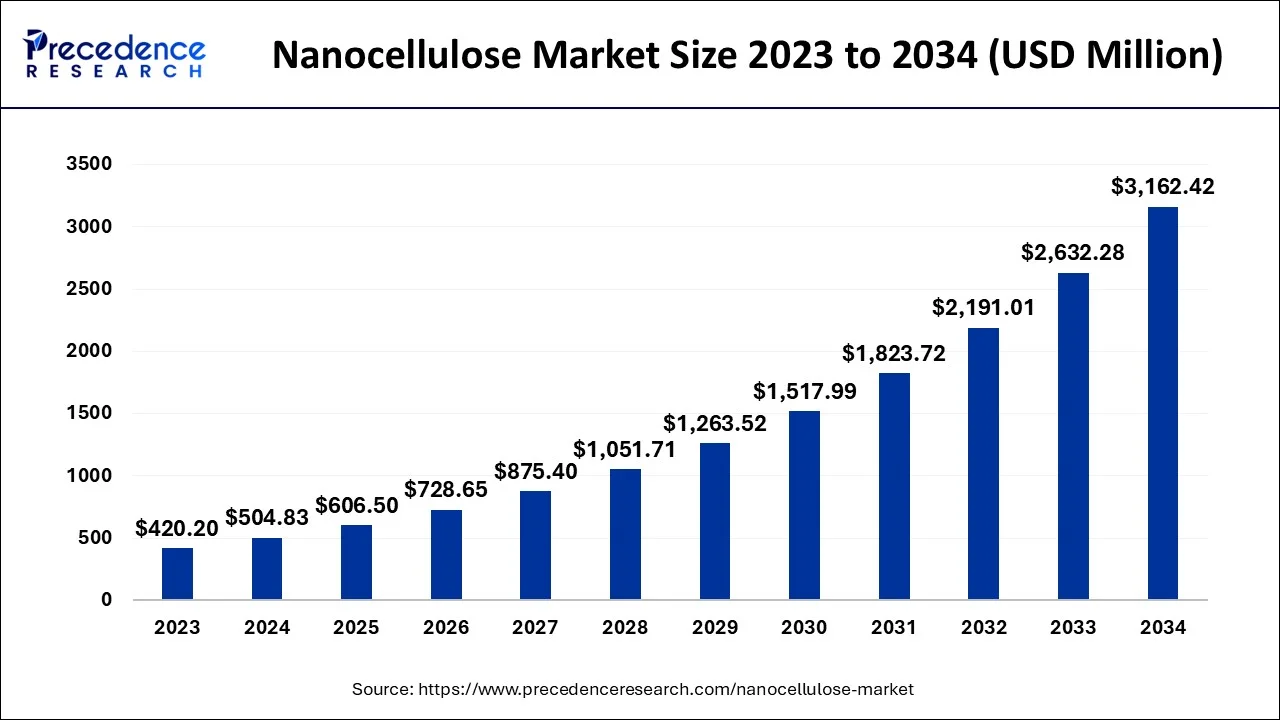
The global nanocellulose market size accounted for USD 504.83 million in 2024, grew to USD 606.5 million in 2025 and is predicted to surpass around USD 3162.42 million by 2034, representing a healthy CAGR of 20.14% between 2024 and 2034.
The global nanocellulose market size is estimated at USD 504.83 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 3162.42 million by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 20.14% from 2024 to 2034.
The Europe nanocellulose market size is estimated at USD 181.74 million in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 1154.28 million by 2034, rising at a CAGR of 20.29% from 2024 to 2034.
