January 2025
The global stem cell banking market size is calculated at USD 7.72 billion in 2025 and is forecasted to reach around USD 27.71 billion by 2034, accelerating at a CAGR of 15.29% from 2025 to 2034. The North America stem cell banking market size surpassed USD 2.34 billion in 2024 and is expanding at a CAGR of 15.28% during the forecast period. The market sizing and forecasts are revenue-based (USD Million/Billion), with 2024 as the base year.
The global stem cell banking market size was estimated at USD 6.68 billion in 2024 and is predicted to increase from USD 7.72 billion in 2025 to approximately USD 27.71 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 15.29% from 2025 to 2034. The general public and medical experts are becoming more aware of the potential advantages of stem cell banking, including its ability to treat a variety of illnesses and ailments.
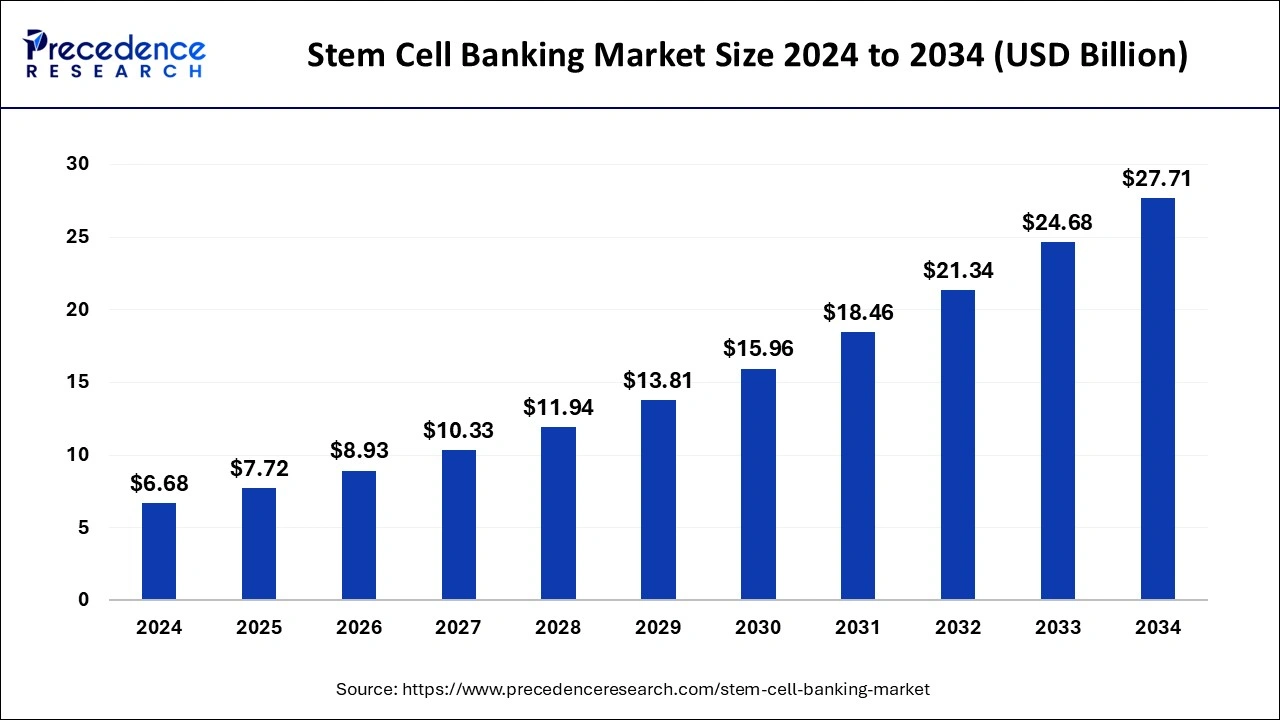
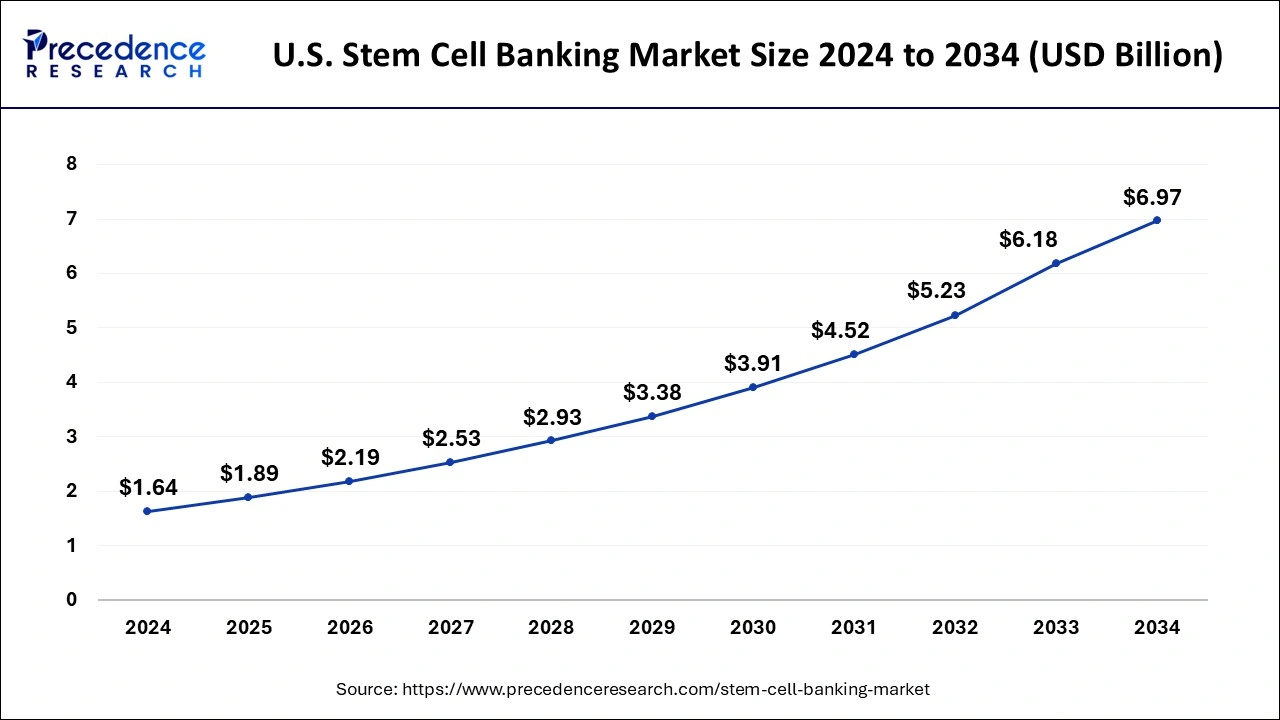
The U.S. stem cell banking market size was exhibited at USD 1.64 billion in 2024 and is projected to be worth around USD 6.97 billion by 2034, poised to grow at a CAGR of 15.57% from 2025 to 2034.
North America registered the largest revenue share of the stem cell banking market in 2024. The North American market for stem cell banking is a sizable portion of the larger healthcare and biotechnology sector. The act of gathering, preparing, and preserving stem cells for possible therapeutic application in the future is known as stem cell banking. North America is one of the world's biggest markets for stem cell banking, especially in the United States and Canada. The increased frequency of chronic diseases and growing awareness of the potential benefits of stem cell therapies have led to a continuous rise in the market. As a kind of biological insurance, families are choosing more and more to collect stem cells from umbilical cord blood and tissue at birth in anticipation of future medical developments that may benefit their offspring or other family members.
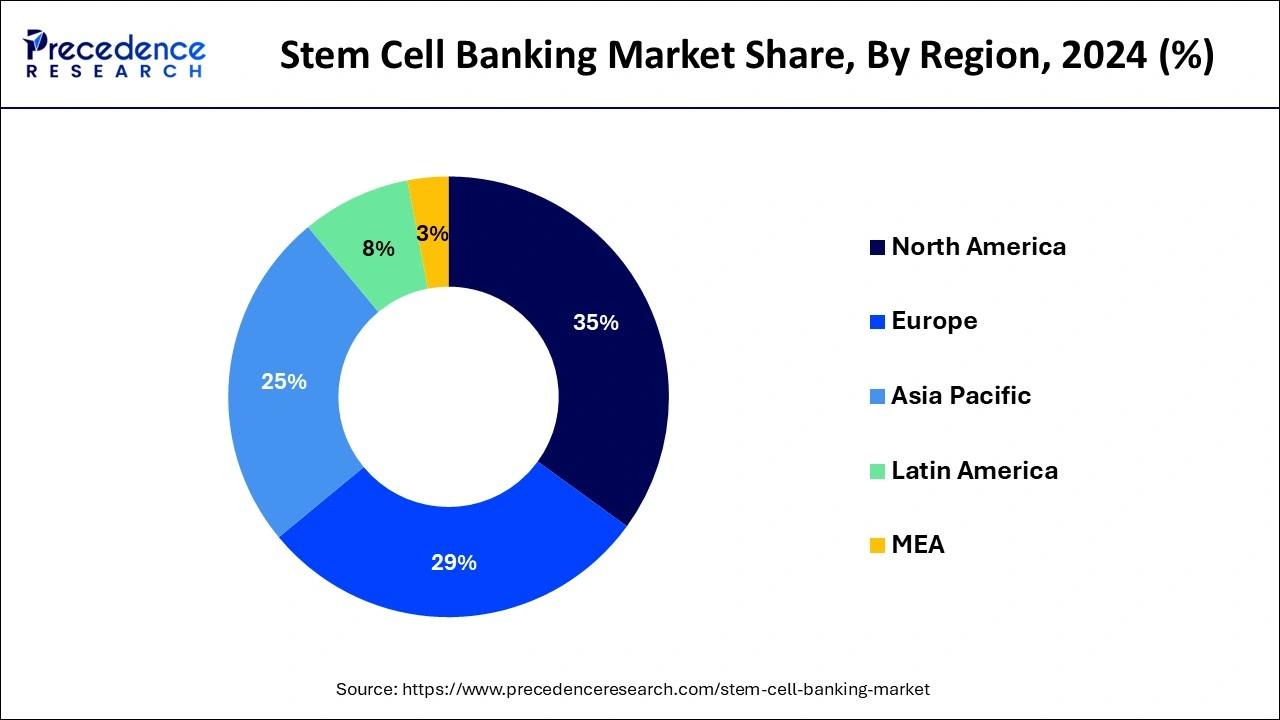
