April 2025
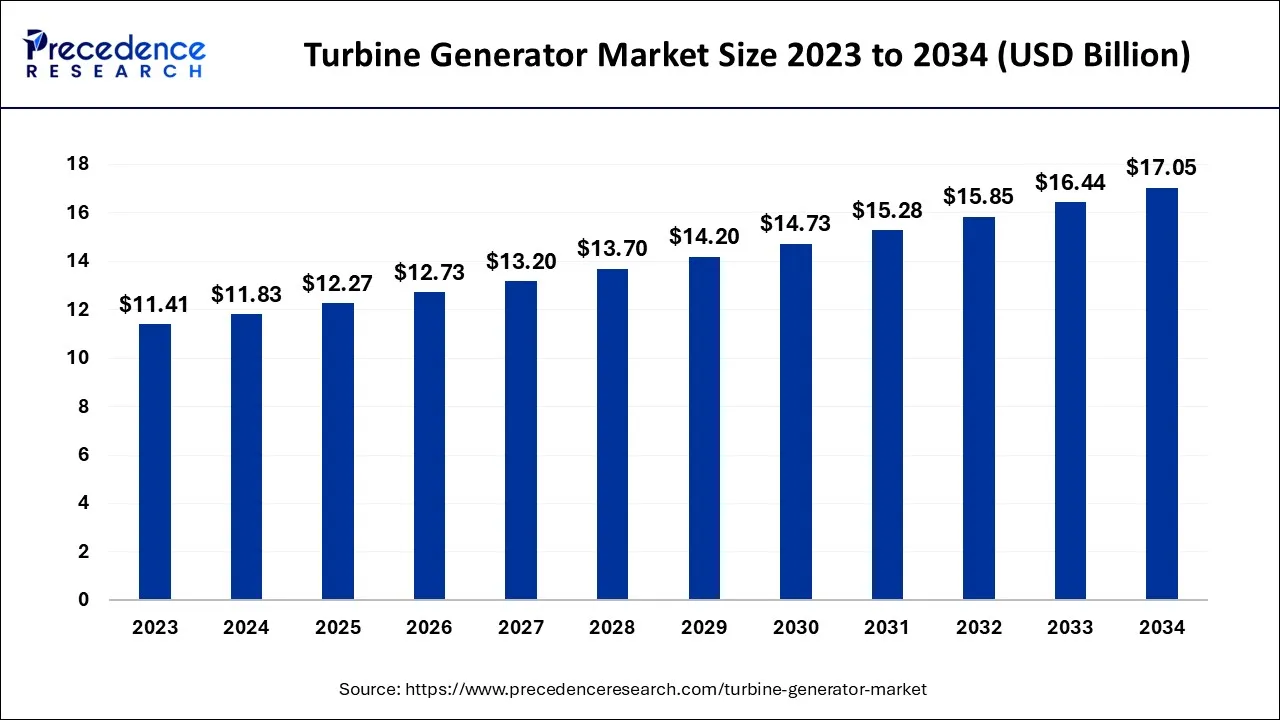
The global turbine generator market size accounted for USD 11.83 billion in 2024, grew to USD 12.27 billion in 2025 and is expected to be worth around USD 17.05 billion by 2034, registering a CAGR of 3.72% between 2024 and 2034.
The global turbine generator market size is calculated at USD 11.83 billion in 2024 and is projected to surpass around USD 17.05 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 3.72% from 2024 to 2034.
A turbo generator is an electricity generator that is linked to the rotor of either a gas turbine or steam turbine, enabling power generation. The majority of global electricity production is attributed to large steam-driven turbo generators, commonly found in steam-powered turbo-electric ships. In contrast, smaller turbo generators that are driven by gas turbines are frequently employed in auxiliary power units (APU), primarily in aircraft. Depending on the energy they utilize, several types of turbines are employed to power generators. While generators solely create energy, turbines are also used to power other things like ships and aeroplanes. Electricity is produced by turbine generators. Depending on the energy required to operate the turbine, many types of turbines are employed.
A wind turbine employs wind energy, whereas an aircraft's turbine is powered by jet fuel. While a steam turbine relies on boiler steam, a gas turbine burns natural gas. The connecting turbine shaft of the turbine then powers the generator. Coils of wire pass through a magnetic field while a generator turns, creating electricity in the wires. Transmission lines carry this electric current to residences where it is used to generate electricity.