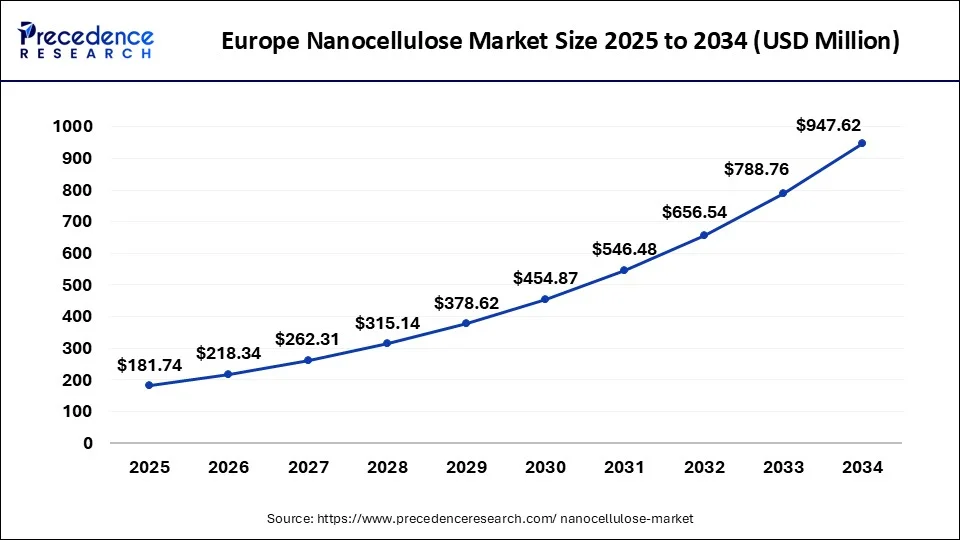
In terms of regions, the Europe is expected to dominate the market during the projected period owing to the growing demand for paper and pulp applications and huge capital investment in R&D of Nanocellulose substances in this region. In Europe, product innovation projects have been financed and supported by both the commercial and public sectors, and these influencing factors are expected to boost the global Nanocellulose market growth during the forecast period.
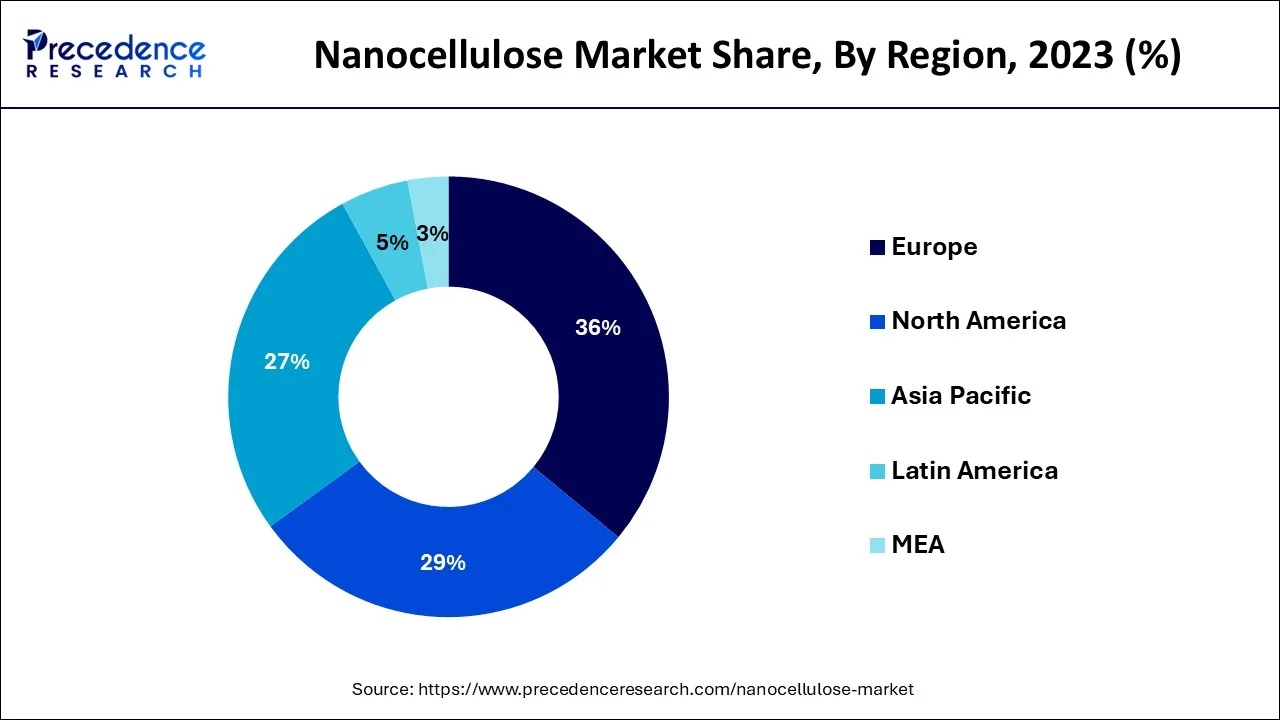
On the other hand, the Asia Pacific market is anticipated to expand at a rapid pace during the forecast period owing to the growth of the automotive, composites, and packaging industries. Moreover, there is a gradual increase in the middle-class population and a rising number of newly purchased lightweight cars. In this region, there are cheap sources of raw materials, labor, and low manufacturing costs are the most influencing drivers for the region's growth during the forecast period. However, North America is expected to experience a moderate increase in the Nanocellulose market owing to the high potential for consumption and expanding production capabilities.