Europe is anticipated to showcase significant growth at the fastest CAGR in the stem cell banking market in the upcoming period. The market for stem cell banking in Europe has been growing consistently as a result of increased R&D spending and the growing need for customized treatment. Important companies in this market include the UK, France, Spain, Germany, and France. Technological developments like cryopreservation methods and automated storage systems have increased the effectiveness and sustainability of stem cell banking services in Europe. This has aided in the market's general expansion. Bank-stored stem cells are employed in numerous therapeutic settings to treat immune system deficits, blood diseases, and certain malignancies. Clinical trials are currently underway to investigate their potential for treating a wider variety of illnesses.
The commercial sector that gathers, prepares, stores, and distributes stem cells for possible medical applications is referred to as the stem cell banking market. Undifferentiated cells, called stem cells, have the capacity to differentiate into many kinds of body cells. Their capacity to renew and repair damaged tissues makes them promising for the treatment of a variety of illnesses and ailments.
The stem cell banking market includes both the governmental and private sectors. Donations of human stem cells are gathered by public stem cell banks for general purposes, usually medical research or patients in need of suitable stem cells for therapy. On the other hand, stem cells are kept in private stem cell banks, especially for usage by individuals and their families.
Rising healthcare costs, more research being done, and the growing range of stem cell applications outside conventional therapies were expected to propel the growth of the worldwide stem cell banking market. Due to their advanced healthcare infrastructure and research spending, North America and Europe have historically held the top two positions in terms of market size.