Although turbine generators are a common type of tiny power production machinery used in drilling, military, and other areas, they currently have no practical use in natural gas pipeline transportation. The working theory and technical details of the turbine generator are discussed in this paper, demonstrating that the method of converting the kinetic energy of natural gas transported in a pipeline to mechanical energy to generate electricity has a good chance of success in engineering applications. Electric power plants that employ a turbine to drive energy generators provide the majority of the electricity used in the U.S. and across the world. A turbine generator consists of a rotor shaft with a series of blades that are propelled by the flow of various fluids, such as air, water, steam, combustion gases, or water. The force exerted by the fluid on the blades causes the rotor shaft to rotate or spin. Consequently, the mechanical energy (kinetic energy) of the rotor is converted into electrical energy by the generator. Turbines come in different types, including steam turbines, gas turbines, hydropower turbines, and wind turbines.
Steam turbines play a significant role in global power generation, accounting for a substantial portion of the world's electricity production. In 2023, steam turbines contributed to 45% of the nation's electricity generation. Typically, steam turbines involve a boiler where fuel is combusted to produce hot water and steam in a heat exchanger. The steam then drives the turbine, which, in turn, powers the generator. Nuclear power reactors utilize fuel rods to generate steam for steam turbines. Steam turbines are also employed in solar thermal power plants and a majority of geothermal power facilities. Furthermore, the largest electric power facilities in the United States rely on steam turbines.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 11.83 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 17.05 Billion |
| Growth Rate from 2024 to 2034 | CAGR of 3.72% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | Type, End-User, and Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Rapidly expanding manufacturing sector fueling demand for generators and power generation systems
The manufacturing industry has been vital to the economy of many nations. The demand for products and services is rising as a result of expanding urbanization, which is boosting the industrial sector's expansion. Additionally, to establish their nations as major centers of manufacturing, the governments of various Asian nations have inked extra-regional trade agreements. The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), if implemented successfully, would be a step towards a more comprehensive Free Trade Area of the Asia Pacific (FTAAP), according to the ASEAN Economic Community (AEC).
It may support the growth of numerous industries, serve as a viable intergovernmental platform for free trade, and support the expansion of the region's manufacturing sector. Power production generators and systems have increased in large numbers across the region as a result of increased demand from the manufacturing industry. In China, India, Brunei, and Thailand, new oil refineries are being constructed, also new power generation projects. Since 2001, the pulp and paper sector in China has grown fast. China is presently one of the world's top producers of pulp and paper goods.
Growing adoption of energy storage technologies
Over the past several years, the energy storage business has experienced exponential growth. The World Bank Group (WBG) pledged to invest USD 1 billion in a program in 2018 to quicken the financing of battery storage for electric power networks in low- and middle-income nations. Additionally, a loan of USD 300 million was approved by the World Bank for the China Renewable Energy and Battery Storage Promotion Project, which targets to expand the integration and use of renewable energy through the large-scale installation of battery storage systems. With this investment, it was hoped to improve grid stability, dependability, and electricity quality in developing nations while reducing carbon emissions. With the help of the batteries they contain, energy storage systems for batteries can store these resources during periods of peak output, resulting in less energy being wasted. Regardless of the energy source, battery storage improves electricity quality and helps the grid maintain balance.
Innovations in the electrical sector
Innovations in the electrical industry are gaining traction, and several steps are being tried to reduce pollution while still obtaining the highest possible production from turbine generators. Environmentally friendly measures are considered to make future generations a better place to live, hence industrial innovation is urgently required. To lower the price of wind energy to coal-fired rates, businesses like Solar Aero are building turbines without blades ergonomically for reduced maintenance costs. These larger turbines turn a generator with the help of thin metal discs.
The jet-engine principle is being used to create turbines that produce four times as much power to increase the output power from a generator. As opposed to traditional turbines, we can generate more electricity with them. Due to their low frictional losses and effective power generation, maglev turbines are the ideal substitute for conventional turbines. These non-stick devices can use slower-rotating turbines to generate more electricity. Hydropower plants' of the future will be air-water-gravity generators.
The AWG is a large hollow cylinder that is filled with air and is anchored at various depths of the ocean floor. The cylinder contains an electrical generator, and the action of the piston produces electricity. Researchers are working on tiny hydropower generators that can power modest domestic appliances. These might be the little hydropower plants that are eventually put in each of our homes.
Wind turbines have diverse applications beyond electricity generation, including activities like sailing, farming, and grinding. Over the past two decades, wind turbine technology has transitioned from an emerging power source to a commercially viable electricity generation technology, now present in over 80 countries. Global wind power installations reached 591 GW in 2018, a significant increase from 14.86 GW in 2006. The growth in turbine installations between 2006 and 2018 can be attributed to cost reductions resulting from advancements in materials and design, as well as favorable government policies supporting wind power in key countries such as China, the United States, Germany, Denmark, the UK, and India. According to the International Energy Agency, global energy consumption rose by 4.6% in 2021, twice the rate of growth observed in 2018.