Nanocellulose is nanostructured cellulose. It can be used to create Nanocellulose fibrils from wood-based materials. Nanocellulose is the elementary building block of natural cellulose.
Nanocellulose is light in weight and of solid material. It consists of the property of certain kinds of gels or fluids that are generally viscous in normal conditions. It is extensively used in a wide range of applications from food, pharmaceuticals, medical industries, and children’s toys. It has the capability to replace several petrochemical-based products.
It occurs naturally and the material is isolated from the cellulose of wood, various plants, bacteria or algae. Nanocellulose can also be separated from natural fiber through the method of acid hydrolysis resulting in hard nanoparticles. Highly crystalline nanocellulose is made from various cellulosic waste biomass, such as microorganisms, crops, and organic waste. It includes the properties such as high tensile strength and biocompatibility which appeals to an extensive range of markets, from construction to medical to aircraft. Nanocellulose is commonly classified as cellulose nanofibers (CNF), cellulose Nanocrystals (CNC), and bacterial Nanocellulose (BNC). These are being generated in various ways. These three major varieties differ in physio-chemical properties from size to size. Production of commercial Nanocellulose is cellulose nanofibers synthesized on a significant scale in Japan.
Nanocellulose is being used in several applications such as biomedical products, catalytic substrates, electronic component templates, electrochemically active polymer, composite, packaging, cosmetics, ultra-capacitor, pharmaceuticals, and batteries. The most crucial application is it is being used as an additive to produce a strong paper. The growing demand for nanocellulose material is due to its biodegradability and compatibility. Nanocellulose applications related to the fields of biomedical engineering and material science due to their exceptional mechanical properties including optical properties and tailorable surface chemistry are driving the demand for nanocellulose. There are mainly two major types of nanocellulose including cellulose nanofibrils and cellulose nanocrystals. The unique properties such as low density, high tensile strength, and a high degree of thermal stability are spurring the demand for nanocellulose for the end-user industries.
The primary growth of the global nanocellulose market is driven by the rapid expansion of the packaging sectors and pharmaceutical sectors. The major competitors in the nanocellulose market use research and development as one of their most important strategies for the growth of the industry's potential applications.
The surging demand for nanocellulose materials is due to their biodegradability and compatibility. Extensive support and funding by governments around the world are expected to boost the nanocellulose market. The government of Canada, the U.S, Australia, Sweden, and Japan have initiated several research as well as technology projects to promote the production of nanocellulose on the pilot and commercial scales. The mission P3 Nano, initiated by the governments of the Canada and U.S with the aim to encourage manufacturers to strategize their business through public-private partnerships is expected to drive the nanocellulose market. The immense potential of nanocellulose to be used in many industrial applications including viscosifiers, composites, and rheology modifier are anticipated to accelerate the growth potential for the nanocellulose market. The growth is also driven by the healthcare applications such as antimicrobial film, bio-barriers, sanitary napkins, bio-polymers, tampons, and wound dressing owing to enhanced absorbent features. There is an exponential growth in the oil and gas industry in North America, the rapidly growing personal care industry in the Asia Pacific, and an increasing demand for eco-friendly paints, composites, and coatings.