Asia Pacific had fast growth as a result of bettering healthcare infrastructure, rising disposable income, and encouraging political initiatives. Country-specific regulations pertaining to stem cell banking differ greatly, which affects market dynamics and bank operational needs. Further developments in technology may result in expanded uses for tissue engineering and personalized medicine.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 27.71 Billion |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 7.72 Billion |
| Growth Rate from 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 15.29% |
| Largest Market | North America |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | Service Type, Utilization, Cell Type, Bank Type, and Regions |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Rising investments in research and development
Because stem cells are able to replenish and mend damaged tissues, they hold great therapeutic promise. Academic institutions, biotech corporations, and pharmaceutical companies have all expressed greater interest as a result of this. Because stem cells are preserved for possible use in therapies in the future, stem cell banking is essential to regenerative medicine. Investments in enhancing storage methods and broadening the range of stem cell uses have increased as a result.
Stem cell banking research and development projects are currently being supported by both public and private financing organizations. This covers financing for basic and clinical research as well as infrastructure development. Additionally, investments are increasing in emerging nations as a result of the potential for medical innovation and cheaper operating costs, which draw both academics and investors.
Risk of misuse
There's a chance that stem cells kept in private banks won't be utilized for the donor's personal health but rather for business or speculation. If donors are not adequately informed about the restrictions and possible uses of the stem cells they have preserved, problems could occur. Insufficient regulation could promote the sale of unproven stem cell treatments, which would be detrimental to patients as well as the standing of respectable research.