Moving on to steam turbines, they are generally considered expensive, with installation costs for a single combined heat and power (CHP) plant in a steam turbine facility typically exceeding $5,000 per kilowatt (kW). Furthermore, steam turbines tend to have lower part-load efficiency compared to reciprocating motors. Additionally, steam turbines require more time to start up compared to gas turbines and reciprocating engines.
Turbine-driven generators are primarily used in coal, geothermal, atomic, and flammable gas control facilities as well as solar electric power plants. Steam turbines are frequently used in the renewable energy industry in facilities including power plants, district heating systems, independent biomass power plants, waste-to-energy facilities, saltwater desalination facilities, and solar thermal power plants.
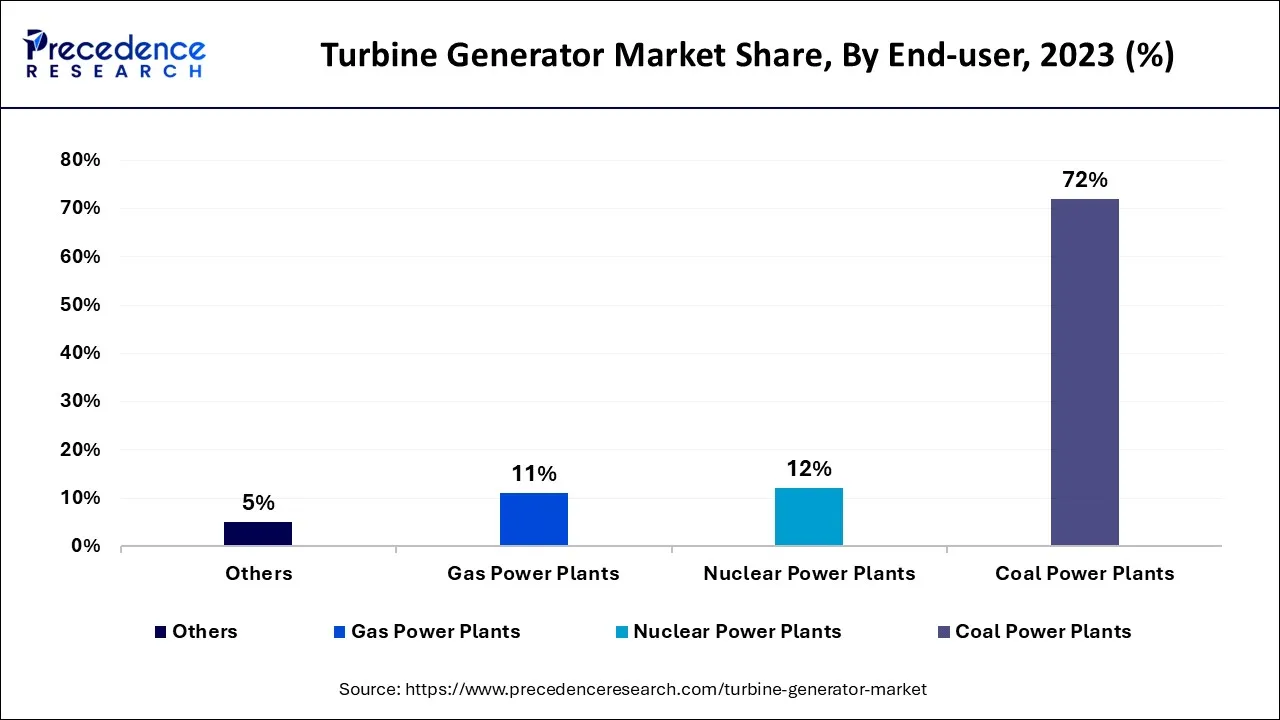
The increased need for energy in both developed and emerging nations have a favorable effect on the market for steam turbines. There will be plenty of prospects for market growth due to the global presence of demand and rising investment in the production of nuclear and renewable energy.
A key market, Asia-Pacific is home to several coal and nuclear-powered power plants. In 2023, China has 46 nuclear reactors and about 53 coal-fired facilities. Additionally, the nation boasts the most hydropower and wind power installations with the largest installed capacity. India is a notable nation that, outside China, produces the majority of its electricity from coal-fired power plants. India has a total capacity in operation of around 80 gigawatts (wind energy and hydro energy) as part of an environmental program, and by 2025, it is anticipated that the installed wind energy capacity would have doubled. The turbine market in the area is anticipated to expand significantly throughout the projected period. A sizable market share in the power-generating industry is projected to remain with coal-powered plants that include steam turbines as a power generation unit.
Segment Covered in the Reports
By Type
By End-User
By Geography
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
April 2025
March 2025
August 2024
October 2024