Impact of COVID-19 on the Global Nanocellulose Market
The global Nanocellulose market had a mixed impact on the covid-19 pandemic. It impeded global industrial supply chains and distribution channels, as various governments around the globe implemented lockdowns and bans on logistics. The nanocellulose market was hampered by the lack of supply of raw materials and the decrease in the demand for end-use applications. Several nations have witnessed a decline in the demand for oil & gas due to stringent restrictions of government on travel and logistics. The severe restrictions on construction activities reduced the demand for cement as well as other composite materials.
COVID-19 offered unpredicted possibilities for the pulp and paper manufacturers such as the increased demand for food packaging products, personal hygiene paper products, food packaging products, medical specialty papers, corrugated packaging materials, and others. The increased demand was experienced by the nonwoven & textiles industries due to the high utilization of products, such as sanitation tissue, masks, and others.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 504.83 Million |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 3162.42 Million |
| Growth Rate from 2024 to 2034 | CAGR of 20.14% |
| Pulp & Paper Board Segment Share in 2023 | 30.6% |
| CNF Type Segment Share in 2023 | 54.1% |
| Segments Covered | Product, Application, Region |
Market Expansion Options for End-use Industries
The natural nanomaterial is featured by stiffness, strength, and high surface area. The nanocellulose market continues to make some striking advances over the decades on the back of technological strides in extraction processes. Suitable environmental friendliness is one of the major underpinnings of a rise in research interest in nanocellulose. The market is evolving from the rise in industry investments for exploring new applications of nanomaterial.
Many of the market applications of the research organizations and industry players are the use of nanocellulose in making renewable textiles, nanocomposite materials, and biomedical products. The rise in the development of petroleum-based polymers has gained momentum for the expansion of opportunities in the nanocellulose market. The surging number of research in seeking industrial applications of lignin-based carbon materials is one of the key trends spurring investments by various industries. Some of the applications where carbon-based materials are resuming new horizons are textiles and papers. In recent months, the market has gained some momentum, with the growth in optimism in many of the emerging economies. The chemical companies have also to a large extent sought new expansion paths by altering their consumer propositions and pivoting on strategic alignments.
Continuous growth in the food & beverage, healthcare, and paper & pulp industry
The unavailability of appropriate instrumental infrastructure
Technological advancement offers significant opportunities
Based on product, the global Nanocellulose market is divided into micro fibrillated cellulose & nano fibrillated cellulose, cellulose nanocrystals or cellulose nanofibers, bacterial cellulose, and others. The microfibrillated cellulose & nanofibrillated cellulose segment is expected to expand at a robust growth rate during the forecast period owing to their nano size and capacity to create a strongly entangled impermeable network. It is gaining more popularity because of its features such as high yield, high particular surface area, ease of preparation, and strength properties. The bio-based nanomaterial has been extensively utilized in several nanocomposites because of its excellent strengthening capability.
On the basis of application, the global nanocellulose market is segregated into pulp & paper, composites manufacturing, paints & coatings, electronics sensors, food and beverage, biomedical & pharmaceuticals, composites, and others. The Pulp & Paper segment is projected to register a considerable CAGR during the forecast period owing to its high utilization application of Nanocellulose as a papermaking ingredient to make stronger, lighter paper and board associated with lower production costs. It makes paper with enhanced qualities such as less transparency, less porosity, and better printing quality.
Nanocellulose is commonly used in paper products as it increases the bonding strength between the two fiber layers and acts as a membrane without permeability in grease-proof papers. Nanocellulose also helps in scaling up the retention properties of materials along with increasing the dry and wet strength of paper and board products. Extensively increasing the usage of sensors in industrial and other applications is primarily driving the growth of the segment.
By Product
By Application
By Geography
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client