Donors can avoid being misled about the possible applications of their stem cells by keeping an eye on matters and implementing informed consent regulations. Encouraging cooperation between the public and business sectors can help to advance stem cell banking responsibly.
Personalized medicine
In the context of stem cell banking, personalized medicine is a major breakthrough in medical science. The process of gathering and preserving stem cells for possible future medical applications is known as stem cell banking. In the past, medical care has been provided on an individual basis. On the other hand, personalized medicine seeks to adjust medical treatment to unique traits, including genetics, environment, and lifestyle.
Stem cells are kept for the person's or their family's own use. This is where customized medicine enters the picture because these cells are kept especially for that person in case they needs them in the future. People who have a family history of genetic illnesses can decide to save their stem cells in case they need to use them in the future to cure such conditions.
The unused segment dominated the stem cell banking market in 2024 and is expected to grow at a rapid pace during the forecast period. An "unused segment" in the stem cell banking business is usually a portion of the market that has not yet reached its full potential or evolved. There could be a number of reasons for this, including ignorance, technical constraints, legal restrictions, or lack of preparation for the market.
A multitude of stem cells, including hematopoietic and mesenchymal stem cells, are found in amniotic fluid. Amniotic fluid stem cell banking is not as common as cord blood or tissue banking despite the potential for regenerative medicine. Another potential source for regenerative therapy is stem cells obtained from dental pulp, which is present in wisdom teeth and infant teeth. Despite being relatively specialized, this field offers room for advancement.
The used segment will grow at the fastest rate in the stem cell banking market over the forecast period. Services related to gathering and transferring stem cells from the donor to the repository. Stem cells that were created at birth from the umbilical cord's blood. Application of stem cells to illness treatment and tissue regeneration.
Applications in the management of metabolic problems, autoimmune diseases, and other long-term illnesses. Increasing prevalence of long-term illnesses and ailments that stem cells can treat. Patients' and healthcare professionals' knowledge of and acceptance of stem cell therapy has increased. The economic standing of various locations and the cost of stem cell banking services.
The umbilical cord stem cell segment held the largest share of the stem cell banking market in 2024. The process of banking umbilical cord stem cells entails gathering, preparing, and preserving stem cells extracted from the blood and tissue of the umbilical cord. Because these stem cells can develop into numerous cell types, they have potential use in the treatment of a wide range of illnesses. This makes them important. Raising awareness among parents about the possible health advantages of preserving umbilical cord blood is happening as a result of state and private education programs. The need for stem cell banking services is increasing as a result of ongoing research and development in regenerative medicine, which is broadening the therapeutic applications of stem cells.
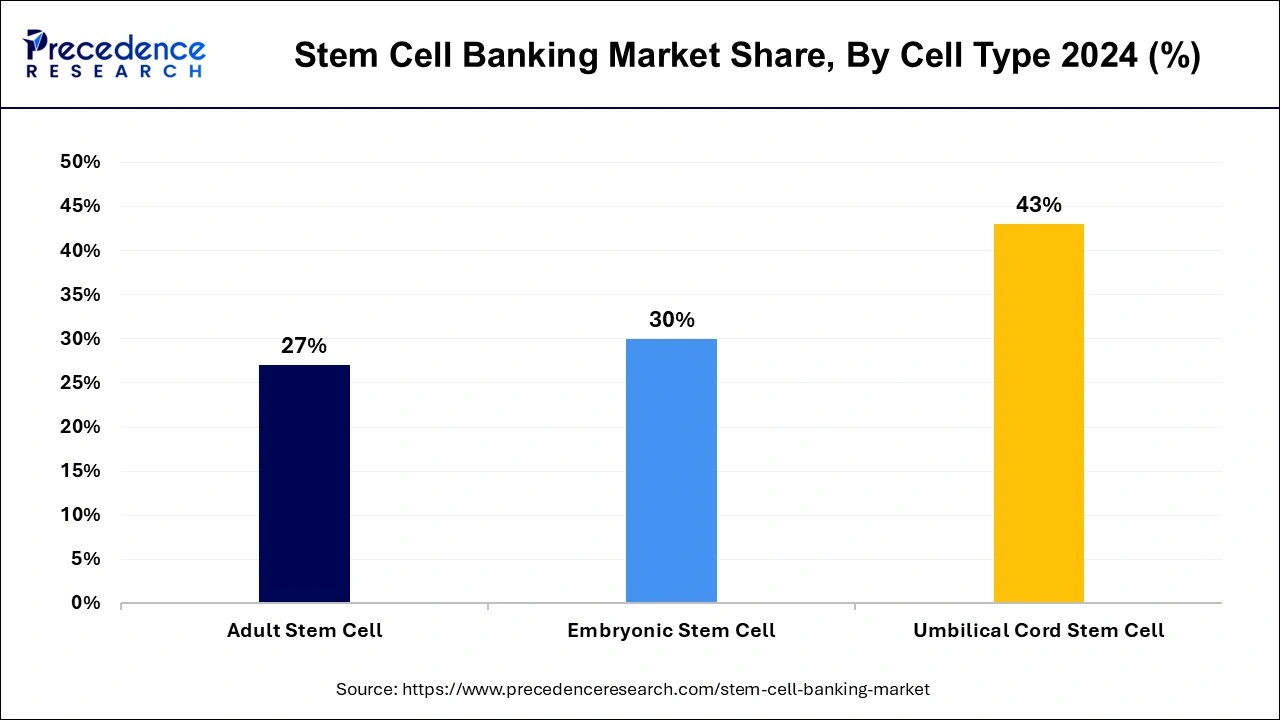
The adult stem cell segment will grow at the fastest rate in the stem cell banking market over the forecast period. Because of its possible medical uses and simplicity of collecting as compared to embryonic stem cells, the adult stem cell industry has attracted a lot of interest and is expected to continue growing. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) from adipose tissue, bone marrow, and umbilical cord tissue, as well as hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) from bone marrow and peripheral blood, are adult stem cells that are extensively researched and banked. Interest in and funding for adult stem cell banking is being driven by the possibility of developing individualized medicines using a person's own stem cells. Strict regulatory clearances for stem cell therapies might cause delays in the commercialization and uptake of novel treatments.
The storage segment held the largest share of the stem cell banking market in 2024. To guarantee the integrity and security of preserved stem cells, stem cell banks are required to abide by strict regulatory requirements. This involves adhering to regulations set forth by organizations like the FDA, AABB, and other local regulatory agencies. Putting in place automated mechanisms to save and retrieve samples in order to increase productivity and reduce human error. Liquid nitrogen, which has a larger risk of contamination but provides a more stable temperature, is used directly to store stem cells. The FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration), AABB (American Association of Blood Banks), and FACT (Foundation for the Accreditation of Cellular Therapy) are just a few of the organizations that stem cell banks have to abide by.
The processing segment will grow at the fastest rate in the stem cell banking market over the forecast period. Basic research, medication development, toxicological investigations, and the comprehension of disease mechanisms are all aided by stem cells. Applications in the treatment of illnesses like diabetes, heart disease, and spinal cord injuries, as well as the replacement or repair of damaged tissues and organs. Has a strong hold on the market as a result of its sophisticated healthcare infrastructure, large R&D expenditures, and rapid uptake of cutting-edge treatments. Numerous major participants, such as stem cell banks, biotechnology firms, and research institutes, are present in the industry. To strengthen their position in the market, these companies are collaborating strategically, making mergers and acquisitions, and developing new products.
The private bank segment dominated the global stem cell banking market in 2024. Commercial organizations known as "private stem cell banks" allow people to preserve their own or their children's stem cells for possible personal usage in the future. The collection, processing, and long-term storage of stem cells are all subject to fees at these institutions. Preservation of umbilical cord tissue-derived stem cells, which may be used in regenerative medicine. Storage of menstrual blood stem cell collections is a relatively new service with promise for future treatments. Examine the processing prices, yearly storage fees, and initial collection. Look at the various terms for payments. Families now have more individualized medical options thanks in large part to private stem cell banks, whose services are in high demand as stem cell therapies progress.
The public bank segment is anticipated to show the fastest growth in the stem cell banking market over the foreseeable period. In the stem cell banking industry, public banks are essential to the distribution, preservation, and procurement of stem cells for the general people's usage. Public stem cell banks gather and retain stem cells contributed willingly by people, usually at no cost to the donor, in contrast to private stem cell banks, which preserve stem cells for personal or family use (sometimes at a high cost). Anybody in need of a stem cell transplant can then access these donations, frequently through national or worldwide registries. Patients from all across the world can use public stem cell banks. When a person needs a stem cell transplant to treat a disease like leukemia or lymphoma and does not have a compatible match in their family, they offer an invaluable resource.

By Service Type
By Utilization
By Cell Type
By Bank Type
By Geography
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
January 2025
January 2025
November 2024
February 2025